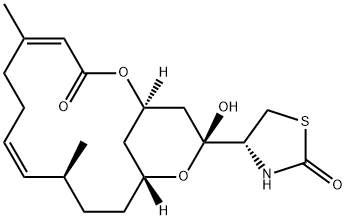
LATRUNCULIN B
Synonym(s):LAT-B;Latrunculin B, Latrunculia magnifica - CAS 76343-94-7 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:76343-94-7
- Empirical Formula: C20H29NO5S
- Molecular Weight: 395.51
- MDL number: MFCD00270879
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 16:48:35
What is LATRUNCULIN B?
Description
Latrunculin B (76343-94-7) inhibits actin polymerization and disrupts microfilament organization.1 Significantly more potent than cytochalasins in the disruption of microfilament mediated processes2, causes shortening and thickening of stress fibers. Active in cell culture.3,4?Effective doses for latrunculin B vary depending upon cell type but are frequently in the low micromolar range. Note: Latrunculin B is slowly inactivated by fetal bovine serum.
The Uses of LATRUNCULIN B
Latrunculin B is an actin polymerization inhibitor.
The Uses of LATRUNCULIN B
In elucidation of molecular mechanisms of motile processes.
The Uses of LATRUNCULIN B
Latrunculin B from Latruncula magnifica has been used for actin depolymerisation in various experiments. It has also been used as a component in bone marrow-derived dendritic cell (BMDC) complete medium, to study the formation of tubules from phagosomes in dendritic cells.
What are the applications of Application
Latrunculin B is an actin polymerization inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A macrolide consisting of a 14-membered bicyclic lactone attached to the rare 2-thiazolidinone moiety. It is obtained from the Red Sea sponge Latrunculia magnifica.
General Description
Latrunculin B is a macrocyclic toxin, which is produced by Latruncula magnifica.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Primary TargetActin polymerization
storage
Store at -20°C
References
1) Coue?et al. (1987),?Inhibition of actin polymerization by latrunculin; FEBS Lett.,?213?316 2) Spector?et al. (1989),?Latrunculins-novel marine macrolides that disrupt microfilament organization and affect cell growth; Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton,?13?127 3) Wakatsuki?et al. (2001),?Effects of cytochalasin D and latrunculin B on mechanical properties of cells; J. Cell. Sci.,?114?1025 4) Cha?et al. (2004),?The lateral mobility of NHE3 on the apical membrane of renal epithelial OK cells is limited by the PDZ domain proteins NHERF1/2 but is dependent on an intact actin cytoskeleton as determined by FRAP; Prog. Clin. Biol. Res.,?230 4 5) Herrera (2021), Cell cultures, transfection and treatments. protocols.io???https://dx.doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.77ehrje [Focus Citation]
Properties of LATRUNCULIN B
| alpha | D24 +112° (c = 0.48 in chloroform) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| form | solid |
| color | light yellow |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for LATRUNCULIN B
Computed Descriptors for LATRUNCULIN B
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Latrunculin B from Latruncula magnifica CAS 76343-94-7View Details
Latrunculin B from Latruncula magnifica CAS 76343-94-7View Details
76343-94-7 -
 Latrunculin B, Latrunculia magnifica CAS 76343-94-7View Details
Latrunculin B, Latrunculia magnifica CAS 76343-94-7View Details
76343-94-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8