Mesna
Synonym(s):2-Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid sodium salt;Coenzyme M sodium salt;HS-CoM Na;MESNA;Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate
- CAS NO.:19767-45-4
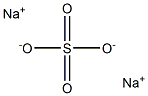
- Empirical Formula: C2H7NaO3S2
- Molecular Weight: 166.18
- MDL number: MFCD00007535
- EINECS: 243-285-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
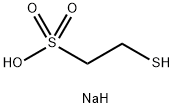
What is Mesna?
Chemical properties
White to Off-White Solid
Originator
Mistabronco,UCB,W. Germany,1973
The Uses of Mesna
Mesna reacts with acrolein and other urotoxic metabolites of oxazaphosphorines (cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide) to form stable, non-urotoxic compounds. Mesna does not have any antitumour activity, nor does it appear to interfere with the antitumour activity of antineoplastic drugs. This medication is used to protect the bladder wall from the harmful effects of some cancer-fighting drugs.
The Uses of Mesna
adrenergic agonist, coronary vasodilator, Ca channel blocker
The Uses of Mesna
2-Mercaptoethanesulfonic acid sodium salt (Coenzyme M sodium salt, MESNA) is used as an antioxidant and cytoprotective agent in a wide variety of applications from protection from toxicity of therapeutic agents, such as cyclophosphamide to prevention from brain injury damage.
What are the applications of Application
Mesna is a compound that reacts with acrolein and other urotoxic metabolites to form stable, non-urotoxic compounds
Definition
ChEBI: Mesna is an organosulfonic acid.
Manufacturing Process
2,100 g of β-S-thiuronium ethanesulfonate were placed in a solution of 2,100 cc of concentrated aqueous ammonia and 400 cc of water. The mixture was carefully warmed on a steam bath and an exothermic reaction ensured, at which point the β-S-thiuronium ethanesulfonate passed into solution. After standing for two hours at room temperature, the solution was concentrated until all of the excess ammonia had been removed.
The resultant clear solution from the ammonolysis reaction was processed through "Amberlite IR-120" ion exchange resin and converted into β-Smercaptoethanesulfonic acid in 93.7% yield (based on β-S-thiuronium ethanesulfonate).
It is expedient not to heat the reaction mixture rapidly since this increases the loss of ammonia and effects an incomplete reaction. Heating the mixture too rapidly may retard the ammonolysis reaction entirely. The amount of ammonia used is considered to be a satisfactory minimum and larger quantities of ammonia are not found to have any beneficial effect on the reaction. It is also expedient to remove the excess ammonia before processing the guanidinium β-mercaptoethanesulfonate solution through the ion exchange resin since the resin will also remove the ammonia with the result that the capacity of the resin for the exchange of guanidinium ions will be reduced.
Although the preparation of β-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid through the ammonolysis reaction is the preferred method, it is also possible to prepare the sulfonic acid by the sodium hydroxide hydrolysis of β-S-thiuronium ethanesulfonate followed by the ion exchange treatment. The resulting acid,
however, is generally not as satisfactory as that prepared by the ammonolysis
reaction.
brand name
Ausobrone;Mexnex;Mistabronco;Mistabronco;Mistalon;Mucofluid;Mucolene;Uromitexan;Uronexitan.
Therapeutic Function
Mucolytic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Mesna, an antidote used to protect patients treated with cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide from haemorrhagic vesiculitis, was introduced on the market in 1984. Shortly afterwards, its use became associated with allergic reactions, which occurred mainly in patients treated with the oral solution. This led to the withdrawal of this formulation in Germany, the only country where it was marketed. An oral liquid dosage form is still registered, but not marketed, in the Netherlands and products for intravenous injection remain available elsewhere.
General Description
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Contact allergens
Mesna is used as a mucolytic agent, and as an antidote to chloro-acetyl-aldehyde and acrolein (a bladder toxic metabolite of ifosfamide or cyclophosphamide). It hasbeen reported as a cause of occupational allergic (hand and airborne) dermatitis in nurses
Clinical Use
Prophylaxis of urothelial toxicity in patients treated with ifosfamide or cyclophosphamide
Metabolism
Rapidly metabolised in the liver to the disulfide, dimesna, and is excreted in the urine as both metabolite and unchanged drug; dimesna is reduced back to mesna, which is the active form, in the kidney.
Purification Methods
It can be recrystallised from H2O and does not melt below 250o. It is purified further by converting to the free acid by passing a 2M solution through an ion-exchange (Amberlite IR-120) column in the acid form, evaporating the eluate in a vacuum to give the acid as a viscous oil (readily decomposes) which can be checked by acid and SH titration. It is then dissolved in H2O, carefully neutralised with aqueous NaOH, evaporated and the salt recrystallised from H2O [Schramm J Am Chem Soc 77 6231 1955]. [Beilstein 4 IV 85.]
Properties of Mesna
| Melting point: | >240°C dec. |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in cyclohexane |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Also soluble in methanol, DMSO (33 mg/ml) and ethanol (<1 mg/ml). |
| Merck | 14,5909 |
| BRN | 3657828 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 19767-45-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Mesna
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Mesna
Mesna manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sodium 2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Sodium 2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate 97% CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate 97% CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 MESNA 98% CAS 19767-45-4View Details
MESNA 98% CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 Mesna CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Mesna CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 Mesna CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Mesna CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4 -
 Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate CAS 19767-45-4View Details
19767-45-4
