Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt
Synonym(s):acetyl-coa
- CAS NO.:102029-73-2
- Empirical Formula: C23H38N7O17P3S.3Na
- Molecular Weight: 809.57
- MDL number: MFCD00078858
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
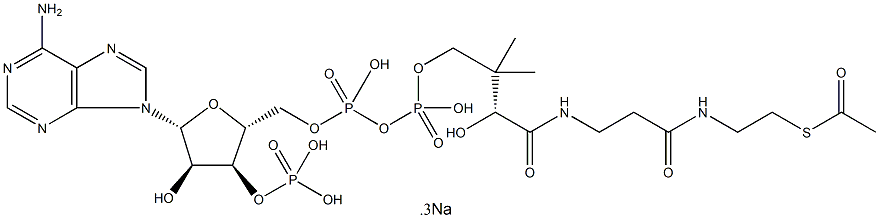
What is Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt?
Description
Acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-
The Uses of Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt
Acetyl-Coenzyme A is used to assay CAT enzyme activity in cell extracts using radioisotopes. CAT enzyme activity in cell extracts catalyzes the transfer of acetyl groups from acetylcoenzyme A to chloramphenicol. A number of assays have been developed to measure CAT activity in cell extracts. Acetyl-Coenzyme A has also been used to determine citrate synthase activity.
What are the applications of Application
Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt is an essential cofactor, metabolic intermediate, and carrier of acyl groups.
General Description
Acetyl-Coenzyme A, trilithium salt
Biochem/physiol Actions
Acetyl-Coenzyme A (Ac-CoA) is the end product of glycolysis and takes part in the Ac-CoA pathway, which is a metabolic pathway for carbon compounds. Ac-CoA is important in cholesterol synthesis. It also takes part in fatty acid biosynthesis and catabolism of polyamines like spermine and spermidine. A low level of Ac-CoA leads to a loss in glial cell and neuronal function. Ketone bodies and triglycerides give rise to Ac-CoA on hydrolysis and this indirectly leads to increased histone acetylation.
Metabolism
Acetyl coenzyme A, the precursor of the acetate-malonare pathway, is a metabolite of extreme importance in both primary and secondary metabolism. In every living organism, there exists a metabolie pool of acetyl CoA which is continually replenished and depleted. Glycolysis and the catabolism of fatty acids and amino acids produce acetyl CoA, while this compound is the precursor of a host of primary and secondary metabolites, including fatty acids, terpenoids, steroids, polyketides, aromatic compounds and acetyl esters and amides. The conversion of acetyl CoA to citrate and other tricarboxylic acids leads to the formation of the amino acids and their products, such as the nucleic acids and alkaloids.
Acetyl CoA is also central to the catabolism of glucose and the fatty acids, which, through the tricarboxylic acid cycle, are the main reaction sequences producing the energy necessary for metabolie processes.
In plants, an enzyme, acetyl CoA synthetase, catalyses the formation of the thiol ester from acetate.
Properties of Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt
Computed Descriptors for Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt
| InChIKey | ZSLZBFCDCINBPY-KMYLAXNMSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

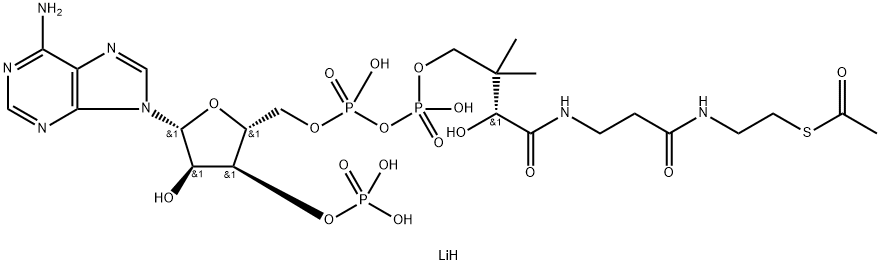

You may like
-
 Acetyl coenzyme A trisodium salt CAS 102029-73-2View Details
Acetyl coenzyme A trisodium salt CAS 102029-73-2View Details
102029-73-2 -
 Acetyl-Coenzyme A CASView Details
Acetyl-Coenzyme A CASView Details -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
