N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
Synonym(s):N-Nitroso-N-phenylaniline;Diphenylnitrosamine;Diphenylnitrosoamine;N-Nitroso-N-phenylaniline
- CAS NO.:86-30-6
- Empirical Formula: C12H10N2O
- Molecular Weight: 198.22
- MDL number: MFCD00019920
- EINECS: 201-663-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
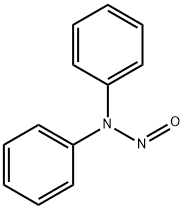
What is N-Nitrosodiphenylamine ?
Chemical properties
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine is a yellow to orangebrown crystalline solid. Soluble in acetone, benzene, ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, carbon tetrachloride, ether and carbon disulfide, soluble in hot alcohol, slightly soluble in gasoline, insoluble in water. In the hydrochloric acid methanol solution, a shift reaction can occur, and it can be transformed into p-nitrosodiphenylamine.
The Uses of N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine is the N-nitroso analogue of diphenylamine that was once used as a rubber additive but is no longer due to undesirable carcinogenic effects (1). N-Nitrosodiphenylamine may have potential carcinogenic activity and is currently classified as a probable carcinogen by EPA with genetic toxicity (2,3). Drinking water contaminant candidate list 3 (CCL 3) compound as per United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), environmental, and food contaminants.
Definition
ChEBI: N-Nitrosodiphenylamine is a member of phenylhydrazines. It is an industrial compound that formerly used as a vulcanization retarder in the rubber industry.
General Description
N-nitrosodiphenylamine appears as yellow to brown or orange powder or flakes or a black solid. Insoluble in water and denser in water. Hence sinks in water. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine may be sensitive to moisture at elevated temperatures in strongly acidic solutions. May react vigorously with oxidizing agents. May undergo trans-nitrosation reactions with secondary amines .
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition N-Nitrosodiphenylamine emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for N-Nitrosodiphenylamine are not available; however, N-Nitrosodiphenylamine is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. An eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidzing materials. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx,. See also NITROSAMINES.
Potential Exposure
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine is not a naturally occurring substance; it is a man-made chemical that is no longer produced in the United States. It was used in the manufacture of plastics, resins, rubber and synthetic textiles; to help control processes involved in making rubber products, such as tires and mechanical goods; however, in the early 1980s, the United States manufacturers stopped producing N-nitrosodiphenylamine because new and more efficient chemicals were found to replace its uses. In addition, the use of N-nitrosodiphenylamine had several undesirable side effects which do not occur with the replacement chemicals.
Carcinogenicity
Two feeding experiments with NDPhA in rats were totally negative (no tumors). One used daily doses of 120 mg/kg body weight to a total dose of 65 g/kg, and another used a lower dose for only 53 weeks. Another experiment involved larger groups of rats and mice and higher doses. In mice, after 2 years, there was occasional hyperplasia of the bladder mucosa, but no tumors; in rats given 4000 mg NDPhA/kg diet for 2 years, 16/45 males and 40/49 females had transitional cell carcinomas of the bladder. IARC classified NDPhA as not classifiable as to carcinogenicity in humans (Group 3).
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. At temperatures greater than 85 °C, technical grades may decompose to
nitrogen oxides (IARC, 1978). N-Nitrosodiphenylamine will not hydrolyze because it does not
contain a hydrolyzable functional group (Kollig, 1993).
At influent concentrations of 10, 1.0, 0.1, and 0.01 mg/L, the GAC adsorption capacities were 510,
120, 91, and 38 mg/g, respectively (Dobbs and Cohen, 1980).
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Contact with reducing agents may form hydrazine; hydrogen bromide. Light sensitive; rapidly decomposes.
Waste Disposal
Burn in admixture with flammable solvent in furnace equipped with afterburner and scrubber.
References
[1] Peng, Xiuying et al. “Electrochemical sensor for facile detection of trace N-nitrosodiphenylamine based on poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)-stabilized graphene/platinum nanoparticles.” New Journal of Chemistry 2 (2018): 820–826.
Properties of N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
| Melting point: | 65-66 °C |
| Boiling point: | 268°C |
| Density | 1.23 |
| vapor pressure | 0.1 at 25 °C (assigned by analogy, Mabey et al., 1982) |
| refractive index | 1.6330 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear |
| form | Yellow to brown or orange
powder or flakes |
| pka | -5.83±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | Yellow to brown to orange power or flakes |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| BRN | 909531 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.33 at 25 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Stability: | Stability Combustible. Incompatible with oxidising agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 86-30-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 27, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenamine, N-nitroso-N-phenyl-(86-30-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N-Nitrosodiphenylamine (86-30-6) |
Safety information for N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H301:Acute toxicity,oral H302:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H320:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H351:Carcinogenicity H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H371:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for N-Nitrosodiphenylamine
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine manufacturer
Riddhesh Pharmachem
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 86-30-6 N-Nitroso diphenyl amine 99.92View Details
86-30-6 N-Nitroso diphenyl amine 99.92View Details
86-30-6 -
 N-Nitrosodiphenylamine 86-30-6 99%View Details
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine 86-30-6 99%View Details
86-30-6 -
 86-30-6 N-Nitroso diphenylamine 98%View Details
86-30-6 N-Nitroso diphenylamine 98%View Details
86-30-6 -
 N-Nitrosodiphenylamine CAS 86-30-6View Details
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine CAS 86-30-6View Details
86-30-6 -
 N-Nitrosodiphenylamine solution CAS 86-30-6View Details
N-Nitrosodiphenylamine solution CAS 86-30-6View Details
86-30-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1