Lorazepam
Synonym(s):(±)-Lorazepam;7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
- CAS NO.:846-49-1
- Empirical Formula: C15H10Cl2N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 321.16
- MDL number: MFCD00063406
- EINECS: 212-687-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
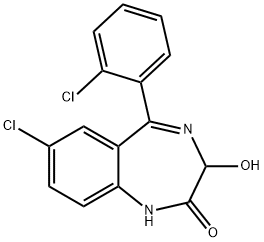
What is Lorazepam?
Absorption
Readily absorbed with an absolute bioavailability of 90% when given orally. When intramuscularly administered a dose of 4 mg, lorazepam is completely and rapidly absorbed and achieves a maximal serum concentration of 48 ng/ml in 15-30 minutes. When administered orally, the time to attained maximum concentration is observed to be of 2 hours.
Toxicity
The LD50 observed by oral administration in a mouse is of 1850 mg/kg. When an overdose administration is registered, signs of CNS and respiratory depression are rapidly observed. An overdose stage can result in profound sedation, deep respiratory depression, coma, and death. When overdose is observed, it is recommended to administer emergency symptomatic medical support with attention to produce an increase in lorazepam elimination.
There is no evidence of carcinogenicity nor mutagenicity. At doses higher than 40 mg/kg there is evidence of fetal resorption and increase in fetal loss.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Tavor,Wyeth,Italy,1972
The Uses of Lorazepam
An anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant. Controlled substance (depressant)
Background
Lorazepam is a short-acting and rapidly cleared benzodiazepine used commonly as a sedative and anxiolytic. It was developed by DJ Richards, presented and marketed initially by Wyeth Pharmaceuticals in the USA in 1977. The first historic FDA label approval is reported in 1985 by the company Mutual Pharm.
Indications
Lorazepam is FDA-approved for the short-term relief of anxiety symptoms related to anxiety disorders and anxiety associated with depressive symptoms such as anxiety-associated insomnia. It is as well used as an anesthesia premedication in adults to relieve anxiety or to produce sedation/amnesia and for the treatment of status epilepticus.
Some off-label indications of lorazepam include rapid tranquilization of an agitated patient, alcohol withdrawal delirium, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, panic disorder, delirium, chemotherapy-associated anticipatory nausea and vomiting, and psychogenic catatonia.
Definition
ChEBI: Lorazepam is a benzodiazepine.
Manufacturing Process
The starting material was 2-amino-2',5-dichlorobenzophenone which was
reacted with hydroxylamine and then with chloroacetyl chloride. The
intermediate thus obtained is reacted with methylamine and then with acetic
anhydride.
To a slightly warm suspension of 3-acetoxy-7-chloro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-
dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one thus obtained was added 4N sodium
hydroxide solution with stirring. All the solid dissolved and soon a thick white
solid precipitated out. The solid was filtered, washed well with water and
recrystallized from ethanol. The product was isolated as a solvate with 1 mol
of ethanol. When heated it loses the ethanol of solvation and melts at 166°C
to 168°C.
brand name
Ativan (Baxter Healthcare); Ativan (Biovail); Loraz (Quantum Pharmics).
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
General Description
Lorazepam, 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-one(Ativan), is the 2'-chloro derivative of oxazepam. In keepingwith overall SARs, the 2'-chloro substituent increases activity.As with oxazepam, metabolism is relatively rapid anduncomplicated because of the 3-hydroxyl group in the compound.Thus, it also has short half-life (2–6 hours) and similarpharmacological activity.
Biological Activity
Ligand at the GABA A receptor benzodiazepine modulatory site. Anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and sedative/hypnotic agent.
Pharmacokinetics
The effect of lorazepam in GABA-A receptors produces an increase in the frequency of opening of the chloride ion channel. However, for its effect to generate, the neurotransmitter is required. The anticonvulsant properties of lorazepam are thought to be related to the binding to voltage-dependent sodium channels in which the sustained repetitive firing gets limited by the slow recovery of sodium channels due to the benzodiazepine effect.
The effect of lorazepam seems to be very compartmental which was observed with a different generation of sleepiness and a dizziness effect.
Metabolism
Lorazepam is hepatically metabolized by CYP450 isoenzymes and extensively conjugated to the 3-0-phenolic glucuronide. This is an inactive metabolite and is eliminated mainly by the kidneys.
Properties of Lorazepam
| Melting point: | 166-168°C |
| Boiling point: | 533.8±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.4835 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6070 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), sparingly soluble or slightly soluble in methylene chloride. |
| pka | pK1 1.3; pK2 11.5(at 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 54mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| Stability: | hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 846-49-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lorazepam(846-49-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lorazepam (846-49-1) |
Safety information for Lorazepam
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H361:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Lorazepam
Lorazepam manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Lorazepam Standard Drug PowderView Details
Lorazepam Standard Drug PowderView Details
846-49-1 -
 Lorazepam PowderView Details
Lorazepam PowderView Details
846-49-1 -
 Lorazepam APIView Details
Lorazepam APIView Details
846-49-1 -
 Lorazepam Standard Drug PowderView Details
Lorazepam Standard Drug PowderView Details
846-49-1 -
 Lorazepam Powder - Lorazepam - Buy Ativan Powder - Order CAS 846-49-1, kgView Details
Lorazepam Powder - Lorazepam - Buy Ativan Powder - Order CAS 846-49-1, kgView Details
846-49-1 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
