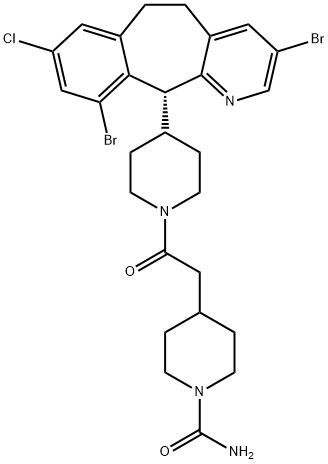
LONAFARNIB
Synonym(s):4-[2-[4-[(11R)-3,10-Dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5Hbenzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl]-1-piperidinyl]-2-oxoethyl]-1-piperidinecarboxamide;SCH66336;SCH-66336
- CAS NO.:193275-84-2
- Empirical Formula: C27H31Br2ClN4O2
- Molecular Weight: 638.82
- MDL number: MFCD06795138
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
What is LONAFARNIB?
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of lonafarnib is unknown; in healthy subjects administration of either 75 or 100 mg of lonafarnib twice daily resulted in mean peak plasma concentrations (%CV) of 834 (32%) and 964 (32%) ng/mL, respectively. Twice daily administration of 115 mg/m2 lonafarnib in HGPS patients resulted in a median tmax of 2 hours (range 0-6), mean Cmax of 1777 ± 1083 ng/mL, mean AUC0-8hr of 9869 ± 6327 ng*hr/mL, and a mean AUCtau of 12365 ± 9135 ng*hr/mL. The corresponding values for a dose of 150 mg/m2 are: 4 hours (range 0-12), 2695 ± 1090 ng/mL, 16020 ± 4978 ng*hr/mL, and 19539 ± 6434 ng*hr/mL, respectively.
Following a single oral dose of 75 mg in healthy subjects, the Cmax of lonafarnib decreased by 55% and 25%, and the AUC decreased by 29% and 21% for a high/low-fat meal compared to fasted conditions.
Toxicity
Toxicity information regarding lonafarnib is not readily available. Patients experiencing an overdose are at an increased risk of severe adverse effects such as altered electrolyte, blood cell, and liver enzyme levels, retinal toxicity, nephrotoxicity, fertility impairment, and embryo-fetal toxicity. Symptomatic and supportive measures are recommended.
The Uses of LONAFARNIB
Lonafarnib is an orally bioavailable tricyclic inhibitor of farnesyl protein transferase. It inhibits Rheb farnesylation and mTOR signaling and enhances taxane and tamoxifen antitumor activity. Studies show that it induces CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein-dependent expression of death receptor 5, leading to induction of apoptosis in human cancer cells
The Uses of LONAFARNIB
Chemotherapeutic (farnesyl transfer ase inhibitor).
Background
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder estimated to affect approximately one in 20 million individuals resulting in adverse symptoms associated with premature ageing: skeletal dysplasia, joint contractures, atherosclerosis, myocardial fibrosis/dysfunction, scleroderma-like cutaneous effects, lipoatrophy, alopecia, and a severe failure to thrive; HGPS is uniformly fatal. Mechanistically, HGPS is underpinned by a single heterozygous C-to-T mutation at position 1824 of the LMNA gene, which results in the accumulation of an aberrant farnesylated form of lamin A called progerin in the inner nuclear membrane. Lonafarnib is a farnesyl transferase (FTase) inhibitor (FTI), which reduces the farnesylation of numerous cellular proteins, including progerin; as progerin farnesylation is important for localization to the nuclear membrane, lonafarnib inhibits progerin accumulation and improves symptoms in HGPS patients.
Merck originally developed Lonafarnib and subsequently licensed it to Eiger Biopharmaceuticals Inc., which currently markets it under the trademark ZOKINVY?. Lonafarnib was granted FDA approval on November 20, 2020, and is the first FDA-approved treatment for HGPS and other related progeroid laminopathies.
Indications
Lonafarnib is a farnesyltransferase inhibitor indicated in patients aged 12 months and older with a body surface area of at least 0.39 m2 to reduce the risk of mortality associated with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS). It is also indicated in this same population for the treatment of processing-deficient progeroid laminopathies that either involve a heterozygous LMNA mutation resulting in the accumulation of a progerin-like protein or homozygous/compound heterozygous mutations in ZMPSTE24.
Definition
ChEBI: A 4-{2-[4-(3,10-dibromo-8-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[5,6]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridin-11-yl)piperidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethyl}piperidine-1-carboxamide that has R configuration. It is used as oral farnesyltransferase nhibitor.
General Description
Lonafarnib (SCH66336) is a farnesyl transferase inhibitor (FTI). K- and N-Ras are substrates of farnesyl transferase.
Biological Activity
lonafarnib (sch66336, sarasar) is an potent, selective, orally, bioavailable tricyclic nonpeptidyl nonsulfhydry inhibitor of farnesyltransferase (ftase).[1] it is a small molecular with the formula of c27h31br2cln4o2 and molecular weight of 638.82. farnesylated ras proteins was found to regulate signal transduction pathways which drive cell proliferation, growth and survival and be required for its membrane localization.[1, 2] lonafarnib inhibits the post-translational farnesylcation of ras proteins, therefore blocking translocation of ras to the plasma membrane.[3][1] eric w, malcolm j. m, kim n. c, d. scott e, et al. a multinomial phase ii study of lonafarnib (sch 66336) in patients with refractory urothelial cancer. urologic oncology: seminars and original investigations. 2005, 23. 143-149.[2] gongjie l, stacey a. t, cindy h. m, yunsheng h, w. robert b, et al. continuous and intermittent dosing of lonafarnib potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel on preclinical human prostate cancer models. int. j. cancer. 2009, 125. 2711–2720.[3] vasiliki a. n, alexander j. s, keith t. f, hensin t, et al. melanoma: new insights and new therapies. j invest dermatol. 2012, 132. 854–863.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lonafarnib prevents the post-translational lipid modification of H-Ras and other farnesylated proteins. Lonafarnib treatment results in microtubule bundling, increased microtubule acetylation and stabilization and suppression of microtubule dynamics.
Mechanism of action
Lonafarnib is a protein farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI) that reversibly binds to the farnesyltransferase CAAX binding site9, thereby inhibiting progerin farnesylation and subsequent intercalation into the nuclear membrane.
Pharmacokinetics
Lonafarnib is a direct farnesyl transferase inhibitor that reduces the farnesylation of numerous cellular proteins, including progerin, the aberrantly truncated form of lamin A that accumulates in progeroid laminopathies such as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. Treatment with lonafarnib has been associated with electrolyte abnormalities, myelosuppression, and increased liver enzyme levels (AST/ALT), although causation remains unclear. Also, lonafarnib is known to cause nephrotoxicity in rats and rod-dependent low-light vision decline in monkeys at plasma levels similar to those achieved under recommended dosing guidelines in humans; patients taking lonafarnib should undergo regular monitoring for both renal and ophthalmological function. In addition, based on observations from animal studies with rats, monkeys, and rabbits with plasma drug concentrations approximately equal to those attained in humans, lonafarnib may cause both male and female fertility impairment and embryo-fetal toxicity.
Side Effects
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- nausea
- stomach pain
- constipation
- gas
- decreased appetite
- decreased weight
Metabolism
Lonafarnib is metabolized in vitro primarily by CYP3A4/5 and partially by CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2E1. Formation of the primary metabolites involves oxidation and subsequent dehydration in the pendant piperidine ring.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of LONAFARNIB
| Melting point: | 214.5-215.9° (monohydrate); mp 222-223° |
| Boiling point: | 710.4±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D25 = +49.1° (c = 0.21 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.536 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| pka | 15.76±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
Safety information for LONAFARNIB
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for LONAFARNIB
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Lonafarnib 98.00% CAS 193275-84-2View Details
Lonafarnib 98.00% CAS 193275-84-2View Details
193275-84-2 -
 Lonafarnib CAS 193275-84-2View Details
Lonafarnib CAS 193275-84-2View Details
193275-84-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
