POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)
Synonym(s):PGA;PGA, Poly(glycolic acid);Poly(2-hydroxyacetic acid)
- CAS NO.:26009-03-0
- Empirical Formula: C6H6O5X2
- Molecular Weight: 158.11
- MDL number: MFCD00868116
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
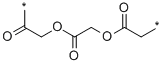
What is POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)?
Chemical properties
Polyglycolic acid (PGA), also known as polyglycolide, was first reported in 1893, but it was not until 1967 that the first commercially successful patent was granted for sutures. Like polylactide, polyglycolide is synthesized from the cyclic diester. An important difference between polylactide and polyglycolide, is that polyglycolide (mp 220 C (428 F) is higher melting than poly-L-lactide (mp 170 C (338 F). Although the polymerization reaction in both cases is reversible at high temperature, melt processing of polyglycolide is more difficult because the melting temperature is close to its decomposition temperature. Unlike poly-L-lactide which is absorbed slowly, polyglycolide is absorbed within a few months post-implantation owing to greater hydrolytic susceptibility. In vitro experiments have shown the effect on degradation by enzymes, pH, annealing treatments, and gamma irradiation. Braided polyglycolide sutures undergo surprisingly rapid hydrolysis in vivo owing to cellular enzymes released during the acute inflammatory response following implantation.
The Uses of POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)
Surgical aid (surgical suture material).
The Uses of POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)
medical device
Definition
ChEBI: A polymer composed of repeating hydroxyacetic acid units.
Properties of POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)
| Melting point: | 229 °C |
| Density | 1.50 g/cm3 |
Safety information for POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)
Computed Descriptors for POLY(2-HYDROXYACETIC ACID)
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 2-Hexyn-1-ol 98+View Details
764-60-3 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
