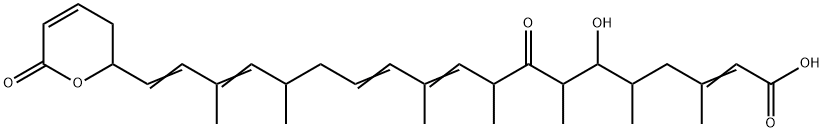
Leptomycin B
Synonym(s):;Elactocin;LMB;LMB, Chromosome Region Maintenance 1 Protein Inhibitor I, CRM1 Inhibitor I, Exportin 1 Inhibitor I, XPO1 Inhibitor I;Mantuamycin
- CAS NO.:87081-35-4
- Empirical Formula: C33H48O6
- Molecular Weight: 540.73
- MDL number: MFCD06795848
- EINECS: 617-954-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
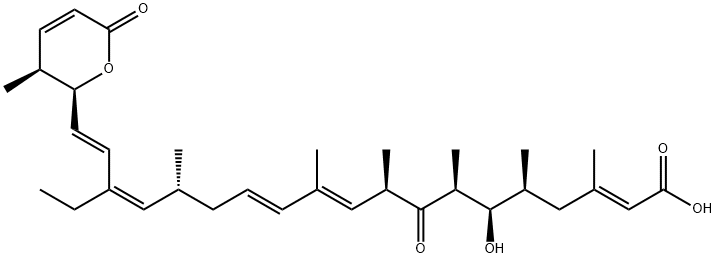
What is Leptomycin B?
Description
Leptomycin B (87081-35-4) is an inhibitor of nuclear export of proteins. Acts via covalent binding to and inhibiting CRM1/exportin-1.1 Inhibits the nuclear export of the HIV regulatory protein Rev.2 Leptomycin B stabilizes p53 by blocking its nuclear export.3
The Uses of Leptomycin B
Leptomycin B is the dominant and most studied member of the leptomycin class, isolated from selected Streptomyces strains. Leptomycin B is a nanomolar active and specific nuclear export inhibitor. Its target is CRM1/exportin1, a protein in the nuclear export sequence (NES). Proteins affected include c-Abl, cyclin B1, HIV-1 Rev, IκB, MPF, MAP/ERK, MDM2/p53, NF-κB/IκB7 and PKA. Leptomycin B inhibits export of many RNAs, e.g. COX-2 and c-FOS mRNA. Leptomycin B also shows antifungal and antibacterial and potent antitumour activities.
The Uses of Leptomycin B
Biological tool for studying nuclear localization and protein trafficking in eukaryotic cells.
The Uses of Leptomycin B
Potent, specific inhibitor of nuclear export signal (NES)-dependent protein export from the nucleus
What are the applications of Application
Leptomycin B, Free Acid is a potent nuclear export and RNA translation inhibitor
What are the applications of Application
Leptomycin B is a potent and specific nuclear export inhibitor that acts as an antifungal agent
Definition
ChEBI: A leptomycin having a (2E,10E,12E,16Z,18E)-double bond configuration as well as an ethyl substituent at position 17.
Biological Functions
Leptomycin B (LMB) is an unsaturated, branched-chain fatty acid that proved a potent tool in nuclear export studies. It was isolated from Streptomyces sp. strain ATS 1287. Until recently, LMB has been the only known small-molecule inhibitor of nuclear transport. The nuclear export inhibitor leptomycin B (LMB) prevents the export of proteins from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, protects p53 from Mdm2-mediated degradation, and potent inducer of p53 transcriptional activity. It is a specific inhibitor of the nuclear export of proteins containing leucine-rich nuclear export signal (NES). Supplementing sub-nanomolar concentrations of LMB to cultured cells caused inhibition of nuclear export of leucine-rich NES-bearing protein. Since its discovery as a potent inhibitor of nuclear export, a large number of shuttling proteins, performing a diverse range of cellular functions, are now known to accumulate in the nucleus.
General Description
Leptomycin B is an anti-fungal antibiotic, anti-tumor cytotoxin that inhibits CRM1-dependent, NES-dependent nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation (nuclear export inhibitor). NES containing proteins include HIV-1 REV; actin, c-Abl, cyclin B1, MDM2/p53, I?B, MPF, PKA and MEK.
Biological Activity
Antifungal antibiotic that is an inhibitor of the nuclear export of proteins; acts by binding directly to and inhibiting CRM1/exportin-1. Inhibits the nuclear export of the HIV regulatory protein Rev and stabilizes p53. Antitumor in vitro and in vivo .
Biochem/physiol Actions
Leptomycin B is an unsaturated, branched-chain fatty acid, and is an important tool in the study of nuclear export. Leptomycin B is a specific inhibitor of proteins containing nuclear export signal. Leptomycin B inhibits nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation of molecules such as the HIV-1 Rev protein and Rev-dependent export of mRNA. The addition of very small amounts to fibroblasts causes accumulation of MEK in the nucleus. Other proteins that are influenced by leptomycin?B are actin, c-Abl, cyclin B1, MDM2/p53, IκB, MPF, and PKA. The suggested inhibition mechanism involves the direct binding of leptomycin?B to CRM1, which blocks the binding of CRM1 to proteins containing the nuclear export signal, via the interaction with cysteine residue in CRM1 control conserved region.
Mechanism of action
The nuclear export inhibition mechanism involves the direct binding of Leptomycin B to exportin1, which blocks the binding of exportin1 to proteins containing the leucine-rich NES. Later, NES-exportin1 interaction was identified on a conserved region near cysteine-529 residue of human exportin1. This cysteine-529 residue on exportin1 provides LMB sensitivity because unsaturated γ-lactone in LMB undergoes a Michael-type reaction by the sulfhydryl group on cysteine residue. Once LMB is bound to exportin1, the NES-bearing nuclear export cargo fails to bind the receptor.
storage
-20°C
References
1) Kudo et al. (1998), Leptomycin B inhibition of signal-mediated nuclear export by direct binding to CRM1; Exp. Cell Res., 242 540 2) Wolff et al. (1997), Leptomycin B is an inhibitor of nuclear export: inhibition of nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Rev protein and Rev-dependent mRNA; Chem. Biol., 4 139 3) Freedman and Levine (1998), Nuclear export is required for degradation of endogenous p53 by MDM2 and human papillomavirus E6; Mol. Cell. Biol., 18 7288
Properties of Leptomycin B
| Melting point: | 41-44°, with prior softening (Hokanson) |
| alpha | D -24.5° (c = 0.70 in MeOH); D23 -157 ° (c = 0.7% in chloroform) |
| Boiling point: | 725.8±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.072±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 11°(52°F) |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | Supplied in solution in ethanol (1 mg/ml). Further dilutions may be made with either ethanol or DMSO. |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 5.10±0.33(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions or dilutions in DMSO are not stable. Solutions should be made fresh and used within one working day. |
Safety information for Leptomycin B
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Leptomycin B
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Leptomycin B solution from Streptomyces sp. CAS 87081-35-4View Details
Leptomycin B solution from Streptomyces sp. CAS 87081-35-4View Details
87081-35-4 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1