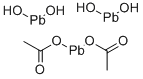
LEAD SUBACETATE
Synonym(s):Horne′s compound;Lead(II) hydroxide acetate
- CAS NO.:1335-32-6
- Empirical Formula: C4H10O8Pb3
- Molecular Weight: 807.72
- MDL number: MFCD00013041
- EINECS: 215-630-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
What is LEAD SUBACETATE?
Description
Lead subacetate is a white, heavy powder orgelatinous solid. Molecular weight = 807.71. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System):Health 3, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
dense white powder
Chemical properties
Lead subacetate is a white, heavy powder or gelatinous solid.
The Uses of LEAD SUBACETATE
In sugar analysis to remove coloring matters, etc., from solutions before polarizing; for clarifying and decolorizing other solutions of organic substances.
The Uses of LEAD SUBACETATE
Lead(II) acetate is used in the production of sweeteners, cosmetics, astringent, used in the cleaning and maintenance of stainless steel firearm suppressors (silencers) and compensators, and also used in making of slow matches.
General Description
White dense powder .
Air & Water Reactions
Keep container well closed.
Reactivity Profile
Acidic organic/inorganic salts, such as LEAD SUBACETATE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.
Potential Exposure
Used as a decolorizing agent in sugar solutions and as an analytical chemical.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Administer saline cathartic and anenema. For relief of colic, administer antispasmodic(calcium gluconate, atropine, papaverine). Consider morphine sulfate for severe pain.Whole blood lead levels, circulating plasma/erythrocytelead concentration ratio, urine ALA, and erythrocyte protoporphyrin fluorescent microscopy may all be useful in monitoring or assessing lead exposure. Chelating agents, such asedetate disodium calcium (Ca EDTA) and penicillamine(not penicillin), are generally useful in the therapy of acutelead intoxication.Antidotes and special procedures for lead: Persons with significant lead poisoning are sometimes treated with CaEDTA while hospitalized. This “chelating” drug causes arush of lead from the body organs into the blood and kidneys, and thus has its own hazards, and must be administered only by highly experienced medical personnel undercontrolled conditions and careful observation. Ca EDTA orsimilar drugs should never be used to prevent poisoningwhile exposure continues or without strict exposure control,as severe kidney damage can result.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from heat, oxidizers, strong acids.Lead is regulated by an OSHA Standard 1910.1025. Allrequirements of the standard must be followed. A regulated,marked area should be established where this chemical ishandled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHAStandard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN1616 Lead acetate, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poison Inhalation Hazard
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, and epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal
Properties of LEAD SUBACETATE
| Melting point: | 75℃ |
| form | Granular Powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5419 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be air-sensitive. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead acetate (1335-32-6) |
Safety information for LEAD SUBACETATE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for LEAD SUBACETATE
LEAD SUBACETATE manufacturer
Nithyasri Chemicals (APURVA CHEMICALS)
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
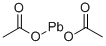
You may like
-
 1335-32-6 Lead acetate, basic 98%View Details
1335-32-6 Lead acetate, basic 98%View Details
1335-32-6 -
 1335-32-6 99%View Details
1335-32-6 99%View Details
1335-32-6 -
 Lead(II) acetate, Basic CAS 1335-32-6View Details
Lead(II) acetate, Basic CAS 1335-32-6View Details
1335-32-6 -
 Lead(II) acetate, Basic CAS 1335-32-6View Details
Lead(II) acetate, Basic CAS 1335-32-6View Details
1335-32-6 -
 Lead Subacetate extrapure CAS 1335-32-6View Details
Lead Subacetate extrapure CAS 1335-32-6View Details
1335-32-6 -
 LEAD ACETATE BASIC SOLUTION CAS 1335-32-6View Details
LEAD ACETATE BASIC SOLUTION CAS 1335-32-6View Details
1335-32-6 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0