Glyoxal
Synonym(s):Ethanedial;Oxalaldehyde
- CAS NO.:107-22-2
- Empirical Formula: C2H2O2
- Molecular Weight: 58.04
- MDL number: MFCD00006957
- EINECS: 203-474-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:22
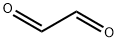
What is Glyoxal?
Description
Glyoxal, the simplest dialdehyde, was first prepared by N. Lubawin in 1875, when he oxidized acetaldehyde with HNO3?or H2SeO3. The HNO3?method is still used commercially, along with metal-catalyzed gas-phase oxidation of ethylene glycol. At low temperatures, glyoxal forms yellow crystals; it melts at 15 °C and boils at 51 °C. Its low flash point (–4 °C) makes its green vapor explosive in air. It’s used chiefly in paper coating and textile finishing processes.
Chemical properties
colourless or light yellow liquid
The Uses of Glyoxal
Glyoxal is used in the production of textilesand glues and in organic synthesis.
The Uses of Glyoxal
Glyoxal is used to prepare 4,5-dihydroxy-2-imidazolidinone by condensation with urea. It finds application in leather tanning process, textile finishes and paper coatings. It is an important building block in the synthesis of imidazoles. It acts as a solubilizer and cross-linking agent in polymer chemistry. Further, it is used as a fixative for histology to preserve cells in order to examine under a microscope.
The Uses of Glyoxal
ermanent-press fabrics; dimensional stabilization of rayon and other fibers. Insolubilizing agent for compounds containing polyhydroxyl groups (polyvinyl alcohol, starch, and cellulosic materials); insolubilizing of proteins (casein, gelatin, and animal glue); embalming fluids; leather tanning; paper coatings with hydroxyethylcellulose; reducing agent in dyeing textiles.
What are the applications of Application
Glyoxal, 40 % Solution is used to denature nucleic acids by forming stable complexes with guanine residues
Definition
ChEBI: Glyoxal is the dialdehyde that is the smallest possible and which consists of ethane having oxo groups on both carbons. It has a role as a pesticide, an agrochemical, an allergen and a plant growth regulator.
General Description
Yellow crystals melting at15°C. Hence often encountered as a light yellow liquid with a weak sour odor. Vapor has a green color and burns with a violet flame.
Air & Water Reactions
Mixtures with air may explode. Polymerizes quickly on standing, or on contact with a trace of water (possibly a violent reaction), or when dissolved in solvents containing water, [Merck, 502(1968)]. Soluble in water. An aqueous solution contains mono molecular Glyoxal. [Hawley]
Reactivity Profile
Glyoxal reacts vigorously with strong oxidizing agents such as nitric acid. Polymerizes rapidly even at low temperature if anhydrous [Noller]. Aqueous solutions are more stable but also polymerize on standing. Reacts with itself in the presence of base to give glyconates. Undergoes addition and condensation reactions that may be exothermic with amines, amides, aldehydes, and hydroxide-containing materials. Mixing in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: chlorosulfonic acid, oleum, ethyleneimine, nitric acid, sodium hydroxide [NFPA 1991].
Hazard
Mixture of vapor and air may explode. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Glyoxal is a skin and eye irritant; the effectmay be mild to severe. Its vapors are irritatingto the skin and respiratory tract. Anamount of 1.8 mg caused severe irritation inrabbits’ eyes. Glyoxal exhibited low toxicityin test subjects. Ingestion may cause somnolenceand gastrointestinal pain.
LD50 value, oral (guinea pigs): 760 mg/kg.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes some irritation of nose and,40% solution throat. Contact with liquid,40% solution irritates eyes and causes mild irritation of skin; stains skin yellow. (No information available on symptoms of ingestion.)
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Heat may cause polymerization to a combustible, viscous material.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by SYN: AEROTEX GLYOXAL 40 ingestion and skin contact. A skin irritant. A powerful reducing agent. May explode on contact with air. Polymerizes violently on contact with water. During storage it may spontaneously polymerize and ignite. Reacts violently with chlorosulfonic acid, ethylene imine, HNO3, oleum, NaOH, can cause violent reactions. Can explode during manufacture. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ALDEHYDES.
Waste Disposal
Glyoxal is mixed with a combustible solventand burned in a chemical incineratorequipped with an afterburner and scrubber.
Properties of Glyoxal
| Melting point: | -14 °C |
| Boiling point: | 104 °C |
| Density | 1.265 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor density | >1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 18 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 104°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | water: soluble(lit.) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to yellow |
| Odor | yel. crystals or lt. yel. liq., mild odor |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| Merck | 14,4509 |
| BRN | 1732463 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stability Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Strong reducing agent. May polyermize exothermically. Incompatible with air, water, oxygen, peroxides, amides, amines, hydroxy-containing materials, nitric acid, aldehydes. Corrodes many metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 107-22-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ethanedial(107-22-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Glyoxal (107-22-2) |
Safety information for Glyoxal
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Glyoxal
| InChIKey | LEQAOMBKQFMDFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Glyoxal manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Glyoxal 99%View Details
Glyoxal 99%View Details -
 Glyoxal 40% aq. solution pure CAS 107-22-2View Details
Glyoxal 40% aq. solution pure CAS 107-22-2View Details
107-22-2 -
 Glyoxal 40 Solution Cas 107 22 2, 250 kgs drumView Details
Glyoxal 40 Solution Cas 107 22 2, 250 kgs drumView Details
107-22-2 -
 Glyoxal 40% industrial, C2H2O2, 107-22-2View Details
Glyoxal 40% industrial, C2H2O2, 107-22-2View Details
107-22-2 -
 Glyoxal 40%View Details
Glyoxal 40%View Details
107-22-2 -
 Glyoxal 40 %, 98%View Details
Glyoxal 40 %, 98%View Details
107-22-2 -
 Glyoxal 40 PercentView Details
Glyoxal 40 PercentView Details
107-22-2 -
 GLYOXAL 40 PCT, 250 KG DRUM, 99%View Details
GLYOXAL 40 PCT, 250 KG DRUM, 99%View Details
107-22-2
