IRON (II) OXIDE
Synonym(s):Ferrous oxide;Iron monooxide
- CAS NO.:1345-25-1
- Empirical Formula: FeO
- Molecular Weight: 71.84
- MDL number: MFCD00016095
- EINECS: 215-721-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
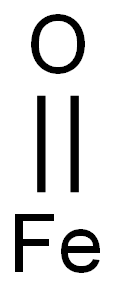
What is IRON (II) OXIDE?
Description
When iron is heated in a low partial pressure of oxygen above 575°C, FeO is formed. However, this is only stable at high temperatures and decomposes into iron and Fe304 when it is cooled slowly. To obtain crystalline FeO the high temperature product must be quenched rapidly to stop this disproportionation.
Chemical properties
solid
Chemical properties
Crystalline FeO (wustite) melts at 1368°C with a heat of fusion ΔH= 7·5 kcal mole-1. It has a heat of formation of - 63·7 kcal mole-1 at 25° and a density of 5·7. Below 198°K (the Néel temperature) FeO is antiferromagnetic. It crystallizes with the rock salt structure having four Fe2+ and four02- ions per unit cell.
Physical properties
Black cubic crystal; density 5.7g/cm3; melts at 1,377°C; insoluble in water and alkalies; dissolves in acids.
Occurrence
Iron(II) oxide occurs in the mineral, wustite. It is used in the manufacture of heat-absorbing green glasses. It also is used in ceramic mixtures and enamels; and as a catalyst.
The Uses of IRON (II) OXIDE
In manufacture of green, heat-absorbing glass; in steel manufacture; and as a catalystIron(II) oxide is used in manufacturing of green, heat-absorbing glass; in steel manufacture; and as a catalyst. It is used as a dye or pigment in pottery, glazes and glasses. It finds application as heat-absorbing glass used in buildings and automobiles. It is used as a precursor in the production of steel. It is also used in cosmetics and some tattoo inks. It can also be used for filtering phosphates from home aquaria and acts as a catalyst in a number of industrial and chemical operations.
The Uses of IRON (II) OXIDE
In manufacture of green, heat-absorbing glass; in steel manufacture; in enamels; as catalyst.
Definition
ChEBI: Ferrous oxide is an iron oxide.
Preparation
Iron(II) oxide may be prepared by thermal decomposition of iron(II) oxalate:
FeC2O4 → FeO + CO + CO2
The product obtained above is impure, that may contain small quantities of triiron tetroxide, Fe3O4 and carbon.
The oxide is stable above 575°C. Thus, it can be prepared by heating iron with oxygen under appropriate pressure at 575°C. Also, iron(II) oxide has been prepared by saturating the fused triiron tetroxide with iron, powdering the mixture, followed by magnetic separation of the oxide from excess iron (Sidgwick, N.V. 1950. The Chemical Elements and Their Compounds, Vol.2, pp 1328, Oxford: Clarendon Press).
Properties of IRON (II) OXIDE
| Melting point: | 1369°C |
| Density | 5.7 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, alkaline solutions; soluble in acid solutions |
| form | 5 Mesh |
| color | black cubic crystals, crystalline |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water and alkalies. Soluble in HCl, H{2}SO{4}. Slightly soluble in HNO{3}Insoluble in water, alcohol and alkali. Soluble in hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid. Slightly soluble in nitric acid. |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,4052 |
| Dielectric constant | 14.2(16.0℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Highly flammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1345-25-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferrous oxide (1345-25-1) |
Safety information for IRON (II) OXIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for IRON (II) OXIDE
IRON (II) OXIDE manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 1345-25-1 Ferrous oxide 98%View Details
1345-25-1 Ferrous oxide 98%View Details
1345-25-1 -
 Iron(II) oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
Iron(II) oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
1345-25-1 -
 Iron(II) oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
Iron(II) oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
1345-25-1 -
 Ferrous oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
Ferrous oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
1345-25-1 -
 Iron(II) oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
Iron(II) oxide CAS 1345-25-1View Details
1345-25-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1