Hinokitiol
Synonym(s):2-Hydroxy-4-isopropyl-2,4,6-cycloheptatrien-1-one;beta-Thujaplicin;Hinokitiol
- CAS NO.:499-44-5
- Empirical Formula: C10H12O2
- Molecular Weight: 164.2
- MDL number: MFCD00040180
- EINECS: 207-880-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
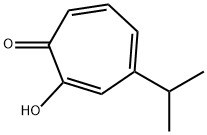
What is Hinokitiol?
Description
Hinokitiol (β-thujaplicin) is a natural monoterpenoid found in the wood of trees in the family Cupressaceae. It is a tropolone derivative and one of the thujaplicins.Hinokitiol is used in oral and skin care products,and is a food additive used in Japan.
Description
The famed Japanese chemist Tetsuo Nozoe first isolated the tropolone monoterpenoid hinokitiol from the wood of the Taiwanese ninoki tree (Chamaecyparis taiwanensis) in 1936. Since then, it has been found in other trees of the Cupressaceae family, although not in the Japanese hinoki.
Beginning in the 2000s, researchers recognized that hinokitiol could be of value as a pharmaceutical, notably for inhibiting the bacterium?Chlamydia trachomatis. But this year, chemist Martin Burke and colleagues at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign and at several other institutions discovered a more significant medical use for hinokitiol.
Burke’s goal was to overcome irregular iron transport in animals. Insufficiencies of several proteins can lead to iron deficiency in cells (anemia) or the opposite effect, hemochromatosis. Using gene-depleted yeast cultures as surrogates, the researchers screened a library of small biomolecules for signs of iron transport and therefore cell growth.?Hinokitiol popped up as the one that restored cell functionality.
Further work by the team established the mechanism by which hinokitiol restores or reduces cell iron. They then switched their study to mammals and found that when rodents that had been engineered to lack “iron proteins” were fed hinokitiol, they regained iron uptake in the gut. In a similar study on zebrafish, the molecule restored hemoglobin production.
A commentary on the work of Burke et al. nicknamed hinokitiol the “Iron Man molecule”. This is fitting (and ironic) because discoverer Nozoe’s first name can translate into English as “iron man”.
The Uses of Hinokitiol
Hinokitiol is a natural monoterpenoid found in the wood of trees in the family Cupressaceae. It is a tropolone derivative and one of the thujaplicins. Hinokitiol has inhibitory effects on Chlamydia trachomatis and may be clinically useful as a topical drug.
The Uses of Hinokitiol
Antibacterial additive in foods, cosmetics, eye drops and toothpaste.
What are the applications of Application
Hinokitiol is an apoptosis inducer and potent metal chelator
Definition
ChEBI: A monoterpenoid that is cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one substituted by a hydroxy group at position 2 and an isopropyl group at position 4. Isolated from Thuja plicata and Chamaecyparis obtusa, it exhibits antimicrobial activities.
Anticancer Research
Studied in xenograft tumors such lung adenocarcinoma cell, EGFR-TKI-resistantlines PC9-IR and H1975 in which the growth inhibition was observed, a novel antitumormechanism was hypothesized. In summary, the hinokitiol can induce DNAdamage and autophagy (Rodrigues et al. 2015).
References
1) Ido et al (1999) Induction of apoptosis by hinokitiol, a potent iron chelator, in teratocarcinoma F9 cells is mediated through the activation of caspase-3; Cell Prolif., 32 63 2) Suzuki et al. (2000) Hinokitiol, a selective inhibitor of the platelet-type isozyme of arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 275 885 3) Morita et al. (2007) The mechanism of the bactericidal activity of hinokitiol; Biocontrol Sci., 12 101 4) Liu and Yamauchi (2006) Hinokitiol, a metal chelator derived from natural plants, suppresses cell growth and disrupts androgen receptor signaling in prostate carcinoma cell lines; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 351 26 5) Lee et al. (2010) Hinokitiol activates the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway through inhibition of HIF hydroxylases; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 396 370
Properties of Hinokitiol
| Melting point: | 50-52 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 140 °C10 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.0041 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5190 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 25 mg/ml) or in Ethanol (up to 25 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| appearance | colorless to pale yellow crystals |
| pka | 7.06±0.30(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. phenolic woody mossy |
| Merck | 14,9390 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or ethanol may be stored at -20° for up to 4 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 499-44-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2,4,6-Cycloheptatrien-1-one, 2-hydroxy-4-(1-methylethyl)-(499-44-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,4,6-Cycloheptatrien-1-one, 2-hydroxy-4-(1-methylethyl)- (499-44-5) |
Safety information for Hinokitiol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Hinokitiol
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Hinokitiol CAS 499-44-5View Details
Hinokitiol CAS 499-44-5View Details
499-44-5 -
 beta-Thujaplicin 98.00% CAS 499-44-5View Details
beta-Thujaplicin 98.00% CAS 499-44-5View Details
499-44-5 -
 β-Thujaplicin CAS 499-44-5View Details
β-Thujaplicin CAS 499-44-5View Details
499-44-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1