Guaifenesin
Synonym(s):3-(o-Methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol;Glycerol guaiacolate;Guaiacol glyceryl ether;Guaifenesin
- CAS NO.:93-14-1
- Empirical Formula: C10H14O4
- Molecular Weight: 198.22
- MDL number: MFCD00016873
- EINECS: 202-222-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
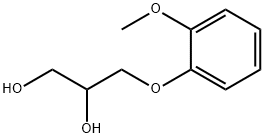
What is Guaifenesin?
Absorption
Studies have shown that guaifenesin is well absorbed from and along the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration .
Toxicity
The most prevalent signs and symptoms associated with an overdose of guaifenesin have been nausea and vomiting .
Although adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women have not been performed, the Collaborative Perinatal Project monitored 197 mother-child pairs exposed to guaifenesin during the first trimester . An increased occurrence of inguinal hernias was found in the neonates . However, congenital defects were not strongly associated with guaifenesin use during pregnancy in 2 large groups of mother-child pairs .
Moreover, guaifenesin is excreted in breast milk in small quantities . Subsequently, caution should be exercised by balancing the potential benefit of treatment against any possible risks .
Additionally, an LD50 value of 1510 mg/kg (rat, oral) has been reported for guaifenesin .
Description
Guaifenesin is an oral expectorant drug. The expectorant action of guaifenesin is mediated by stimulation of the gastrointestinal tract. It is a common ingredient in prescription and over-the-counter medications used to treat cough due to colds and minor upper respiratory infections. Additionally, Guaifenesin is also a centrally-acting muscle relaxant and is used routinely in combination with analgesics and sedatives in large-animal veterinary surgery.
Chemical properties
This substance is a white crystalline powder with a melting point of 78.5-79°C and a boiling point of 215°C (2.53kPa). It is soluble in 20ml of water and ethanol, chloroform, glycerin, and dimethylformamide. It is easily soluble in benzene but insoluble in petroleum ether. It has a slightly bitter taste and a slightly particular odor.
Originator
GG Cen,Central,US,1975
History
Guaifenesin was originally derived from the guaiac tree and used by Native Americans for health purposes. Synthesis of guaifenesin was first reported in 1912. Guaifenesin has been used in the treatment of respiratory diseases since the nineteenth century. The United States’ Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved guaifenesin for use in overthe- counter medications in 1989. Guaifenesin is widely consumed alone and combined with antihistamines, cough suppressants, and decongestants. Guaifenesin is also a centrally acting muscle relaxant and is used routinely in combination with analgesics and sedatives in large-animal veterinary surgery.
The Uses of Guaifenesin
Guaifenesin is commonly used as an expectorant.
Guaifenesin comes in tablet and capsule form, as syrup, as
dissolving granules, and recently as an extended-release (longacting)
tablet. The tablets, capsules, dissolving granules, and
syrup are usually taken with or without food every 4 h as
needed. The extended-release tablet is usually taken with or
without food every 12 h.
In veterinary medicine, guaifenesin is given intravenously
to induce muscle relaxation when administering anesthesia. It
relaxes both laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles, allowing easier
intubation. Guaifenesin is also used in the treatment of horses
with exertional rhabdomyolysis and in dogs with strychnine
intoxication.
Background
Guaifenesin possesses a storied history, having been originally formally approved by the US FDA in 1952 and continues to be one of very few - if not perhaps the only drug that is readily available and used as an expectorant . Since that time the agent has been a combination component of various prescription and non-prescription over-the-counter cough and cold products and is currently a widely available over-the-counter generic medication . Although it is principally believed that guaifenesin elicits an action to facilitate productive cough to manage chest congestion , it is not known whether the agent can reliably mitigate coughing.
Regardless, on March 1, 2007, the FDA received a petition asking the FDA to notify the public that some antitussives, expectorants, decongestants, antihistamines, and cough/cold combinations are not known to be safe and effective in children under the age of 6 years . After the negotiation between FDA and major manufacturers, a voluntary transition of labels for not using guaifenesin in children under the age of 4 years was endorsed by FDA in 2008 .
Furthermore, there has also been contemporary research to suggest that guaifenesin possesses and is capable of demonstrating anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant effects to some degree possibly by acting as an NMDA receptor antagonist .
Indications
Guaifenesin is an expectorant that is indicated for providing temporary symptomatic relief from congested chests and coughs which may be due to a cold, bronchitis, and/or other breathing illnesses .
Definition
ChEBI: Guaifenesin is a member of methoxybenzenes.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of o-methoxyphenol (57 g), glycidol (32 g) and pyridine (1 g) is warmed to 95°C at which temperature a vigorous reaction takes place. The reaction mixture is cooled to prevent the temperature rising above 110°C. When the exothermic reaction has subsided the reactants are heated at 95°C for one hour longer and then distilled under low pressure. The main fraction boils in the range 176°C to 180°C/0.5 mm. It crystallizes on cooling. Recrystallization from benzene gives the pure product, MP 78.5°C to 79.0°C.
brand name
Mucinex (Adams).
General Description
Guaifenesin is an expectorant, widely used in the treatment of cough. Its mode of action involves the alleviating of cough discomfort by increasing sputum volume and decreasing its viscosity, thus resulting in effective cough.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Mechanism of action
Guaiphenesin facilitates secretion from bronchial mucous membranes, thus relieving a cough in colds, bronchitis, and bronchial asthma.
Pharmacokinetics
Guaifenesin is categorized as an expectorant that acts by enhancing the output of phlegm (sputum) and bronchial secretions via decreasing the adhesiveness and surface tension of such material . Furthermore, guaifenesin elicits an increased flow of less viscous gastric secretions that subsequently promote ciliary action - all actions that ultimately change dry, unproductive coughing to coughs that are more productive and less frequent . Essentially, by decreasing the viscosity and adhesiveness of such secretions, guaifenesin enhances the efficacy of mucociliary activity in removing accumulated secretions from the upper and lower airway .
Synthesis
Guaiphenesin, 3-(o-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propandiol (23.2.3), is synthesized by reacting guiacol with 3-chloropropan-1,2-diol or with glycidol.

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In veterinary medicine, guaifenesin is used to induce muscle relaxation
and restraint
as an adjunct to anesthesia for short procedures
(30 – 60 minutes) in large and small animal species. There are combination
oral products containing guaifenesin for treating respiratory
conditions in horses.
In human medicine, guaifenesin has long been touted as an oral
expectorant, but definitive proof of its efficacy is lacking.
Environmental Fate
Guaifenesin’s production and use as veterinary and human
medicines may result in its release to the environment through
various waste streams.
If released to air, an estimated vapor pressure of
1.5× 10–6 mm Hg at 25 ℃ indicates that guaifenesin will
exist in both the vapor and particulate phase.
Based upon an estimated Henry’s law constant of
4.4 × 10-11 atm-m3 mol-1, volatilization from moist soil
surfaces or from water surfaces are not expected to be important
fate processes for guaifenesin.
Guaifenesin is expected to have high mobility in soil based
upon an organic carbon–water partition coefficient (Koc) of
140, which indicates that it will have more solubility in water
and is less likely to adsorb onto organic matter in soil and
plants.
Metabolism
After the oral administration of 400 mg guaifenesin, the agent experiences rapid hydrolysis (more than 60% of the dose hydrolyzed over a range of seven hours) with β-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-lactic acid found as the major urinary metabolite but no parent drug detectable in the urine . Moreover, it has been observed that guaifenesin also experiences both oxidation and demethylation . In particular, the medication is quickly metabolized hepatically by way of oxidation to β-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-lactic acid . Furthermore, guaifenesin is also demethylated by O-demethylase in liver microsomes to the point where about 40% of an administered dose is excreted as this metabolite in the urine within 3 hours . In fact, O-demethylase appears to be the primary enzyme for the metabolism of guaifenesin and the primary metabolites of the substance are β-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-lactic acid and the demethylated hydroxyguaifenesin, both of which are themselves inactive moieties .
Toxicity evaluation
Guaifenesin is an adrenergic antagonist in a class of medications
called expectorants. It stimulates afferent receptors in the
gastric mucosa, reflexively increasing glandular secretion by the
respiratory epithelium promoting lower respiratory tract
drainage by thinning bronchial secretions, lubricating irritated
respiratory tract membranes through increased mucous flow,
and facilitating removal of viscous mucus. The onset of action
appears to be within 15–30 min. Guaifenesin is believed to
alleviate cough discomfort by improving sinus and bronchial
drainage, increasing sputum volume, and decreasing sputum
viscosity, thereby promoting effective cough. In one study, the
effect of guaifenesin to increase mucociliary clearance from the
lung was greater in patients with chronic bronchitis than in
healthy subjects.
In another study, guaifenesin inhibited the cough reflex
sensitivity in subjects with an upper respiratory tract infection
(cough receptors are transiently hypersensitive), but not in
healthy volunteers. Possible mechanisms include a central
antitussive effect or a peripheral effect by increased sputum
volume serving as a physical barrier, shielding cough receptors
within the respiratory epithelium.
As a centrally acting muscle relaxant, guaifenesin is believed
to depress or block nerve impulse transmission at the internuncial
neuron level of the subcortical areas of the brain, brain
stem, and spinal cord. It also has mild analgesic and sedative
actions.
References
[1] Peter V. Dicpinigaitis and Yvonne E. Gayle, Effect of Guaifenesin on Cough Reflex Sensitivity, 2003, vol. 124, 2178-2181 DOI:10.1378/CHEST.124.6.2178
[2] Leonid Kagan, Eran Lavy and Ammon Hoffmann, Effect of mode of administration on guaifenesin pharmacokinetics and expectorant action in the rat model, Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2009, vol. 22, 260-265 DOI:10.1016/j.pupt.2008.12.020
[3] Sittig's Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia
[4] Synthesis of Essential Drugs (2006, Elsevier)
[5] Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook
[6] https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Guaifenesin
Properties of Guaifenesin
| Melting point: | 77-81 °C |
| Boiling point: | 215 °C (19 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.1825 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5550 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 215°C/19mm |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 50g/l (experimental) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 13.53±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 5 g/100 mL (25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,4555 |
| BRN | 2049375 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 93-14-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 3-(O-methoxyphenoxy)-1,2-propanediol(93-14-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Guaifenesin (93-14-1) |
Safety information for Guaifenesin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Guaifenesin
| InChIKey | HSRJKNPTNIJEKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Guaifenesin manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Guaifenesin 99%View Details
Guaifenesin 99%View Details -
 GUAIFENESIN 99%View Details
GUAIFENESIN 99%View Details -
 Guaiphenesin 99%View Details
Guaiphenesin 99%View Details -
 Guaifenesin 99%View Details
Guaifenesin 99%View Details -
 Guaifenesin Powder USP, 25Kg DrumView Details
Guaifenesin Powder USP, 25Kg DrumView Details
93-14-1 -
 Guaifenesin USP PowderView Details
Guaifenesin USP PowderView Details
93-14-1 -
 Guaifenesin Agent API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
Guaifenesin Agent API MANUFACTURER INDIAView Details
93-14-1 -
 Guaifenesin Ip Bp Usp EpView Details
Guaifenesin Ip Bp Usp EpView Details
93-14-1
