N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine
Synonym(s):N-Acetyl-L -tyrosine
- CAS NO.:537-55-3
- Empirical Formula: C11H13NO4
- Molecular Weight: 223.23
- MDL number: MFCD00037190
- EINECS: 208-671-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
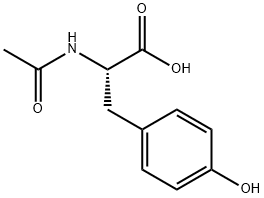
What is N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine?
Chemical properties
N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine is a white crystalline powder that is an acetyl derivative of the amino acid, L-tyrosine. It is freely soluble in water compared to L-tyrosine and is commonly used as a parenteral nutrition supplement. N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine , a stable and more soluble form of tyrosine , has been incorporated in some currently available commercial parenteral amino acid formulations such as TrophAmine and Aminosyn-II.
The Uses of N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is involved in catecholamine production. It can be used as a cell culture media component in the commercial biomanufacture of therapeutic recombinant proteins and monoclonal antibodies.
Indications
N-acetyltyrosine is indicated, in combination with several other amino acids and dextrose, as a peripherally administered source of nitrogen for nutritional support in patients with adequate stores of body fat in whom, for short periods, oral administration cannot be tolerated, is undesirable, or inadequate .
It is also indicated, with other amino acids, 5-10% dextrose, and fat emulsion, for parenteral nutrition to preserve protein and reduce catabolism in stress conditions where oral administration is inadequate .
When administered with other amino acids and concentrated dextrose, it is indicated for central vein infusion to prevent or reverse negative nitrogen balance in patients where the alimentary tract by the oral, gastrostomy, or jejestomy routes cannot or should not be used or in patients in which gastrointestinal absorption of protein is impaired, metabolic requirements for protein are substantially increased, or morbidity and mortality may be reduced by replacing amino acids lost from tissue breakdown
Background
N-acetyltyrosine, also referred to as N-acetyl-L-tyrosine, is used in place of as a tyrosine precursor. Tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. N-acetyltyrosine is administered as parenteral nutrition or intravenous infusion due to its enhanced solubility compared to tyrosine . It is typically administered as a source of nutritional support where oral nutrition is inadequate or cannot be tolerated.
What are the applications of Application
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is a derivative of tyrosine involved in catecholamine production
Definition
ChEBI: N-acetyl-L-tyrosine is an N-acetyltyrosine in which the chiral centre has L configuration. It has a role as an EC 2.1.1.4 (acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase) inhibitor, a biomarker and a human urinary metabolite. It is a N-acyl-L-tyrosine and a N-acetyltyrosine. It is a conjugate acid of a N-acetyl-L-tyrosinate.
What are the applications of Application
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine is a tyrosine derivative with a chemical structure similar to that of an amino acid. It is used as a model system in biochemistry and molecular biology to study the transfer reactions of tyrosine, which are important for energy metabolism, protein synthesis, and metal chelation. N-acetyl-L-tyrosine may be used as an indicator to distinguish neurosyphilis patients from syphilis/non-neurosyphilis patients. N-acetyl-L-tyrosine is a precursor of the essential neurotransmitter dopamine.
Benefits
N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine (NALT) plays a necessary part in the synthesis of dopamine and other hormones in your body. It can boost levels of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. It helps to support higher levels of focus and cognitive function. It can increase working memory and feelings of well-being.
Pharmacokinetics
N-acetyltyrosine is used as a high solubility precursor to Tyrosine used due to Tyrosine's poor solubility . It is deacetylated to form Tyrosine.
Side Effects
L-tyrosine gets the generally regarded as safe (GRAS) stamp of approval from the FDA. Some side effects of N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine (NALT) include nausea, headache, fatigue, and heartburn. It can be safely taken for extended periods of time.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine
| Melting point: | 149-152 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 364.51°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 47.5 º (c=2, water) |
| Density | 1.2446 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4960 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | H2O: soluble25mg/mL |
| form | Crystalline |
| pka | 3.15±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (25 mg/ml), and ethanol. |
| BRN | 2697172 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 537-55-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | N-acetyl-Tyr(537-55-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine (537-55-3) |
Safety information for N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine
Abamectin manufacturer
TEADUS PHARMA PRIVATE LIMITED
SV CHEM INTERMEDITES PRIVATE LIMITED
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 537-55-3 N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine 95%View Details
537-55-3 N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine 95%View Details
537-55-3 -
 537-55-3 99%View Details
537-55-3 99%View Details
537-55-3 -
 N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine, 98% CAS 537-55-3View Details
N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine, 98% CAS 537-55-3View Details
537-55-3 -
 N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine CAS 537-55-3View Details
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine CAS 537-55-3View Details
537-55-3 -
 N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine CAS 537-55-3View Details
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine CAS 537-55-3View Details
537-55-3 -
 N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine,98% 99%View Details
N-Acetyl-L-tyrosine,98% 99%View Details
537-55-3 -
 N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine 98% CAS 537-55-3View Details
N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine 98% CAS 537-55-3View Details
537-55-3 -
 N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine CAS 537-55-3View Details
N-Acetyl-L-Tyrosine CAS 537-55-3View Details
537-55-3