Isoamyl nitrite
Synonym(s):Isoamyl nitrite;iso-Amyl nitrite, iso-Pentyl nitrite, Nitrous acid isoamyl ester;Isopentyl nitrite
- CAS NO.:110-46-3
- Empirical Formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 117.15
- MDL number: MFCD00002057
- EINECS: 203-770-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
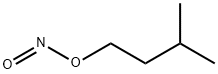
What is Isoamyl nitrite?
Description
Amyl nitrite had been used clinically as early as 1867, when the Scottish physician Sir Thomas Brunton used it as a vasodilator as treatment for angina pectoris in his patients. In the late 1880s, a protective effect on cyanide toxicity in canines was noted when amyl nitrite was inhaled postexposure. Amyl nitrite has been used clinically in a multicomponent cyanide antidote kit and is also a recreational drug of abuse (‘poppers’).
Chemical properties
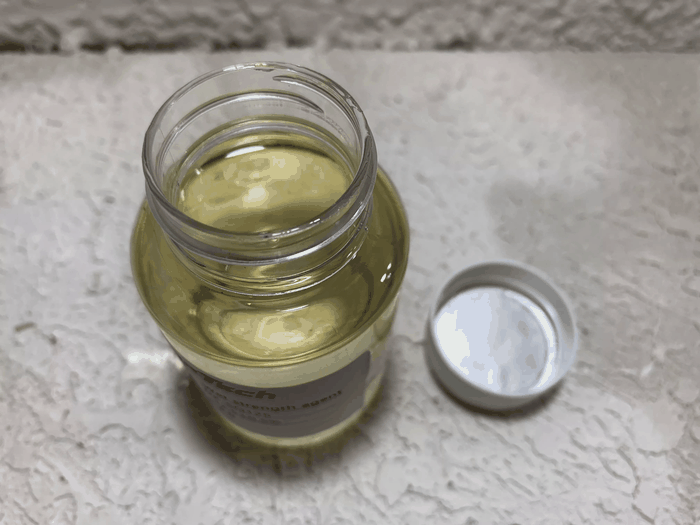
Amyl nitrites are flammable, yellowish liquid with a penetrating, fruity odor. Sp.Gr. 0.88. B.P. 99℃. Slightly soluble in water, miscible with alcohol and oils.
Chemical properties
Isoamyl Nitrite is flammable and explosive and decomposes when exposed to air and sunlight.
The Uses of Isoamyl nitrite
Isoamyl nitrite is a light yellow, transparent liquid with a
pleasant, fragrant, fruity odor. Amyl nitrite was introduced to
medicine in 1859 and has been under considerable pharmacological
investigation since that time. Its major use was for
treating angina pectoris through its vasodilative effect on the
coronary arteries. However, this effect is transient, and
nitroglycerin and longer acting nitrates have largely replaced
it. Amyl nitrite has been most helpful in clarifying the
differential diagnosis of murmurs. For example, left ventricular
outflowobstruction increases followingamyl nitrite administration.
Mitral regurgitation decreases following amyl nitrite
as does the apical diastolic rumble of mitral stenosis. The
Austin–Flint rumble decreases followingamyl nitrite as does a
ventricular septal defect and acyanotic tetralogy of Fallot. Pulmonic stenosis increases as does isolated valvular pulmonary
stenosis following amyl nitrite.
Isoamyl nitrite has also been reportedly used for inhalation
abuse. The symptoms following inhalation of
large doses by humans are flushing of the face, pulsatile
headache, disturbing tachycardia, cyanosis (methemoglobinemia),
weakness, confusion, restlessness, faintness, and
collapse, particularly if the individual is standing. The
symptoms are usually of short duration. Industrial intoxication
has not been reported.
The Uses of Isoamyl nitrite

To ACN (350 mL) at RT was added CuBr2 (67 g, 300 mmol). The mixture was cooled to 0-5 C and was treated dropwise with t-BuONO (72.5 mL, 535 mmol). The mixture was stirred for 5 min, then was added the SM (35 g, 238 mmol). The reaction was stirred at RT for 2 h. EtOAc (525 mL) was added to the mixture and the reaction was quenched with 10% aq NH4Cl (350 mL) and 2% aq NH3 (175 mL). The layers were separated and the aq layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organics were dried and concentrated. The resulting material was purified by silica gel chromatography (eluting with 5% EtOAc/hexane) to provide the product as a yellow solid. [35 g, 70%]
The Uses of Isoamyl nitrite
Vasodilator.
The Uses of Isoamyl nitrite
Isopentyl nitrite is used in the conversion of 2,6-disubstituted phenols to diphenoquinones and aminophenols to quinone diazides. It acts as an oxidant and nitrosating agent. It finds application in aromatic arylation, deamination of arylamines using tetrahydrofuran as a hydrogen donor. It is also useful for the preparation of benzyne using anthranilic acid. It is an antihypertensive and vasodilator to treat heart diseases such as angina and an antidote for cyanide poisoning. Further, it is used as a solvent and cleaning agent for a printed circuit board. In addition to this, it is considered to be a replacement for freon.
What are the applications of Application
Isopentyl nitrite is a compound for vascular research
Definition
ChEBI: Isoamyl nitrite is a nitrite ester having isopentyl as the alkyl group. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and an antihypertensive agent. It derives from an isoamylol.
Preparation
Isoamyl nitrite is produced from iso-Amyl alcohol, Sodium nitrite, water and diluted Sulfuric acid.
General Description
Clear yellow liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Decomposes on exposure to air and light. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Isoamyl nitrite is an oxidizing agent but can serve as a reducing agent. Forms explosive mixtures with air or oxygen. .
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk, a strong oxidizer. Vapor may explode if ignited.
Fire Hazard
Isoamyl nitrite is flammable.
Potential Exposure
Amyl nitrite is used to make pharmaceuticals; perfumes, diazonium compounds, and other chemicals.
Environmental Fate
The primary mechanism of toxicity develops from the
powerful oxidative effects of nitrites on hemoglobin. Methemoglobinemia,
which develops when the iron atom in
hemoglobin loses one electron to an oxidant, causing a change
from the ferrous (2+) state to the ferric (3+) state, may cause
cellular hypoxia. When methemoglobin levels exceed
10–15%, cyanosis may be evident. Nitrites also cause vasodilation
by direct action on smooth muscle. Physical effects
include decreases in blood pressure, headache, flushing of the
face, increased heart rate, dizziness, and relaxation of involuntary
muscles, especially of the blood vessels and the anal
sphincter.
Amyl nitrite may be irritating to the lungs and throat when
breathed in. With exposure to the skin, amyl nitrite has irritant
properties. It can also be readily absorbed, causing systemic
effects with skin contact.
Shipping
UN1993 Flammable liquids, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, Technical Name Required.
Toxicity evaluation
A volatile liquid, amyl nitrite is slightly soluble in water and is commonly supplied in ampoules that are broken and administered by inhalation. Inhalation is likely the most common route of exposure, though reports of ingestion of the liquid itself have been seen. Amyl nitrite may also be absorbed through the skin when skin comes in contact with the liquid.Amyl nitrite is an unstable compound. It is air and light sensitive and flammable. Amyl nitrite forms explosive mixtures with air or oxygen, and it is incompatible with oxidizing agents and reducing agents.
Incompatibilities
Vapors may form explosive mixture with air. Slowly decomposes in light, heat, and on contact with water. A strong oxidizer. Contact with reducing agents and easily oxidizable materials may cause fire and explosions. Reported to be an explosion hazard when exposed to air and light. Keep away from alcohols, antipyrine, alkaline materials; alkaline carbonates; potassium iodide; bromides, and ferrous salts. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture.
Waste Disposal
Incineration with scrubber to remove nitrogen oxides from the combustion gases.
Properties of Isoamyl nitrite
| Boiling point: | 99 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.872 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 35-59.995hPa at 20-25℃ |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 50 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | Chloroform (Soluble), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear yellow |
| Water Solubility | <0.01 g/100 mL at 18 ºC |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,5123 |
| BRN | 969510 |
| Stability: | Unstable. Air and light sensitive. Flammable. Forms explosive mixtures with air or oxygen. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-46-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Amyl Nitrite(110-46-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Isoamyl nitrite (110-46-3) |
Safety information for Isoamyl nitrite
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H341:Germ cell mutagenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Isoamyl nitrite
| InChIKey | OWFXIOWLTKNBAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Isoamyl nitrite manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
NSR Amino Organics
Sainor Laboratories Pvt Ltd Unit III
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 110-46-3 Iso amyl Nitrite 90% 98%View Details
110-46-3 Iso amyl Nitrite 90% 98%View Details
110-46-3 -
 Isoamyl nitrite 98%View Details
Isoamyl nitrite 98%View Details -
 Isopentyl nitrite, 96% CAS 110-46-3View Details
Isopentyl nitrite, 96% CAS 110-46-3View Details
110-46-3 -
 Isoamyl Nitrite CAS 110-46-3View Details
Isoamyl Nitrite CAS 110-46-3View Details
110-46-3 -
 Isopentyl nitrite, stabilized with 0.2% anhyd. sodium carbonate CAS 110-46-3View Details
Isopentyl nitrite, stabilized with 0.2% anhyd. sodium carbonate CAS 110-46-3View Details
110-46-3 -
 Isoamyl nitrite 97% CAS 110-46-3View Details
Isoamyl nitrite 97% CAS 110-46-3View Details
110-46-3 -
 Isopentyl nitrite CAS 110-46-3View Details
Isopentyl nitrite CAS 110-46-3View Details
110-46-3 -
 Isoamyl NitriteView Details
Isoamyl NitriteView Details
110-46-3
