1335-32-6
Product Name:
LEAD SUBACETATE
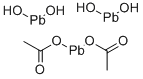
Formula:
C4H10O8Pb3
Synonyms:
Horne′s compound;Lead(II) hydroxide acetate
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Lead subacetate is a white dense powder. (NTP, 1992) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | White, heavy powder |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes at 200 °C |
| Melting Point | 75 °C |
| Solubility | Sol in water with alkaline reaction; on exposure to air absorbs carbon dioxide and becomes incompletely soluble |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /lead/. |
| Other Experimental Properties | Lead is derived from the decay of radon. /Inorganic lead/ |
| Chemical Classes | Metals -> Lead Compounds, Inorganic |
SAFETY INFORMATION
| Signal word | Danger |
|---|---|
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 8.1e+02 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 811.99664 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 813.99882 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 56.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 111 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 7 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Lead subacetate is a white dense powder. (NTP, 1992)
RELATED SUPPLIERS
All suppliers(2)
