L-Ornithine
- CAS NO.:70-26-8
- Empirical Formula: C5H12N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 132.16
- MDL number: MFCD00242584
- EINECS: 200-731-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
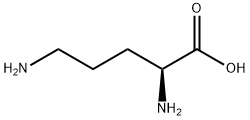
What is L-Ornithine?
Absorption
Absorbed from the small intestine via a sodium-dependent active transport process
Toxicity
Oral, rat LD50 = 10000 mg/kg
The Uses of L-Ornithine
hepatoprotectant, anticholesteremic
Background
Produced during the urea cycle, ornithine is an amino acid produced from the splitting off of urea from arginine. L-Ornithine allows for the disposal of excess nitrogen and acts as a precursor of citrulline and arginine.
Indications
Used for nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance. It has been claimed that ornithine improves athletic performance, has anabolic effects, has wound-healing effects, and is immuno-enhancing.
Definition
ChEBI: An optically active form of ornithine having L-configuration.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 31, p. 1060, 1953 DOI: 10.1139/v53-139
Pharmacokinetics
A non-essential and nonprotein amino acid, ornithine is critical for the production of the body's proteins, enzymes and muscle tissue. Ornithine plays a central role in the urea cycle and is important for the disposal of excess nitrogen (ammonia). Ornithine is the starting point for the synthesis of many polyamines such as putrescine and spermine. Ornithine supplements are claimed to enhance the release of growth hormone and to burn excess body fat. Ornithine is necessary for proper immune function and good liver function.
Safety Profile
Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx.
Metabolism
Ornithine undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver to L-arginine, polyamines, and proline, and several other metabolites.
Purification Methods
Crystallise L-ornithine from water containing 1mM EDTA (to remove metal ions). [Perrin J Chem Soc 3125 1958, Rivard Biochemical Preparations 3 97 1955, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2477-2491 1961, Beilstein 4 III 1346, 4 IV 2644.]
Properties of L-Ornithine
| Melting point: | 140°C |
| Boiling point: | 244.08°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 +11.5° (c = 6.5) |
| Density | 1.1740 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4496 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2–8 °C |
| solubility | Water: 50 mg/mL (378.33 mM); DMSO: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) |
| pka | 1.705(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C5H12N2O2/c6-3-1-2-4(7)5(8)9/h4H,1-3,6-7H2,(H,8,9)/t4-/m0/s1 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 70-26-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Ornithine (70-26-8) |
Safety information for L-Ornithine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Ornithine
| InChIKey | AHLPHDHHMVZTML-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
| SMILES | C(O)(=O)[C@H](CCCN)N |
L-Ornithine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 L-Ornithine 99%View Details
L-Ornithine 99%View Details -
 Powder L OrnithineView Details
Powder L OrnithineView Details
70-26-8 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
