Mica
- CAS NO.:12001-26-2
- Empirical Formula: Al2K2O6Si
- Molecular Weight: 256.24
- MDL number: MFCD00147600
- EINECS: 601-648-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:56
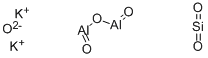
What is Mica?
Description
Cosmetic mica, potassium aluminum silicate dehydrate, is refined and ground to particles of ≤150 μm. This material imparts a natural translucence when used up to 20% in formulations of face powder blushes. Mica is available as wet ground (creamy) or as dry ground (matte).
Chemical properties
Soft, translucent solid; colorless to slightred (ruby), brown to greenish yellow (amber). Noncombustible.Heat resistant to 600C.
Chemical properties
Mica (muscovite), takes the form of a colorless, odorless solid that separates into flakes or thin sheets of hydrous silicates.
Occurrence
Mica exists in nature in a wide variety of compositions. Muscovite and phlogopite are the only natural micas of commercial importance. Vermiculite, although not considered a true mica by most mineralogists, is a micaceous mineral formed from the weathering of phlogopite or biotite and is also of commercial importance.
The Uses of Mica
mica is used as a texturizer and coloring agent in cosmetics, it provides a “glimmer” or “shimmering” quality in makeup powders. Mica is the group name for a series of ground silicate minerals with similar physical properties but varied chemical composition. Micas range in color from colorless to pale green, brown, or black.
The Uses of Mica
Electrical equipment, vacuum tubes, incan-descent lamps, dusting agent, lubricant, windowsin high-temperature equipment, filler in exteriorpaints, cosmetics, glass and ceramic flux, roofing,rubber, mold-release agent, specialty paper for insu-lation and filtration, wallpaper and wallboard jointcement, oil-well drilling muds.
The Uses of Mica
Mica is a generic term that applies to a wide range of hydrous aluminum silicate minerals characterized by sheet or plant-like structure, and possessing to varying degrees, depending on composition and weathering, flexibility, elasticity, hardness, and the ability to be split into thin (1 μm) sheets.
Definition
Any of several silicates of vary-ing chemical composition but with similar physicalproperties and crystalline structure. All character-istically cleave into thin sheets that are flexible andelastic. Synthetic mica is available. It has electri-cal and mechanical properties superior to those ofnatural mica; it is also water free.
Definition
A member of an important group of aluminosilicate minerals that have a characteristic layered structure. The three main types are biotite, lepidolite, and muscovite, which differ in their content of other elements (such as potassium, magnesium, and iron). Mica flakes are used as electrical insulators, dielectrics, and small heat-proof windows.
Definition
mica: Any of a group of silicate mineralswith a layered structure. Micasare composed of linked SiO4 tetrahedrawith cations and hydroxyl groupingsbetween the layers. The generalformula is X2Y4-6Z8O20(OH,F)4, whereX = K,Na,Ca; Y = Al,Mg,Fe,Li; and Z = Si,Al. The three main mica mineralsare:
muscovite, K2Al4(Si6Al2O20)(OH,F)4;biotite, K2(Mg,Fe2+)6-4(Fe3+,Al,Ti)0-2-(Si6-5Al2-3O20)(OH,F)4;
lepidolite, K2(Li,Al)5-6(Si6-7Al2-1O20)-(OH,F)4.
Micas have perfect basal cleavage andthe thin cleavage flakes are flexibleand elastic. Flakes of mica are used aselectrical insulators and as the dielectricin capacitors.
Production Methods
Mica is a nonfibrous, natural silicate, found in plate form in nine different species. These materials are hydrous silicates, and the predominant minerals of commerce are muscovite, a hydrous aluminosilicate, and phlogophite, a magnesium silicate. Sheet forms of mica in the form of muscovite have historically been mined by hand from pegmatites.
General Description
MICA, a generic term, refers to any of a group of approximately 30 silicate minerals occurring as non-fibrous plates. Muscovite (hydrated aluminium potassium silicate[KAl2(AlSi3O10)(F, OH)2 ])and phlogopite (potassium magnesium aluminum silicate hydroxide) are the two major micas of commerce. Micas are commonly found in ordinary rocks. Inhalation of mica dust presents an occupational hazard.
Reactivity Profile
MICAS have generally low chemical reactivity.
Hazard
(Dust) Irritant by inhalation, may be dam-aging to lungs. Pneumoconiosis.
Health Hazard
Mica dust causes pneumoconiosis.
Agricultural Uses
Biotite is a widely distributed and important rockforming
mineral of the mica group. The general term
designates all ferro-magnesium micas, also called black
mica or magnesium-iron mica. This black and plate-like
mineral is found in some igneous rocks, such as granite.
It is tetrahedral mica with aluminum substituted for
silicon in the tetrahedral sheet, and ferrous (Fe2+) or
magnesium (Mg2+)io ns in the octahedral sheet.
Potassium release occurs more easily
with biotite than with muscovite. Biotite is used as the
source of soil potassium. It is more easily weathered to
chlorite than muscovite and, therefore, is less common in
sediments. Although commercially unimportant under
hydrothermal conditions, biotite transforms to
vermiculite which expands on heating and has
widespread application as light-weight concrete, plaster
aggregate, insulation, plant growing medium and
lubricant.
Industrial uses
Commercial mica is of two main types: sheet,and scrap or flake. Sheet muscovite is used asa dielectric in capacitors and vacuum tubes inelectronic equipment. Lower-quality muscoviteis used as an insulator in home electrical productssuch as hot plates, toasters, and irons.
Scrap and flake mica is ground for use in coatingson roofing materials and waterproof fabrics,and in paint, wallpaper, joint cement, plastics,cosmetics, well-drilling products, and avariety of agricultural products.For many years, glass-bonded mica hasbeen used in every type of electrical and electronicsystem where the insulation requirementsare preferably low-dissipation factor at high frequencies,a high-insulation resistance anddielectric-breakdown strength, along withextreme dimensional stability. Glass-bondedmicas are made in both machinable grades andprecision-moldable grades. Basically, the materialconsists of natural mica flake bonded witha low-loss electrical glass.
The availability of synthetic mica resultedin the development of so-called ceramoplastics,consisting of high-temperature electricalglass filled with synthetic mica. Ceramoplasticsprovide an increase in the electrical characteristicsover those of natural mica, and, inaddition, are more easily molded and havegreater thermal stability.
Safety Profile
The dust is injurious to lungs.
Potential Exposure
Mica is used as reinforcing filler for plastics, substitute for asbestos; for insulation in electrical equipment; used in the manufacture of roofing shingles, wallpaper and paint.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately. If a personbreathes in large amounts of this chemical, move theexposed person to fresh air at once
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area
Incompatibilities
Silicates react with lithium.
Waste Disposal
Consider recycling, otherwise, this chemical must be disposed of in compliance with existing federal and local regulations. Landfill.
Properties of Mica
| Density | 2,77 g/cm3 |
| refractive index | 1.55-1.61 |
| RTECS | VV876000 |
| form | Light gray to dark-colored
flakes or particles |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6-3.2(0.0℃) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Mica group minerals (12001-26-2) |
Safety information for Mica
Computed Descriptors for Mica
Mica manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




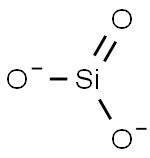
You may like
-
 12001-26-2 Mica 99%View Details
12001-26-2 Mica 99%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 12001-26-2 98%View Details
12001-26-2 98%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 Mica 98%View Details
Mica 98%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 Mica 98%View Details
Mica 98%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 Mica 12001-26-2 98%View Details
Mica 12001-26-2 98%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 12001-26-2 Mica 98%View Details
12001-26-2 Mica 98%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 12001-26-2 98%View Details
12001-26-2 98%View Details
12001-26-2 -
 Mica powder CAS 12001-26-2View Details
Mica powder CAS 12001-26-2View Details
12001-26-2
