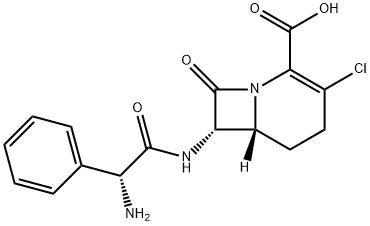
LF163892 MONOHYDRATE
- CAS NO.:76470-66-1
- Empirical Formula: C16H16ClN3O4
- Molecular Weight: 349.77
- MDL number: MFCD05664608
- EINECS: 617-954-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-04-26 16:55:04
What is LF163892 MONOHYDRATE?
Absorption
Well absorbed with approximately 90% absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral ingestion.
Toxicity
Adverse effects include diarrhea, nausea, stomach upset, vomiting, headache, dizziness, rash, bone marrow depression.
Description
Loracarbef is a synthetic C-5 “carba” analogue of cefaclor. The smaller methylene moiety (as compared to sulfur) would be expected to make loracarbef more reactive/potent, and this seems to be the case. It is more stable chemically, however, and this adds to its virtues.
Originator
Lorabid,Eli Lilly and Company
The Uses of LF163892 MONOHYDRATE
An antibiotic, a synthetic carbacephem analogue of cefaclor, and is more stable chemically.
Background
Loracarbef is a carbacephem antibiotic sometimes grouped together with the second-generation cephalosporin antibiotics. It is marketed under the trade name Lorabid.
Indications
Used to treat upper respiratory tract bacterial infections, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, pharyntitis and tonsillitis, skin absceses, urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis caused by E. coli, S. pyogenes, S. aureus, S. saprphyticus, S. penumoniae, H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis.
Definition
ChEBI: A synthetic "carba" analogue of cefaclor, with carbon replacing sulfur at position 1. Used to treat a wide range of infections caused by both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Manufacturing Process
Loracarbef was obtained by biochemical method.
a) Cultivation of a microorganism having an ability of optically selective
acylation
As a seed strain, Pseudomonas melanogenum ATCC 17808 [Biological
properties are described in Journal of the Agricultural Chemical Society of
Japan 37, 71 (1963)] is used.
As the seed medium, an aqueous solution containing 1% polypepton, 1%
yeast extract, 0.5% meat extract, 0.5% sodium glutamate and 0.25% sodium
chloride and adjusted to a pH of 7.0 with 5 N NaOH is used. One loopful of
the seed strain is inoculated into 10 ml the seed medium and culturing is
carried out at of 30°C for 24 hours. The whole amount of the seed medium is
put into 300 ml of the culture medium in a 2 L Erlenmeyer flask and culturing
is carried out at a temperature of 30°C. The composition of the culture
medium is the same as that of the seed medium.
b) Preparation of cell suspension
After culturing for 24 hours, cell bodies are recovered from the culture broth
by centrifugation and washed 2 times with 50 ml of 0.9% saline solution. The
cells are suspended in a concentration of 20 mg/ml by dry weight in 1/30 M
phosphate buffer (pH 6.5).
c) Preparation of a substrate solution
200 mg of the trifluoroacetate of ()-cis-7-amino-3-chloro-1-azabicyclo[4,2,0]
oct-2-en-8-on-2-carboxylic acid (obtained by the method described in JPUPA
No. 87791/80) and 800 mg of the hydrochloride of D-phenylglycine
methylester are added in 9 ml of 1/30 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH6.5). 5 N KOH is added in a small portion and the mixture is again adjusted to
a pH of 6.5 to dissolve two starting compounds. Finally, deionized water is
added to make 10 ml of a solution.
d) Enzyme reaction
In this step, 10 ml of the disrupted cell suspension is added to 10 ml of the
substrate solution and enzyme reaction is carried out at a temperature of
30°C for 2 hours. The reaction is monitored by high speed liquid
chromatography. Elution is carried out with 7% methanol - 0.2 M KH2PO4
solution. Reaction reaches maximum in a yield of 90% to the starting
compound in 2 hours.
After the completion of reaction, cell bodies are removed from the reaction
solution by centrifugation. The supernatant is concentrated under reduced
pressure and charged on a column with 100 ml of Diaion HP-10. After adding
200 ml of deionized water, elution is carried out with 25% aqueous methanol
solution. Then, the fractions containing the desired compound are
concentrated under reduced pressure to make a 5 ml of concentrate. The
concentrate is charged on a column packed with 130 ml of Sephadex-LH20
and elution is carried out with a solvent of water and methanol (50:50). The
desired product is eluted in 55 ml to 75 ml of fractions. The fractions are
concentrated under reduced pressure and lyophilized to obtain 78 mg
(6R,7S)-7-(R)-phenylglycinamido-3-chloro-1-azabicyclo[4,2,0]oct-2-en-8-on-
2-carboxylic acid of a white powder [α]D21 = -75.8° (c = 0.4, H2O), melting
point 300°C or more (browning).
brand name
Lorabid (King).
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Antimicrobial activity
An oral carbacephem, with carbon replacing sulfur in the
fused ring structure. Its structure and properties are otherwise
closely related to those of cefaclor, but it has improved
chemical stability. Activity and stability to β-lactamases correspond
closely to those of cefaclor.
It is almost completely absorbed by the oral route, but
food delays absorption. A 500 mg oral dose achieves a serum
concentration of around 16 mg/L after 1.3 h. Adequate concentrations
are achieved for the treatment of upper respiratory
tract infection. Sputum concentrations have been found
to be around 2% of the corresponding plasma level. The
plasma half-life is about 1 h and protein binding is 25%.
Most of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine, 60%
within 12 h. The elimination half-life is increased in patients
with impaired renal function. Probenecid delays excretion.
Diarrhea is the most prominent side effect, occurring in
about 4% of patients. Other gastrointestinal upsets are also
reported. It has been used for the oral treatment of upper
respiratory tract infection, skin and soft-tissue infections, and
uncomplicated urinary tract infection caused by sensitive
organisms, but is not widely available.
Pharmacokinetics
Loracarbef is considered a second generation cephalosporin antibiotic. The advantages of cephalosporin antibiotics include a broad range of activity, a safe record in children with almost no dose-related toxicity, and the lack of need to monitor levels. Adverse reactions are rare and consist primarily of hypersensitivity reactions with urticaria, nonspecific rash, and pruritus. Loracarbef can be used to treat a large number of bacterial infections caused by gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, including upper respiratory tract bacterial infections, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, pharyntitis and tonsillitis, skin absceses, urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis caused by E. coli, S. pyogenes, S. aureus, S. saprphyticus, S. penumoniae, H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis.
Clinical Use
Loracarbef (Lorabid) is the first of a series of carbacephemsprepared by total synthesis to be introduced. Carbacephemsare isosteres of the cephalosporin (or △ 3-cephem) antibioticsin which the 1-sulfur atom has been replaced by a methylene(CH2) group. Loracarbef is isosteric with cefaclor and hassimilar pharmacokinetic and microbiological properties.Thus, the antibacterial spectrum of activity resembles thatof cefaclor, but it has somewhat greater potency againstH. influenzae and M. catarrhalis, including β-lactamase–producing strains. Unlike cefaclor, which undergoes degradationin human serum, loracarbef is chemically stable inplasma. It is absorbed well orally. Oral absorption is delayedby food. The half-life in plasma is about 1 hour.
Side Effects
Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect with loracarbef and, along with certain other adverse effects, is seen more frequently with children, so this lessens enthusiasm for the drug in patients younger than 12 years.
Metabolism
There is no evidence of metabolism in humans.
Properties of LF163892 MONOHYDRATE
| Melting point: | >196°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 662.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.52±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Aqueous Acid (slightly) |
| pka | 3.10±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
Safety information for LF163892 MONOHYDRATE
Computed Descriptors for LF163892 MONOHYDRATE
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4