Lithium acetate
Synonym(s):Lithium ethanoate
- CAS NO.:546-89-4
- Empirical Formula: C2H3LiO2
- Molecular Weight: 65.99
- MDL number: MFCD00013057
- EINECS: 208-914-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 14:24:08
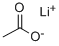
What is Lithium acetate?
Description
Lithium acetate (CH3COOLi) is a salt of lithium and acetic acid.
Chemical properties
solid
The Uses of Lithium acetate
Lithium acetate is used in the laboratory as buffer for gel electrophoresis of DNA and RNA. It has a lower electrical conductivity and can be run at higher speeds than can gels made from TAE buffer (5-30V/cm as compared to 5 - 10 V / cm). Lithium boric acid or sodium boric acid are usually preferable to lithium acetate or TAE when analyzing smaller fragments of DNA (less than 500 bp) due to the higher resolution of borate-based buffers in this size range as compared to acetate buffers.
Lithium acetate is also used to permeabilize the cell wall of yeast for use in DNA transformation. It is believed that the beneficial effect of LiAc is caused by its chaotropic effect denaturing both DNA, RNA and proteins.
The Uses of Lithium acetate
Lithium acetate hydrate is used in the laboratory as buffer for gel electrophoresis of DNA and RNA. It is also used to permeabilize the cell wall of yeast for use in DNA transformation. It is a metal acetate for proteomics research.
The Uses of Lithium acetate
Lithium acetate (LiOAc) is a lithium source and a doping salt which can be used in the preparation of plasticized polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. It can be used as a monovalent cation, which improves the transformation efficiency of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
What are the applications of Application
Lithium acetate is a metal acetate for proteomics research
Definition
ChEBI: An acetate salt comprising equal numbers of acetate and lithium ions.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ALUMINUM and LITHIUM COMPOUNDS.
Properties of Lithium acetate
| Melting point: | 283-285 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.3[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | H2O: 5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder or Crystals |
| color | White to yellow |
| Water Solubility | 40.8 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,5521 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 546-89-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lithium acetate (546-89-4) |
Safety information for Lithium acetate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Lithium acetate
| InChIKey | XIXADJRWDQXREU-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Lithium acetate manufacturer
PARAD CORPORATION PRIVATE LIMITED
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Lithium acetate 99%View Details
Lithium acetate 99%View Details -
 Lithium acetate hydrate CAS 546-89-4View Details
Lithium acetate hydrate CAS 546-89-4View Details
546-89-4 -
 Lithium acetate hydrate CAS 546-89-4View Details
Lithium acetate hydrate CAS 546-89-4View Details
546-89-4 -
 Lithium acetate CAS 546-89-4View Details
Lithium acetate CAS 546-89-4View Details
546-89-4 -
 Lithium acetate 99% CAS 546-89-4View Details
Lithium acetate 99% CAS 546-89-4View Details
546-89-4 -
 Powder Technical Grade Lithium acetateView Details
Powder Technical Grade Lithium acetateView Details
546-89-4 -
 Pure Lithium AcetateView Details
Pure Lithium AcetateView Details
546-89-4 -
 Powder White Crystal Parad Lithium Acetate, For LaboratoryView Details
Powder White Crystal Parad Lithium Acetate, For LaboratoryView Details
546-89-4
