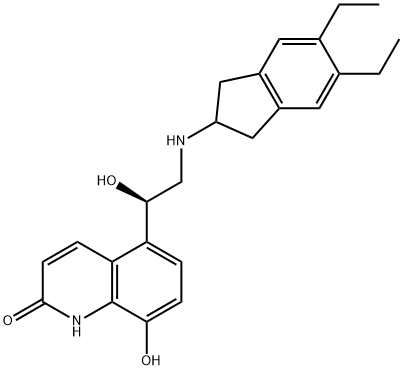
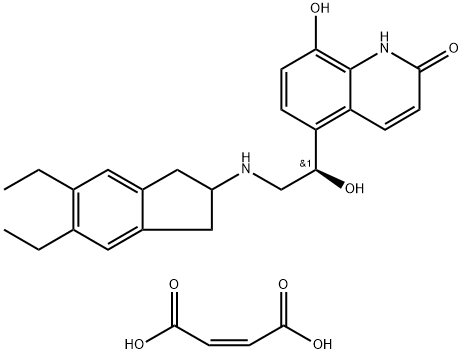
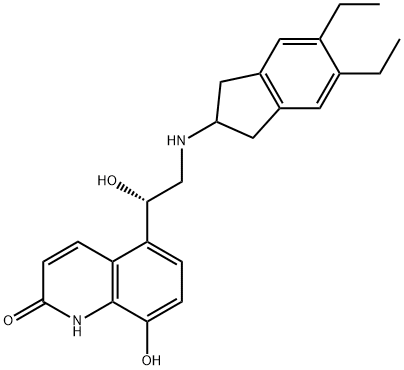
Indacaterol
- CAS NO.:312753-06-3
- Empirical Formula: C24H28N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 392.49
- MDL number: MFCD18782702
- EINECS: 691-091-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-07 17:33:14
What is Indacaterol?
Absorption
The median time to reach peak serum concentrations of indacaterol was approximately 15 minutes after single or repeated inhaled doses. Absolute bioavailability of indacaterol after an inhaled dose was on average 43-45%.
Toxicity
The expected signs and symptoms associated with overdosage of indacaterol are those of excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation and occurrence or exaggeration of any of the signs and symptoms, e.g., angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia, with rates up to 200 bpm, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, dry mouth, palpitation, muscle cramps, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis and insomnia. As with all inhaled sympathomimetic medications, cardiac arrest and even death may be associated with an overdose of indacaterol.
Description
Inhaled β2 adrenoceptor agonists are effective in the management of asthma and COPD, primarily through their bronchodilating properties. These drugs induce bronchodilation by causing direct relaxation of airway smooth muscle through activation of adenylate cyclase, which in turn increases intracellular cAMP levels. Indacaterol is the newest β2 agonist to reach the market. It is an ultra-long-acting agent with a duration of action suitable for once-a-day dosing. Indacaterol is supplied as an aerosol formulation of its maleate salt and is administered via a dry powder inhaler device. It is specifically approved for once-daily maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in adult patients with COPD. In preclinical models, indacaterol is close to a full agonist at the human b2 adrenoceptor (Emax = 73 ± 1% of isoprenaline′s maximal effect, pEC50 = 8.06 ±0.02) while salmeterol displays only partial efficacy (38 ±1%). The functional selectivity profile of indacaterol over β1 human adrenoceptors is similar to that of formoterol, whereas its β3 adrenoceptor selectivity profile is similar to that of formoterol and salbutamol.
Originator
Novartis (United Kingdom)
The Uses of Indacaterol
Indacaterol is a β-adrenoreceptor agonists for treatment of asthma and bronchodilator treatment for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases.
Background
Indacaterol is a novel, ultra-long-acting, rapid onset β(2)-adrenoceptor agonist developed for Novartis for the once-daily management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) on 30 November 2009 and by the FDA on 1 July 2011. It is marketed in Europe as Onbrez and in America as Arcapta Neohaler. Indacaterol is provided as its maleate salt form. Indacaterol is also a chiral molecule but only the pure R-enantiomer is dispensed.
Indications
For the long term, once-daily-dosing maintenance of airflow obstruction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema.
Definition
ChEBI: A monohydroxyquinoline that consists of 5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-hydroxyethyl]-8-hydroxyquinolin-2-one having a 5,6-diethylindan-2-yl group attached to the amino function. Used as the maleate salt for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary di ease.
brand name
Onbrez Breezhaler
Pharmacokinetics
Bronchodilator drugs are the foundation for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The principal inhaled bronchodilator treatments used are β(2) -agonists and anticholinergics, either alone or in combination. Currently available β(2) -agonists are of either short duration and used multiple times/day, or of long duration, which requires twice-daily administration. Indacaterol is considered an ultra-long-acting β(2) -agonist and was recently approved for use in the United States. Its duration of action is approximately 24 hours, allowing for once-daily administration. Furthermore, this chiral compound it is given as the R-enantiomer and acts as a full agonist. Cough was the most commonly reported adverse effect with use of indacaterol. Compared to salmeterol, it has 35% more agonist activity. Cough usually occurred within 15 seconds of inhalation of the drug, lasted around 6 seconds, was not associated with bronchospasm, and did not cause discontinuation of the drug. Otherwise, the drug's safety profile was similar to that of other bronchodilators. [PMID: 22499359]
Side Effects
The most commonly reported adverse events associated with indacaterol treatment were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and headache and cough following inhalation. Adverse events were mild or moderate in most cases, and became less frequent with continued treatment.
Synthesis
The chemical synthesis of indacaterol begins with a-chlorination of 5-acetyl-8-benzyloxy-2-quinolone with benzyltrimethylammonium dichloro-iodate. The resultant chloroketone is reduced with borane in tetrahydrofuran in the presence of the chiral boron catalyst R-tetrahydro-1-methyl-3,3-diphenyl-1H,3H-pyrrolo[1,2c][ 1,3,2]oxazaborole to produce the corresponding chlorohydrin intermediate in high enantiomeric excess. The chlorohydrin intermediate is cyclized to the corresponding epoxide by treatment with potassium carbonate, the epoxide is condensed with 5,6-diethylindan-2-amine, and the benzyl protecting group is removed by hydrogenolysis to produce indacaterol. The 5,6-diethylindan-2-amine intermediate is derived from 1,2-diethylbenzene via Friedel-Crafts acylation with 3-chloropropionyl chloride, cyclization of the resultant 3-chloro- 1-(3,4-diethylphenyl)-1-propanone by means of concentrated sulfuric acid to 5,6-diethylindan-1-one, oximation with butyl nitrite, and reduction of the oxime to an amine via treatment with hydrogen over palladium- carbon.
Metabolism
After oral administration of radiolabeled indacaterol, unchanged indacaterol was the main component in serum, accounting for about one third of total drug-related AUC over 24 hours. The monohydroxylated derivative, glucuronide conjugate, and the 8-O-glucuronide were the most prominent metabolites in serum. Other metabolites identified include a diastereomer of the hydroxylated derivative, a N-glucuronide of indacaterol, and C- and N-dealkylated products.
In vitro investigations indicated that UGT1A1 was the only UGT isoform that metabolized indacaterol to the phenolic O-glucuronide. CYP3A4 is the predominant isoenzyme responsible for hydroxylation of indacaterol.
Properties of Indacaterol
| Melting point: | >165°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 660.3±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.27 |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 8.68±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Light Yellow |
Safety information for Indacaterol
Computed Descriptors for Indacaterol
| InChIKey | QZZUEBNBZAPZLX-QFIPXVFZSA-N |
| SMILES | N1C2=C(C([C@@H](O)CNC3CC4=C(C3)C=C(CC)C(CC)=C4)=CC=C2O)C=CC1=O |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 312753-06-3 Indacaterol 98%View Details
312753-06-3 Indacaterol 98%View Details
312753-06-3 -
 ?312753-06-3 98%View Details
?312753-06-3 98%View Details
?312753-06-3 -
 Indacaterol 98%View Details
Indacaterol 98%View Details
312753-06-3 -
 Indacaterol 312753-06-3 98%View Details
Indacaterol 312753-06-3 98%View Details
312753-06-3 -
 Indacaterol 98%View Details
Indacaterol 98%View Details
312753-06-3 -
 Indacaterol CAS 312753-06-3View Details
Indacaterol CAS 312753-06-3View Details
312753-06-3 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
