methoxamine
- CAS NO.:390-28-3
- Empirical Formula: C11H17NO3
- Molecular Weight: 211.26
- EINECS: 206-867-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:38
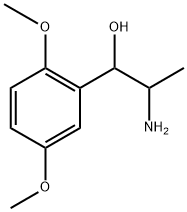
What is methoxamine?
Originator
Vasoxyl ,Burroughs-Wellcome,US,1949
Background
An alpha-adrenergic agonist that causes prolonged peripheral vasoconstriction. It has little if any direct effect on the central nervous system.
Indications
Indicated for the treatment and management of hypotension.
Definition
ChEBI: Methoxamine is an amphetamine in which the parent 1-phenylpropan-2-amine skeleton is substituted at position 1 with an hydroxy group and the phenyl ring is 2- and 5-substituted with methoxy groups. It is an antihypotensive agent (pressor), an agonist acting directly at alpha-adrenoceptors with selectivity for the alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtype similar to phenylephrine. It has a role as an antihypotensive agent and an alpha-adrenergic agonist.
Manufacturing Process
2,5-Dimethoxypropiophenone is treated in absolute ether with methyl nitrite and hydrogen chloride. The hydrochloride of 2,5-dimethoxy-αisonitrosopropiophenone crystallizes out of the solution. It is removed, the base is liberated and crystallized from benzene-heptane forming yellow leaflets that melt at about 97° to 98°C. This isonitrosoketone is dissolved in absolute alcohol containing an excess of hydrogen chloride and is hydrogenated with palladized charcoal, yielding β-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-βketoisopropylamine hydrochloride, a salt that melts at about 176°C with decomposition.
12.3 g (1/20 mol) of β-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-β-ketoisopropylamine hydrochloride (MP 176°C) is dissolved in 50 cc of water and hydrogenated with platinum oxide platinum black in the customary Adams-Burgess Parr apparatus. About 1/20 mol of hydrogen is absorbed, after which the solution is filtered off from the catalyst, evaporated to dryness in vacuo and recrystallized from absolute alcohol, absolute ether being added to decrease solubility. The hydrochloride is thus obtained in substantially theoretical yield. It crystallizes in plates and melts at 215°C.
Therapeutic Function
Hypertensive
Pharmacokinetics
Methoxamine is a potent sympathomimetic amine that increases both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Methoxamine is indicated for prevention and treatment of the acute hypotensive state occurring with spinal anesthesia. It is also indicated as adjunctive treatment of hypotension due to hemorrhage, reactions to medications, surgical complications, and shock associated with brain damage due to trauma or tumor. Methoxamine acts on both α1-adrenergic receptors but appears to have no effect on β-adrenergic receptors. It acts by increasing the force of the heart's pumping action as well as constricting peripheral blood vessels.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of methoxamine
| Melting point: | 85-86 °C |
| Boiling point: | 368.4±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.117±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 11.87±0.45(Predicted) |
Safety information for methoxamine
Computed Descriptors for methoxamine
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1