Lusutrombopag
- CAS NO.:1110766-97-6
- Empirical Formula: C29H32Cl2N2O5S
- Molecular Weight: 591.55
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
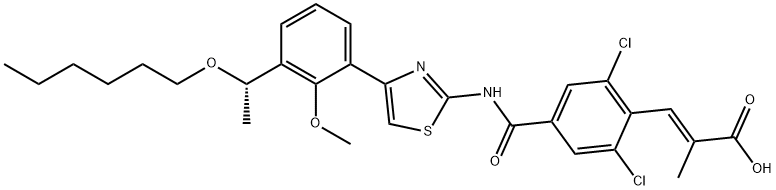
What is Lusutrombopag?
Absorption
Lusutrombopag is rapidly absorbed following oral administration . It exhibited a dose‐proportional pharmacokinetic profile over the single dose range of 1 mg to 50 mg, which was similar in both healthy subjects and those with chronic liver disease. A geometric mean (%CV) maximal concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) in healthy subjects receiving 3 mg of lusutrombopag were 111 (20.4) ng/mL and 2931 (23.4) ng.hr/mL . The accumulation ratios of Cmax and AUC were approximately 2 with once‐daily multiple‐dose administration, and steady‐state plasma lusutrombopag concentrations were achieved after Day 5. The time to reach peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) were approximately 6 to 8 hours after oral administration in patients with chronic liver disease . Food consumption is not reported to affect the absorption and bioavailability of lusutrombopag .
Toxicity
There is no known antidote for lusutrombopag: hemodialysis is not expected to enhance the elimination of lusutrombopag from the plasma as there is high protein binding. Overdose may be characterized by excessive platelet counts that may result in thrombotic and thromboembolic complications. In the event of overdose, closely monitor patients and platelet count and treat thrombotic complications in accordance with standard of care .
In animal and in vitro studies, lusutrombopag did not display any carcinogenicity, genotoxicity, or reproductive toxicity .
The Uses of Lusutrombopag
Lusutrombopag is a newly discovered thrombopoietin receptor agonist used in the treatment of patients with chronic ITP.
Background
Lusutrombopag is an orally bioavailable thrombopoietin receptor (TPOR) agonist developed by Shionogi & Company (Osaka, Japan). TPOR is a regulatory target site for endogenous thrombopoietin, which acts as a primary cytokine to promote megakaryocyte proliferation and differentiation, and affect other hematopoietic lineages as well, including erythroid, granulocytic and lymphoid lineages . Thrombocytopenia, which indicates abnormally low levels of platelets, is a common complication related to chronic liver disease. This hematological abnormality, especially in cases of severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count <50,000/μL), creates challenges to patients requiring invasive medical procedures where there is a significant risk for spontaneous bleeding . Lusutrombopag binds to the transmembrane domain of TPOR expressed on megakaryocytes, and causes the proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocytic progenitor cells from hematopoietic stem cells .
In September 2015, lusutrombopag received its first global approval in Japan to reduce the need for platelet transfusion in adults with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia who are schedule to undergo an invasive medical procedure . Lusutrombopag was approved by the FDA on July 31st, 2018 for the same therapeutic indication under the market name Mulpleta. In two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, patients with chronic liver disease and severe thrombocytopenia who were undergoing an invasive procedure with a platelet count less than 50 x 10^9/L were administered lusutrombopag orally . Higher percentages (65-78%) of the patients receiving lusutrombopag required no platelet transfusion prior to the primary invasive procedure compared to those receiving placebo . Lusutrombopag is currently in phase III development in various European countries including Austria, Belgium, Germany, and the UK .
Indications
Lusutrombopag is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adults with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a medical or dental procedure.
Definition
ChEBI: Lusutrombopag is a member of cinnamic acids.
Pharmacokinetics
The AUC of lusutrombopag was found to correlate the increased platelet counts. Following administration of 3 mg daily dose in patients with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia, the mean (standard deviation) maximum platelet count in patients (N=74) without platelet transfusion was 86.9 (27.2) × 10^9/L, and the median time to reach the maximum platelet count was 12.0 (5 to 35) days . Lusutrombopag was not shown to induce any clinically significant QTc prolongation at a dose 8 times the recommended dosage .
Metabolism
CYP4 enzymes predominantly contribute to the metabolism of lusutrombopag, especially CYP4A11 . Lusutrombopag is reported to mainly undergo ω- and β-oxidation, as well as glucuronidation .
Properties of Lusutrombopag
| Density | 1.299±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| solubility | DMSO: 30 mg/ml |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | 4.33±0.21(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Lusutrombopag
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Lusutrombopag
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1