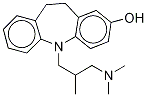
TRIMIPRAMINE
- CAS NO.:739-71-9
- Empirical Formula: C20H26N2
- Molecular Weight: 294.43
- MDL number: MFCD00242595
- EINECS: 212-008-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
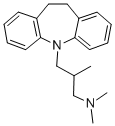
What is TRIMIPRAMINE?
Absorption
Rapid absorption
Toxicity
Side effects include agitation, coma, confusion, convulsions, dilated pupils, disturbed concentration, drowsiness, hallucinations, high fever, irregular heart rate, low body temperature, muscle rigidity, overactive reflexes, severely low blood pressure, stupor, vomiting
Originator
Surmontil Wyeth-Ayerst,Laboratories
The Uses of TRIMIPRAMINE
Antidepressant.
Background
Tricyclic antidepressant similar to imipramine, but with more antihistaminic and sedative properties.
Indications
For the treatment of depression and depression accompanied by anxiety, agitation or sleep disturbance
Definition
ChEBI: A dibenzoazepine that is 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine substituted by a 3-(dimethylamino)-2-methylpropyl group at the nitrogen atom. It is used as an antidepressant.
Manufacturing Process
Bis(3-dimethylamino-2-methylpropyl)-5-iminodibenzylyl carboxylic acid at 185-250°C up to discontinue a separation of oxyde carbonique. The product was dissolved in ether, then washed with the hydrochloric acid. Then this solution was extracted with ether. The solvent was evaporated under vacuum, to give pure oil bis(3-dimethylamino-2-methyl-1-propyl)-5-iminodibenzyle with boiling point 153-154°C at 0.4 mm. Maleate of bis(3-dimethylamino-2-methyl- 1-propyl)-5-iminodibenzyle have melting point 145-146°C.
brand name
Surmontil (Wyeth-Ayerst);Apo-trimip;Herphonal;No-tripramine;Novo-tripramine;Rhotromine;Sapilant;Stangyl;Surmantil;Tydamine.
Therapeutic Function
Antidepressant
World Health Organization (WHO)
Trimipramine, a tricyclic antidepressant was introduced in 1961 for the management of endogenous depression. Much of the adverse effects are caused by its antimuscarinic actions. These include dry mouth, cardiac arrhythmias, central nervous system disturbances, blood disorders and risk of suicide. The risk of suicide and dangers related to overdosage led Norwegian Medicines Control Authority to put the higher strength formulation under prescribing restriction in 1992. The risk of death following overdosage is apparently higher for products containing tricyclic compounds as compared with nontricyclic products.
Pharmacokinetics
Trimipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant. It was thought that tricyclic antidepressants work by inhibiting the re-uptake of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and serotonin by nerve cells. However, this response occurs immediately, yet mood does not lift for around two weeks. It is now thought that changes occur in receptor sensitivity in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, a part of the brain involved in emotions. Presynaptic receptors are affected: a1 and b1 receptors are sensitized, a2 receptors are desensitised (leading to increased noradrenaline production). Tricyclics are also known as effective analgesics for different types of pain, especially neuropathic or neuralgic pain. A precise mechanism for their analgesic action is unknown, but it is thought that they modulate anti-pain opioid systems in the CNS via an indirect serotonergic route. They are also effective in migraine prophylaxis, but not in abortion of acute migraine attack. The mechanism of their anti-migraine action is also thought to be serotonergic.
Pharmacokinetics
Trimipramine is one of the antidepressants with the most pronounced differences in pharmacokinetics caused by the CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism. Its bioavailability and systemic clearance depended significantly on the CYP2D6 isoform with a linear dose relationship. Its mean bioavailability was 44% in individuals without CYP2D6 (poor metabolizers) but 16 and 12% in those individuals with two and three active genes of CYP2D6 (fast and ultrafast metabolizers), respectively. Consequently, the mean total clearances of the oral dose were 27, 151, and 253 L/hour in poor, extensive, and ultrarapid metabolizers, respectively. The 44% bioavailability combined with low systemic clearance of trimipramine in poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 substrates results in a very high exposure to trimipramine with the risk of adverse drug reactions. On the other hand, the presystemic elimination may result in subtherapeutic drug concentrations in carriers of CYP2D6 gene duplications with a high risk of poor therapeutic response
Clinical Use
Although trimipramine has the weakest binding affinity for the monoamine transporters, it shares the pharmacological and toxicity actions of the other TCAs and is used primarily in the treatment of depression.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alcohol: increased sedative effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of CNS toxicity with
tramadol; possibly increased risk of side effects with
nefopam; possibly increased sedative effects with
opioids.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with amiodarone - avoid; increased
risk of ventricular arrhythmias with disopyramide,
flecainide or propafenone; avoid with dronedarone.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with delamanid and moxifloxacin and possibly
telithromycin - avoid with delamanid and moxifloxacin.
Anticoagulants: may alter anticoagulant effect of
coumarins.
Antidepressants: enhanced CNS excitation and
hypertension with MAOIs and moclobemide -
avoid; concentration possibly increased with SSRIs;
risk of ventricular arrhythmias with citalopram
and escitalopram - avoid; possible increased risk of
convulsions with vortioxetine.
Antiepileptics: convulsive threshold lowered;
concentration reduced by carbamazepine,
phenobarbital and possibly fosphenytoin, phenytoin
and primidone.
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether/lumefantrine
and piperaquine with artenimol.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias especially with droperidol, fluphenazine,
haloperidol, pimozide, sulpiride and zuclopenthixol
- avoid; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with risperidone; increased antimuscarinic effects
with clozapine and phenothiazines; concentration
increased by antipsychotics.
Antivirals: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with saquinavir - avoid; concentration possibly
increased with ritonavir.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias and possibly convulsions.
Beta-blockers: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol.
Clonidine: tricyclics antagonise hypotensive effect;
increased risk of hypertension on clonidine withdrawal.
Dapoxetine: possibly increased risk of serotonergic
effects - avoid.
Dopaminergics: avoid use with entacapone; CNS
toxicity reported with selegiline and rasagiline.
Pentamidine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias.
Sympathomimetics: increased risk of hypertension
and arrhythmias with adrenaline and noradrenaline;
metabolism possibly inhibited by methylphenidate.
Metabolism
Hepatic
Metabolism
Trimipramine is metabolised in the liver to its major metabolite desmethyltrimipramine, which is active. Trimipramine is excreted in the urine mainly in the form of its metabolites.
Properties of TRIMIPRAMINE
| Melting point: | 45° |
| Boiling point: | 426.2°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 0.9912 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6450 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| pka | pKa 8.0 (Uncertain) |
Safety information for TRIMIPRAMINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for TRIMIPRAMINE
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
