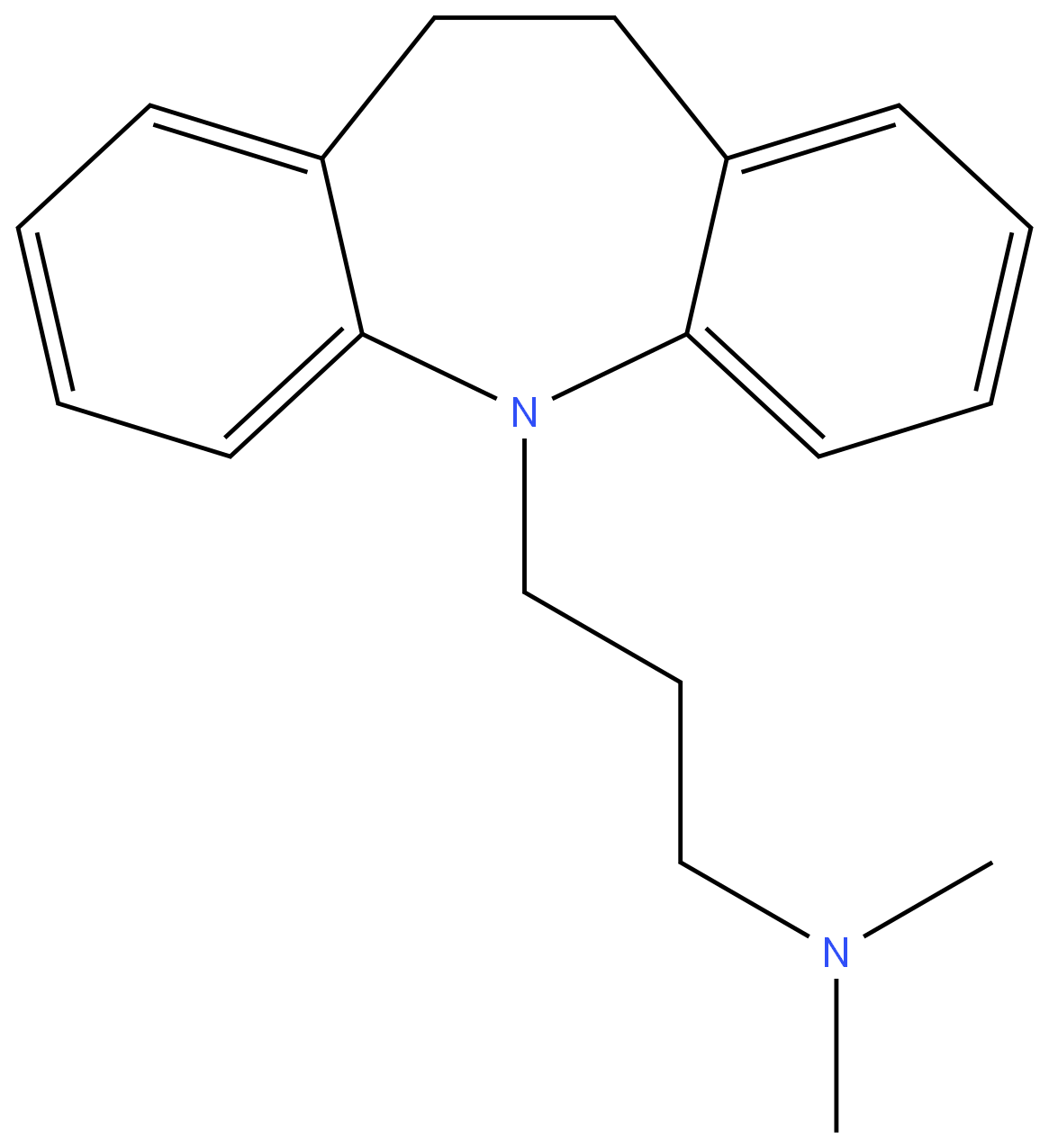
IMIPRAMINE
- CAS NO.:50-49-7
- Empirical Formula: C19H24N2
- Molecular Weight: 280.41
- MDL number: MFCD00242921
- EINECS: 200-042-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 09:00:29

What is IMIPRAMINE?
Absorption
Rapidly and well absorbed (>95%) after oral administration . The primary site of absorption is the small intestine as the basic amine groups are ionized in the acidic environment of the stomach, preventing movement across tissues. Bioavailability ranges from 29-77% due to high inter-individual variability. Peak plasma concentration is usually attained 2-6 hours following oral administration. Absorption is unaffected by food.
Toxicity
The anticholinergic actvity of imipramine can produce dry mucous membranes, blurred vision, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthermia, constipation, adynamic ileus, urinary retention, delayed micturition, and dilation of the urinary tract .
Central nervous system and neuromuscular effects include drowsiness, lethargy, fatigue, agitation, excitement, nightmares, restlessness, insomnia, confusion, disturbed concentration, disorientation, delusions, and hallucinations.
Effects on the GI tract include anorexia, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, increases in pancreatic enzymes, epigastric distress, stomatitis, peculiar taste, and black tongue.
Rarely agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, leukopenia, and purpura have occured.
Infants whose mothers were receiving tricyclic antidepressants prior to delivery have experienced cardiac problems, irritability, respiratory distress, muscle spasms, seizures, and urinary retention.
Serotonin syndrome can occur when used in conjunction with other pro-serotonergic drugs.
Rat
- Oral 250 mg/kg
- Intraperitoneal 79mg/kg
- Subcutaneous 250 mg/kg
- Intravenous 15.9 mg/kg
Mouse
- Oral 188 mg/kg
- Intraperitoneal 51.6 mg/kg
- Subcutaneous 195 μg/kg
- Intravenous 21 mg/kg
Human range of toxicity is considered to include single dosages greater than 5 mg/kg.
Originator
Tofranil,Ciba Geigy,France,1959
The Uses of IMIPRAMINE
Imipramine is used in depression of various etiology accompanied by motor clumsiness and enuresis in children and Parkinson’s disease.
The Uses of IMIPRAMINE
antidepressant
Background
Imipramine, the prototypical tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), is a dibenzazepine-derivative TCA. TCAs are structurally similar to phenothiazines. They contain a tricyclic ring system with an alkyl amine substituent on the central ring. In non-depressed individuals, imipramine does not affect mood or arousal, but may cause sedation. In depressed individuals, imipramine exerts a positive effect on mood. TCAs are potent inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. Tertiary amine TCAs, such as imipramine and amitriptyline, are more potent inhibitors of serotonin reuptake than secondary amine TCAs, such as nortriptyline and desipramine. TCAs also block histamine H1 receptors, α1-adrenergic receptors and muscarinic receptors, which accounts for their sedative, hypotensive and anticholinergic effects (e.g. blurred vision, dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention), respectively . Imipramine has less sedative and anticholinergic effects than the tertiary amine TCAs, amitriptyline and clomipramine. Imipramine may be used to treat depression and nocturnal enuresis in children . Unlabeled indications include chronic and neuropathic pain (including diabetic neuropathy), panic disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) .
Indications
For the relief of symptoms of depression and as temporary adjunctive therapy in reducing enuresis in children aged 6 years and older .
May also be used off-label to manage panic disorders with or without agoraphobia, as a second line agent for ADHD in children and adolescents, to manage bulimia nervosa, for short-term management of acute depressive episodes in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, for the treatment of acute stress disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder, and for symptomatic treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy .
Definition
ChEBI: Imipramine is a dibenzoazepine that is 5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine substituted by a 3-(dimethylamino)propyl group at the nitrogen atom. It has a role as an adrenergic uptake inhibitor, an EC 3.4.21.26 (prolyl oligopeptidase) inhibitor and an antidepressant. It derives from a hydride of a 5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine.
Manufacturing Process
20 parts of imino dibenzyl are dissolved in 100 parts by volume of absolutely
dry benzene. A suspension of 4 parts NaNH2 in 50 parts by volume of
absolute benzene are then added dropwise at 50° to 60°C after which the
mixture is boiled for an hour under reflux. 13 parts of 3-dimethylamino n_x0002_propyl chloride are then added dropwise at 40° to 50°C and the mixture is
boiled for 10 hours under reflux. After cooling, the benzene solution is
thoroughly washed with water, whereupon the basic constituents are extracted
with dilute hydrochloric acid.
The hydrochloric extract is then made alkaline and the separated base is
extracted with ether. After drying, the solvent is evaporated and the residue is
distilled in the high vacuum, whereby the N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-imino
dibenzyl passes over at a temperature of 160°C under 0.1 mm pressure. The
chlorohydrate with a melting point of 174° to 175°C is obtained therefrom
with alcoholic hydrochloric acid.
brand name
Janimine (Abbott); Pramine (Alra); Presamine (Sanofi Aventis); Tofranil (Novartis); Tofranil (Tyco).
Therapeutic Function
Antidepressant
Mechanism of action
Besides being used in the clinical treatment of depression, imipramine also has been used for the treatment of functional enuresis in children who are at least 6 years of age (25 mg daily administered 1 hour before bedtime, not to exceed 2.5 mg/kg daily).
Pharmacokinetics
Imipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant with general pharmacological properties similar to those of structurally related tricyclic antidepressant drugs such as amitriptyline and doxepin. While it acts to block both, imipramine displays a much higher affinity for the serotonin reuptake transporter than for the norepinephrine reuptake transporter . Imipramine produces effects similar to other monoamine targeting antidepressants, increasing serotonin- and norepinephrine-based neurotransmission.
This modulation of neurotransmission produces a complex range of changes in brain structure and function along with an improvement in depressive symptoms. The changes include increases in hippocampal neurogenesis and reduced downregulation of this neurogenesis in response to stress . These implicate brain derived neurotrophic factor signalling as a necessary contributor to antidepressant effect although the link to the direct increase in monoamine neurotransmission is unclear.
Serotonin reuptake targeting agents may also produce a down-regulation in β-adrenergic receptors in the brain .
Clinical Use
Imipramine is a 10,11-dihydrodibenzazepine tertiary amine TCA that is marketed as hydrochloride and pamoate salts, both of which are administered orally. Although the hydrochloride salt may be administered in divided daily doses, imipramine's long duration of action suggests that the entire oral daily dose may be administered at one time.On the other hand, imipramine pamoate usually is administered as a single daily oral dose.
Synthesis
Imipramine, 5-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f] azepine (7.1.1), is synthesized by the alkylation of 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine using 3-dimethylaminopropylchloride in the presence of sodium amide [1¨C3].

Metabolism
Imipramine is nearly exclusively metabolized by the liver . Imipramine is converted to desipramine by CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP2C19. Both imipramine and desipramine are hydroxylated by CYP2D6 . Desipramine is an active metabolite.
Minor metabolic pathways include dealkylation to form an imidodibenzyl product as well as demethylation of desipramine to didemethylimipramine and subsequent hydroxylation .
Less than 5% of orally administered imipramine is excreted unchanged.
Properties of IMIPRAMINE
| Melting point: | 174°C |
| Boiling point: | bp0.1 160° |
| Density | 0.9935 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5640 (estimate) |
| pka | pKa 9.66(H2O,t = 25,I=0.025) (Uncertain) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | 18.23mg/L(24 ºC) |
| Solvent | Ethanol under nitrogen |
| Concentration | 1 mCi/ml |
| Specific Activity | 60-90 Ci/mmol |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Imipramine (50-49-7) |
Safety information for IMIPRAMINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P312:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell. P321:Specific treatment (see … on this label). P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P307+P311:IF exposed: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for IMIPRAMINE
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

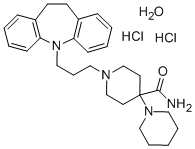
![1'-[3-(3-chloro-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenz(b,f)azepin-5-yl)propyl][1,4'-bipiperidine]-4'-carboxamide dihydrochloride](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/28058-62-0.gif)
You may like
-
 50-49-7 Imipramine 99%View Details
50-49-7 Imipramine 99%View Details
50-49-7 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
