MILNACIPRAN HYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS NO.:92623-85-3
- Empirical Formula: C15H22N2O
- Molecular Weight: 246.35
- MDL number: MFCD00901293
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
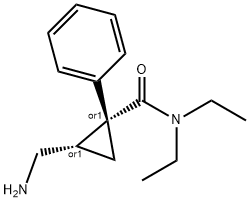
What is MILNACIPRAN HYDROCHLORIDE?
Absorption
Racemic milnacipram demonstrates an absolute bioavailability of about 85-90% following oral administration . Maximum concentrations of the racemic agent are reached within 2-4 hours after oral dosing, and steady-state levels are obtained by 36-48 hours .
Conversely, the relative bioavailability of levomilnacipram has been documented as 92% . The median time to peak concentration Tmax for levomilnacipram is about 6-8 hours after oral administration . After daily dosing of levomilnacipram 120 mg, the mean Cmax value is 341 ng/mL, and the mean steady-state AUC value is 5196 ng.h/mL.
In general, the administration of either racemic milnacipram or levomilnacipram with food does not affect the medication's oral bioavailability .
Toxicity
There is limited clinical experience with milnacipran overdose in humans. In clinical trials, cases of acute ingestions up to 1000 mg daily were reported with none being fatal . In postmarketing experience, fatal outcomes have been reported for acute overdoses primarily involving multiple drugs but also with milnacipran only . The most common signs and symptoms of overdose included increased blood pressure, cardio-respiratory arrest, changes in the level of consciousness (ranging from somnolence to coma), confusional state, dizziness, and increased hepatic enzymes .
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women . In fact, milnacipram should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus .
Neonates exposed to SSRIs or SNRIs, late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding . Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying . These features are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of SNRI class drugs like milnacipran or, possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome . It should be noted that, in some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome .
The effect of milnacipran on labor and delivery in humans is unknown . Milnacipran should be used during labor and delivery only if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks .
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in nursing mothers . It is not known if milnacipran is excreted in human milk . Studies have shown that levomilnacipran is excreted into the milk of lactating rats . Subsequently, possible excretion into human milk possesses the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants . As a consequence, breastfeeding by women treated with levomilnacipran should be considered only if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks to the child .
Milnacipran is not indicated for use in children under 18 years of age due to concerns over the potential for agitation-type emotional and behavioral changes, as well as suicidal ideation and/or behavior .
SNRIs like milnacipran have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse event .
Levomilnacipran was not mutagenic when evaluated in vitro in a bacterial mutagenicity study (Ames test) and not genotoxic in a mouse lymphoma study . It was not clastogenic in an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats .
The potential effects of levomilnacipran on gonadal function, mating behavior, reproductive performance and early pregnancy were evaluated in rats at oral doses of 0, 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg/day . The NOAEL was 100 mg/kg/day based on reductions in body weight gain and food consumption . There were no levomilnacipran effects on male and female fertility parameters .
In the rat and rabbit embryo/fetal development studies, decreases in maternal body weight gain and food consumption were noted . In the fetuses, increases in the incidence of ossification anomalies were noted but were of no toxicological significance . In both species, the NOAEL was determined to be 100 mg/kg/day, a dose which represents a rat or rabbit animal-to-human exposure margin of 9-fold and 4-fold, respectively relative to the human exposure from 120 mg/day of levomilnacipran .
Material safety data for milnacipran has documented the LD50 oral value in the rat model as being 213 mg/kg .
Description
Ixel was launched in France as an antidepressant. There are several synthetic routes, the shortest of which is five steps using benzyl cyanide as the starting material. It is a specific serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). This dual mechanism of action makes it superior to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) like fluoxetine and fluvoxamine. Ixel has no significant effect on postsynaptic receptors, very limited effect on cardiac function, and no quinidine-like arrhythmal effects. It has a good side effect profile with lower incidence of anticholinergic-like side effects, less sedation due to histamine H1-receptor binding, and a lack of α1- adrenoceptor antagonism. Ixel has a short half-life (7 hr) with no active metabolites. It is not metabolized by CYP450 therefore drug interaction is unlikely. It is superior in the treatment of serious depression with no need to titrate drug dose.
Originator
Pierre Fabre (France)
Background
Milnacipran is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) and like many agents in this category was originally developed for and continues to be approved and indicated for the treatment of depression . Furthermore, in 2009 the US FDA approved milnacipran for the additional indication of treating fibromyalgia , although other regional regulatory authorities like the EMA, among others, have not yet approved the agent for such treatment, citing lack of robust evidence of efficacy, insufficient demonstration of maintenance of effect, and other concerns . Nevertheless, milnacipran demonstrates a somewhat unique characteristic among SNRIs to elicit a relatively balanced reuptake inhibition of both serotonin and noradrenaline, with a somewhat increased preference for noradrenaline reuptake inhibition - which is potentially a point of interest given the plausible proposal that noradrenaline plays an important role in the mitigation of pain signals in the descending inhibitory pain pathways in the brain and spinal cord .
Moreover, recent research has shown that the levorotatory enantiomer of milnacipran, levomilnacipran, may have the capacity to inhibit the activity of beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme-1 (BACE-1), which has investigationally been associated with β-amyloid plaque formation - making the agent a possible course of treatment for Alzheimer's disease .
Indications
Milnacipran is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) indicated for the management of fibromyalgia in patients that are 18 years old or above .
While milnacipran may be used for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), it is only recommended in adult patients who are 18 years old or above due to an increased risk for suicidal ideation, thinking, and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults taking antidepressants for major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Some regional prescribing information notes that the use of the medication is specifically for the short-term symptomatic relief of MDD . Nevertheless, it is important to note that the regulatory approval of and/or indications listed here for milnacipran may or may not exist and/or vary greatly between regions and nations .
Definition
ChEBI: (1R,2S)-2-(aminomethyl)-N,N-diethyl-1-phenyl-1-cyclopropanecarboxamide is a member of acetamides.
brand name
Ixel
Mechanism of action
Milnacipran selectively inhibits the reuptake of 5-HT (selectivity ratio, 9) at the presynaptic membrane site, thus increasing the concentration of 5-HT in the synaptic cleft. Although milnacipran is not a TCA, its mechanism of action is similar to that of imipramine, and its binding and reuptake inhibition profile more closely resembles that of the TCAs. Milnacipran has weak affinity for adrenergic, muscarinic, and H1 receptors and, therefore, is expected to be devoid of the prominent side effects observed for the TCAs. In clinical studies, milnacipran showed antidepressant efficacy similar to that of TCAs and SSRIs.
Pharmacokinetics
When utilized to treat fibromyalgia, the effect of milnacipran on the QTcF interval in patients was measured in a double-blind placebo-and positive-controlled parallel study in 88 healthy subjects using three to six times the recommended therapeutic dose for fibromyalgia at 600 mg/day . After baseline and placebo adjustment, the maximum mean QTcF change was 8 ms - an increase that is generally not considered to be clinically significant .
Conversely, when used for treating major depressive disorder (MDD), non-clinical studies have shown that levomilnacipran binds with high affinity to the norepinephrine (NE) and serotonin (5-HT) transporters (Ki = 71-91 nM and 11 nM respectively at human transporters) . Levomilnacipran inhibits the uptake of both NE and 5-HT in vitro and in vivo; preferentially inhibiting reuptake of NE over 5-HT by approximately 2-fold . Levomilnacipran does not directly affect the uptake of dopamine or other neurotransmitters . Levomilnacipran has no significant affinity for serotonergic (5-HT1-7), α- and β-adrenergic, muscarinic (M1-5), histamine (H1-4), dopamine (D1-5), opiate, benzodiazepine, and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in vitro . Levomilnacipran has no significant affinity for Ca++, K+, Na+, and Cl– channels and does not inhibit the activity of human monoamine oxidases (MAO-A and MAO-B) or acetylcholinesterase .
Moreover, in ECG studies with levomilnacipran used to treat MDD, although no clinically significant changes in QTcF interval (QTcF=QT/RR0.33) were noted, it appears that the agent can cause increases in heart rate and blood pressure . In particular, it appears that the maximum therapeutic dose of levomilnacipran at 120 mg/day is capable of causing a maximum mean difference in heart rate from placebo of 20.2 bpm and a mean difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressure from placebo ranging from 3.8 to 7.2 mmHg and 6.1 to 8.1 mmHg, respectively . Alternatively, a supratherapeutic dose of 300 mg/day is capable of causing a maximum mean difference in heart rate from placebo of 22.1 bpm and a mean difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressure from placebo ranging from 5.4 to 7.9 mmHg and 7.9 to 10.6 mmHg, respectively .
Pharmacokinetics
In humans, milnacipran distinguishes itself from many other antidepressants by its simple pharmacokinetics. It is rapidly absorbed, with a high oral bioavailability, and it exhibits linear pharmacokinetics over a dose range of 25 to 200 mg/day. It circulates in the blood and distributes in the body principally as unmetabolized drug. Steady-state plasma levels are reached within 32 to 48 hours after twice-daily oral administration, and its metabolism does not involve the CYP enzyme system. Approximately 50% of the dose is excreted in urine as unmetabolized drug, and another 14% is excreted as its N-glucuronide conjugate. The remaining eliminated drug is composed of conjugated Phase I inactive metabolites. Because the unmetabolized drug is the only compound responsible for the activity of milnacipran, no dosage adjustment is needed in patients presenting liver impairment.
Clinical Use
(±)-Milnacipran is the ci s-aminomethyl derivative of phenylcyclopropanecarboxamide that acts by inhibiting both NE and 5-HT reuptake. It is structurally different from the other NSRIs and currently is only available in Europe as a racemic mixture, with both enantiomers exhibiting antidepressant activity. Substituting the aminomethyl group of milnacipran with an aminopropyl gives a milnacipran homologue that exhibits antidepressant activity as a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist. A glutamate hypothesis is being investigated as an alternative mechanism of depression.
Side Effects
Milnacipran has proven to be a very safe drug, with an adverse-event profile clearly superior to that of TCAs and, to a certain extent, that of SSRIs. Only approximately 10% of patients experience side effects, and only dysuria occurred more frequently (2%) with milnacipran than with TCAs or SSRIs. Milnacipran therefore appears to be an antidepressant with a very favorable benefit:risk ratio, although with a slower onset of action than the TCAs.
Metabolism
It has been determined that levomilnacipran undergoes desethylation and hydroxylation to generate desethyl levomilnacipran and p-hydroxy-levomilnacipran, respectively . Both oxidative metabolites undergo further conjugation with glucuronide to form the conjugate milnacipran carbamoyl-O-glucuronide . The desethylation is catalyzed primarily by CYP3A4 with minor contribution by CYP2C8, 2C19, 2D6, and 2J2 . Additionally, it is the general understanding that there is no interconversion between the enantiomers of milnacipran in the body .
Properties of MILNACIPRAN HYDROCHLORIDE
| Boiling point: | 393.0±21.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.077±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 19 mg/mL |
| form | solid |
| pka | 10.36±0.29(Predicted) |
| color | white |
Safety information for MILNACIPRAN HYDROCHLORIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for MILNACIPRAN HYDROCHLORIDE
MILNACIPRAN HYDROCHLORIDE manufacturer
HRV Global Life Sciences
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 92623-85-3 Milnacipran 99%View Details
92623-85-3 Milnacipran 99%View Details
92623-85-3 -
 92623-85-3 96%View Details
92623-85-3 96%View Details
92623-85-3 -
 Milnacipran 98%View Details
Milnacipran 98%View Details
92623-85-3 -
 Milnacipran 92623-85-3 99%View Details
Milnacipran 92623-85-3 99%View Details
92623-85-3 -
 92623-85-3 Milnacipran 98%View Details
92623-85-3 Milnacipran 98%View Details
92623-85-3 -
 92623-85-3 98%View Details
92623-85-3 98%View Details
92623-85-3 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1