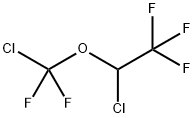
Isoflurane
Synonym(s):1-Chloro-1-(difluoromethoxy)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane;1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether;Isoflurane
- CAS NO.:26675-46-7
- Empirical Formula: C3H2ClF5O
- Molecular Weight: 184.49
- MDL number: MFCD00066609
- EINECS: 247-897-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
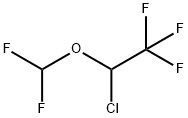
What is Isoflurane?
Toxicity
LC50=15300 ppm/3 hrs (inhalation by rat)
Chemical properties
colourless liquid
Originator
Forane,Ohio Medical,US,1980
The Uses of Isoflurane
Isoflurane is a halogenated ether used for inhalational anesthesia. Recent studies suggest that there might be a relationship between administration of isoflurane and postoperative cognitive dysfunct ion (POCD).
The Uses of Isoflurane
Solvent and dispersant for fluorinated materials.
The Uses of Isoflurane
Isoflurane is a volatile anesthetic agent mainly used to study its interaction with the biological system.
Background
A stable, non-explosive inhalation anesthetic, relatively free from significant side effects.
Indications
For induction and maintenance of general anesthesia.
What are the applications of Application
Isoflurane is a halogenated ether with anesthetic properties, useful solvent for dispersing fluorinated materials.
Definition
ChEBI: Isoflurane is an organofluorine compound. It has a role as an inhalation anaesthetic. It is functionally related to a methoxyethane.
Manufacturing Process
A 1-liter 3-necked stainless steel flask was fitted with a copper "Dry Ice" cold finger condenser, a stainless steel stirring shaft and gland and a copper gas inlet tube. To the flask there was then added 50 g (0.23 mol) of CF3CHClOCHCl2 and 1.5 g of SbCl5 · HF gas was then slowly bubbled through the stirred mixture which was maintained at 0°C. The reaction was run until 0.35 mol of HCl was collected, as indicated by the titration of the effluent gas which was dissolved in water. Following the fluorination 26 g of material were recovered and determined to be 90% pure by vapor phase chromatography. Fractional distillation using a 30 x 0.5 cm column packed with glass helices gave the pure product, BP 48°C to 48.5°C.
brand name
Forane (Baxter Healthcare).
Therapeutic Function
Inhalation anesthetic
Biological Functions
Isoflurane (Forane) is a structural isomer of enflurane
and produces similar pharmacological properties: some
analgesia, some neuromuscular blockade, and depressed
respiration. In contrast, however, isoflurane is considered
a particularly safe anesthetic in patients with ischemic
heart disease, since cardiac output is maintained,
the coronary arteries are dilated, and the myocardium
does not appear to be sensitized to the effects of catecholamines.
Also, blood pressure falls as a result of vasodilation,
which preserves tissue blood flow. Isoflurane
causes transient and mild tachycardia by direct sympathetic
stimulation; this is particularly important in the
management of patients with myocardial ischemia.
Unlike enflurane, isoflurane does not produce a
seizurelike EEG pattern. Furthermore, the metabolic
transformation of isoflurane is only one-tenth that of
enflurane, so fluoride production is quite low. Among
the halogenated hydrocarbons, isoflurane is one of the
most popular, since it preserves cardiovascular stability
and causes a low incidence of untoward effects.
General Description
Isoflurane is a volatile liquid (bp=48.5°C) with an MAC of1.15, a blood:gas partition coefficient of 1.43 and high solubilityin fat. Isoflurane is a structural isomer of enflurane. Itis a known respiratory irritant, but less so than desflurane.Approximately 0.2% of the administered drug undergoesmetabolism, the rest is exhaled unchanged. The metabolismof isoflurane yields low levels of the nephrotoxic fluoride ionas well as a potentially hepatotoxic trifluoroacetylating compound). The relatively low concentrations ofthese compounds have resulted in very low risks of hepatotoxicityand nephrotoxicity. There have been no reports ofseizures caused by isoflurane and only transient increases inheart rate have been reported.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Isoflurane is a tandem pore potassium channel activator. It is also a very widely used anesthetic for animal research and for in vitro studies on anesthesia mechanisms.
Pharmacokinetics
Isoflurane is a general inhalation anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. It induces muscle relaxation and reduces pains sensitivity by altering tissue excitability. It does so by decreasing the extent of gap junction mediated cell-cell coupling and altering the activity of the channels that underlie the action potential.
Clinical Use
Isoflurane was introduced in the United States in 1981 and is a potent anesthetic agent with many similarities to its isomer enflurane (potent, nonflammable, and intermediate blood solubility). It does produce significantly fewer cardiovascular effects than enflurane, however, and it can be used safely with epinephrine without as great a concern for arrhythmia production. Isoflurane has a more pungent odor than halothane and, thus, can cause irritation to the throat and respiratory tract, triggering coughing and laryngospasm. To overcome this problem, it often is supplemented with intravenous agents. Less than 0.2% of an administered dose is metabolized, mostly to fluoride and trifluoroacetic acid. Some minimal potential for hepatotoxicity is associated with a trifluoroacetyl halide metabolite.
Synthesis
Isoflurane is prepared by chlorination
of 2,2,2-trifluoroethoxydifluoromethane, itself
obtained by alkylation of trifluoroethanol with
difluorochloromethane , :
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Isoflurane is an inhalant anesthetic that has some distinct advantages
over either halothane or methoxyflurane due to its lessened
myocardial depressant and catecholamine sensitizing effects, and
the ability to use it safely in patients with either hepatic or renal
disease. Isoflurane’s higher cost than either methoxyflurane or halothane
is a disadvantage.
Horses may recover more rapidly than with halothane, but be
more susceptible to anesthetic associated-
myopathy.
Metabolism
Minimal
Properties of Isoflurane
| Melting point: | 48.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 48.5 °C |
| Density | 1.510 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | 238 mmHg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.3002 |
| Flash point: | 48-49°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol and trichloroethylene. |
| form | neat |
| color | Colorless to Almost colorless |
| Specific Gravity | approximate 1.50 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in chloroform and ethyl acetate. Not miscible or difficult to mix in water. |
| Merck | 14,5175 |
| BRN | 1852087 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26675-46-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether(26675-46-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isoflurane (26675-46-7) |
Safety information for Isoflurane
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Isoflurane
| InChIKey | PIWKPBJCKXDKJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether CAS 26675-46-7View Details
1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether CAS 26675-46-7View Details
26675-46-7 -
 1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl Difluoromethyl Ether CAS 26675-46-7View Details
1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl Difluoromethyl Ether CAS 26675-46-7View Details
26675-46-7 -
 Isoflurane CAS 26675-46-7View Details
Isoflurane CAS 26675-46-7View Details
26675-46-7 -
 Isoflurane CAS 26675-46-7View Details
Isoflurane CAS 26675-46-7View Details
26675-46-7 -
 Isoflurane CAS 26675-46-7View Details
Isoflurane CAS 26675-46-7View Details
26675-46-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1