Isobutyraldehyde
Synonym(s):2-Methylpropanal;2-Methylpropionaldehyde;Isobutanal;Isobutyraldehyde
- CAS NO.:78-84-2
- Empirical Formula: C4H8O
- Molecular Weight: 72.11
- MDL number: MFCD00006980
- EINECS: 201-149-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:09
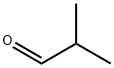
What is Isobutyraldehyde?
Description
Isobutyraldehyde has a characteristic odor. Synthesized via oxidation of isobutyl alcohol with potassium dichromate and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Chemical properties
Isobutyraldehyde has a characteristic sharp, pungent odor. Industrially, it is mainly hydrogenated to produce isobutanol. The addition reaction of isobutyraldehyde and formaldehyde produces hydroxytrimethylacetaldehyde, which is then hydrogenated to form neopentyl glycol, which is used as a raw material for varnishes, resins, fibers and lubricants.
Physical properties
colourless liquid with an extremely unpleasant smell. Miscible in ethanol, benzene, carbon disulfide, acetone, toluene, chloroform and ether, slightly soluble in water (1:125).
Occurrence
Reported found in apple and currant aromas and in the essential oils from tobacco leaves and tea leaves, also in the essential oils of Pinus jeffreyi Murr. leaves, Citrus aurantium leaves, and Datura stramonium. Reported found in apple, banana, sweet and sour cherry, currants, kohlrabi, carrots, celery, peas, potato, tomato, peppermint, corn mint and spearmint oil, vinegar, wheat and rye breads, cheeses, butter, yogurt, egg, caviar, fatty fish, meats, hop oil, beer, brandy, rum, sherry, cider, whiskies, grape wines, cocoa, coffee, tea, filberts, peanuts, popcorn, oats, soybeans, honey, mushrooms, macadamia nuts, cauliflower, pear and apple brandy, rice, sukiyaki, malt, loquat, clary sage, shrimps, truffle, scallops and squid
The Uses of Isobutyraldehyde
Isobutyraldehyde is used in the synthesisof cellulose esters, resins, and plasticizers;in the preparation of pantothenic acid andvaline; and in flavors.
The Uses of Isobutyraldehyde
In the synthesis of pantothenic acid, valine, leucine, cellulose esters, perfumes, flavors, plasticizers, resins, gasoline additives.
The Uses of Isobutyraldehyde
Isobutyraldehyde is used as an intermediate in the preparation of isobutanol, methacrolein, hydroxypivaldehyde and neopentyl glycol. It is actively involved in the Cannizaro reaction. It is also used as an intermediate to prepare pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, vitamins, antioxidants, rubber accelerators, textile auxiliaries, perfumery and flavors.
Definition
ChEBI: Isobutyraldehyde is a member of the class of propanals that is propanal substituted by a methyl group at position 2. It has a role as a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite. It is a member of propanals and a 2-methyl-branched fatty aldehyde.
Preparation
By oxidation of isobutyl alcohol with potassium dichromate and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Catalytic synthesis of isobutyraldehyde from methanol and n-propyl alcohol over titanium oxide-supported vanadium oxide catalysts
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 0.4 to 43 ppb
General Description
Isobutyl aldehyde appears as a clear colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Flash point of -40°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Hence floats on water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Oxidizes slowly on exposure to air. Stable (less than 10% decomposition) for four hours when exposed to light and air in a closed system. Stable for two weeks when stored under nitrogen at temperatures up to 77°F. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Isobutyraldehyde can react vigorously with reducing agents, with oxidizing agents, strong bases and mineral acids. Can undergo exothermic self-condensation or polymerization reactions that are often catalyzed by acid. Generates flammable and/or toxic gases in combination with azo, diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. Reacts slowly when exposed to air with air to give peroxides and other products. These reactions are activated by light, catalyzed by salts of transition metals, and are autocatalytic (catalyzed by their products). The addition of stabilizers (antioxidants) retards autoxidation.
Hazard
Highly flammable, dangerous fire and explosion risk. Irritant to skin and eyes.
Health Hazard
Vapor is irritating to the eyes and mucous membranes.
Health Hazard
Isobutyraldehyde is a moderate skin and eyeirritant; the effect may be slightly greaterthan that of n-butyraldehyde. An amounttotaling 500 mg in 24 hours produced severeskin irritation in rabbits; 100 mg causedmoderate eye irritation.
The toxicity of isobutyraldehyde determinedon test animals was very low. Exposureto 8000 ppm (23,600 mg/m3) for 4 hours waslethal to rats.
LD50 value, oral (rats): 2810 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Vapors are heavier than air and may travel considerable distance to a source of ignition and flash back. Fires are difficult to control due to ease of reignition.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Carcinogenicity
Isobutyraldehyde is not mutagenic in various strains of S. typhimurium and is noncarcinogenic in rats and mice.
Purification Methods
Dry isobutyraldehyde with CaSO4 and use it immediately after distillation under nitrogen because of the great difficulty in preventing oxidation. It can be purified through its acid bisulfite derivative. [Beilstein 1 IV 3262.]
Waste Disposal
Isobutyraldehyde is burned in a chemicalincinerator equipped with an afterburner andscrubber.
Properties of Isobutyraldehyde
| Melting point: | -65 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 63 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.79 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 66 mm Hg ( 4.4 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2220 | ISOBUTYRALDEHYDE |
| Flash point: | −40 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble11g/100mL at 20°C(lit.) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear |
| Odor | Pungent. |
| explosive limit | 1.6-11.0%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.00035ppm |
| Water Solubility | 75 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5154 |
| JECFA Number | 252 |
| BRN | 605330 |
| Stability: | Stable. Refrigerate. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, strong acids, strong reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 78-84-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Propanal, 2-methyl-(78-84-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isobutyraldehyde (78-84-2) |
Safety information for Isobutyraldehyde
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P242:Use only non-sparking tools. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Isobutyraldehyde
Isobutyraldehyde manufacturer
Madan Minerals & Chemicals Industries
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Isobutyraldehyde CAS 78-84-2View Details
Isobutyraldehyde CAS 78-84-2View Details
78-84-2 -
 Isobutyraldehyde CAS 78-84-2View Details
Isobutyraldehyde CAS 78-84-2View Details
78-84-2 -
 Isobutyraldehyde CAS 78-84-2View Details
Isobutyraldehyde CAS 78-84-2View Details
78-84-2 -
 Iso butyraldehyde 99% CAS 78-84-2View Details
Iso butyraldehyde 99% CAS 78-84-2View Details
78-84-2 -
 White Crystal Iso butyraldehyde, Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, 20 kgView Details
White Crystal Iso butyraldehyde, Grade Standard: Industrial Grade, 20 kgView Details
78-84-2 -
 Liquid Isobutyraldehyde, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
Liquid Isobutyraldehyde, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
78-84-2 -
 2-Methylpropionaldehyde CAS Number: 78-84-2View Details
2-Methylpropionaldehyde CAS Number: 78-84-2View Details
78-84-2 -
 Industrial Grade Isobutyraldehyde CAS Number: 78-84-2View Details
Industrial Grade Isobutyraldehyde CAS Number: 78-84-2View Details
78-84-2
