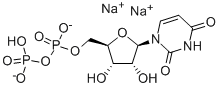
Guanosine
Synonym(s):9-(β-D -Ribofuranosyl)guanine;Guanine-9-β-D -ribofuranoside
- CAS NO.:118-00-3
- Empirical Formula: C10H13N5O5
- Molecular Weight: 283.24
- MDL number: MFCD00010182
- EINECS: 204-227-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
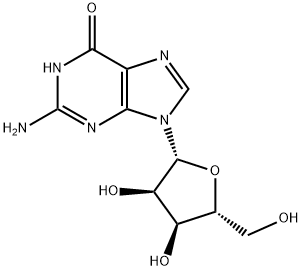
What is Guanosine?
Description
Guanosine is a purine nucleoside that is comprised of the purine base guanine attached to a ribose moiety. Mono-, di-, tri-, and cyclic monophosphorylated forms of guanosine (GMP, GDP, GTP, and cGMP, respectively) are essential for a variety of endogenous biochemical processes, such as signal transduction, metabolism, and RNA synthesis.
Chemical properties
White, crystalline powder; odorless; mild saline taste. Very slightly soluble in cold water; soluble in boiling water, dilute mineral acids, hot acetic acid, and dilute bases; insoluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, and benzene.
The Uses of Guanosine
Guanosine is used as a constituent of nucleic acids. It is used in metallic paints, simulated pearls,plastics,cosmetics industry etc,. It has been also used in pharmacokinetics as a prodrug. Guanosine is used in cell culture applications as a precursor of GMP.
The Uses of Guanosine
Guanosine has been used:
- as a reference standard for the analysis of glucosinolates by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS)
- as a component of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) culture
- as a standard for the detection of residual RNA contaminant in oil palm plant genome samples by HPLC
What are the applications of Application
Guanosine is Guanosine is a purine nucleoside.
Definition
ChEBI: A purine nucleoside in which guanine is attached to ribofuranose via a beta-N9-glycosidic bond.
Definition
A NUCLEOSIDE present in DNA and RNA and consisting of guanine linked to D-ribose via a β-glycosidic bond.
General Description
Guanosine is an aromatic organic molecule and a purine nucleoside. It is present in the cerebrospinal fluid, intestinal cells, blood-brain barrier and in brain microvessels.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Guanosine nucleoside elicits cellular effect as the guanine-based purinergic system. It modulates glutamate uptake by glutamate transporters. It may have neuroprotective functionality in central nervous system disorders. Guanosine promotes neurite arborization, outgrowth, proliferation and differentiation. Administration of guanosine replenished GTP and elicits protective function in renal ischemic injury.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from water as a dihydrate. Dry it at 110o.[Beilstein 26/18 V 81.]
Properties of Guanosine
| Melting point: | 250 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 425.8°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | -62 º (c=3, in 0.1 N NaOH) |
| Density | 1.3790 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -76 ° (C=1, 1mol/L NaOH) |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | 0.1 M NaOH: 0.1 g/mL, clear, slightly yellow |
| form | Powder |
| pka | pK1:1.9(+1);pK2:9.25(0);pK3:12.33(OH) (25°C) |
| color | White to light yellow |
| Odor | Odorless |
| optical activity | [α]20/D -73±2°, c = 1.5% in 1 M NaOH |
| Water Solubility | 0.75 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,4566 |
| BRN | 625911 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 118-00-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | guanosine(118-00-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Guanosine (118-00-3) |
Safety information for Guanosine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Guanosine
| InChIKey | NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-N |
Guanosine manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
(R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Guanosine extrapure CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine extrapure CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 Guanosine 95% CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine 95% CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 GUANOSINE For Biochemistry CAS 118-00-3View Details
GUANOSINE For Biochemistry CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 Guanosine 98% (HPLC) CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine 98% (HPLC) CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3 -
 Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
Guanosine CAS 118-00-3View Details
118-00-3
