Gemfibrozil
Synonym(s):2,2-Dimethyl-5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)pentanoic acid;2,2-Dimethyl-5-(2,5-xylyloxy)valeric acid;5-(2,5-Dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethylpentanoic acid
- CAS NO.:25812-30-0
- Empirical Formula: C15H22O3
- Molecular Weight: 250.33
- MDL number: MFCD00079335
- EINECS: 247-280-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
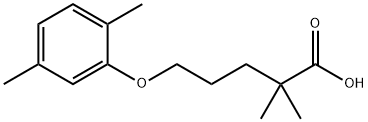
What is Gemfibrozil?
Absorption
Gemfibrozil is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
In healthy volunteers, a 900mg oral dose of gemfibrozil has a Cmax of 46±16μg/mL with a Tmax of 2.2±1.1h. In patients with chronic renal failure, gemfibrozil has a Cmax of 13.8±11.1μg/mL with a Tmax of 2.3±1.0h. In patients with liver disease, gemfibrozil has a Cmax of 23.0±10.3μg/mL with a Tmax of 2.6±1.7h.
Toxicity
The oral TDLO of gemfibrozil in humans is 18gm/kg/3Y. The oral LD50 in mice is 2218mg/kg and in rats is 1414mg/kg. The intraperitoneal LD50 in rats is 445mg/kg.
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with abdominal cramps, adnormal liver function tests, diarrhea, increased CPK, joint and muscle pain, nausea, and vomiting. Patients should be treated with symptomatic and supportive measures.
Description
Gemfibrozil is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) and PPARγ agonist (EC50s = 193.3 and 147.8 μM, respectively, in transactivation assays). In vivo, gemfibrozil (50 mg/kg, p.o.) reduces serum total cholesterol, triglyceride, and LDL levels in a rat model of high-cholesterol diet-induced hyperlipidemia. Gemfibrozil (100 mg/kg per day) reduces atherosclerotic plaque area, superoxide production, and expression of the genes encoding the NF-κB subunit p65 and chemokine (C-C) motif ligand 2 (CCL2) in ApoE-/- mice. Formulations containing gemfibrozil have been used in the treatment of high cholesterol.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Powder
Originator
Lopid,Warner Lambert,US,1982
The Uses of Gemfibrozil
Gemfibrozil has been used to to study its effects on cell cycle progression in yeast. It has been used to study the effects of fibrates on cell proliferation and gene expression in human cell lines.
The Uses of Gemfibrozil
A serum lipid regulating agent used as an antihyperlipoproteinemic
The Uses of Gemfibrozil
This drug is used for hyperlipoproteinemia that cannot be corrected by a special diet or by physical exertion.
Background
Gemfibrozil is a fibric acid agent, similar to clofibrate, used to treat Type IIb, IV, and V hyperlipidemias. Gemfibrozil is not a first line treatment and is prescribed to patients who have not responded adequately to weight loss, diet, exercise, and other medications.
Gemfibrozil was granted FDA approval on 21 December 1981.
Indications
Gemfibrozil is indicated to treat patients with Types IV and V hyperlipidemia who have elevated serum triglycerides (usually above 2000mg/dL), elevated VLDL cholesterol, fasting chylomicrons, are at risk of developing pancreatitis, and do not adequately respond to dietary restrictions. Gemfibrozil is also indicated to reduce the risk of developing coronary heart disease in patients with Type IIb hyperlipidemia without history or symptoms of coronary heart disease; who do not adequately respond to weight loss, diet, exercise, and other medications; and have low HDL, raised LDL, and raised triglycerides.
What are the applications of Application
Gemfibrozil is a hyperlipidemic agent
Definition
ChEBI: Gemfibrozil is an aromatic ether. It has a role as an antilipemic drug. It is functionally related to a valeric acid.
Manufacturing Process
With stirring, 44.1 g of isobutyric acid is added to a mixture of 51.0 g of
diisopropylamine, 23.2 g of a 57% sodium hydride dispersion in mineral oil,
and 350 ml of tetrahydrofuran. When gas evolution subsides, the mixture is
heated at reflux for 15 minutes, cooled to 0°C, and treated with 345 ml of a
1.45M solution of n-butyl lithium in heptane. After 5 hr, the mixture is
warmed one-half hour at 30°C, cooled to 0°C, and treated with 122.0 g of 3-
(2,5-xylyloxy)propyl bromide. After one more hour, it is stirred with 500 ml of
water and the aqueous phase is separated and acidified with 150 ml of 6N hydrochloric acid. The acidic mixture is extracted with ether and the ether
extract is washed with saturated sodium chloride solution, dried over
magnesium sulfate, concentrated almost to dryness, and distilled in vacuo. A
distillate of 2,2-dimethyl-5-(2,5-xylyloxy)valeric acid is collected at boiling
point 158°C to 159°C at 0.02 mm of Hg; melting point 61°C to 63°C following
crystallization from hexane.
The same product is obtained by substituting 4.4 g of lithium hydride for the
sodium hydride in the above procedure.
The same product is also obtained in the following manner. A mixture of 26.4
g of isobutyric acid, 6.0 g of magnesium oxide powder, and 250 ml of toluene
is stirred and heated at reflux with continuous removal of the water formed in
the reaction. When water formation ceases, the resulting mixture containing
magnesium isobutyrate is concentrated to one-half its original volume, cooled
in an ice bath, and treated with 31.0 g of diisopropylamine in 200 mi of dry
tetrahydrofuran and then with 179 ml of 1.68M n-butyl lithium in heptane
while the temperature is maintained below 10°C. After 15 more minutes, the
mixture is warmed at 30°C for one-half hour, cooled to 0°C to 10°C, and
treated with 75.0 g of 3-(2,5-xylyloxy)propyl bromide. The mixture is then
stirred for 18 hr at room temperature and diluted with 125 ml of 6N
hydrochloric acid and 250 ml of water. The organic phase is separated,
concentrated, and the residue distilled in vacuo to give 2,2-dimethyl-5-(2,5-
xylyloxy)valeric acid.
brand name
Lopid (Pfizer);Gevilon;Hipolixan;Ipolipid;Lipur;Tenorac.
Therapeutic Function
Antihyperlipidemic
World Health Organization (WHO)
Gemfibrozil, an antihyperlipidaemic derivative of clofibrate, was introduced in the early 1980's. It is registered in several countries for the treatment of hyperlipidaemia unresponsive to dietary measures. (See also the WHO comment for clofibrate).
General Description
Gemfibrozil, 5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethylpentanoic acid (Lopid), is a congener of clofibratethat was used first in the treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia inthe mid-1970s. Its mechanism of action and use are similar tothose of clofibrate. Gemfibrozil reduces plasma levels ofVLDL triglycerides and stimulates clearance of VLDL fromplasma. The drug has little effect on cholesterol plasma levelsbut does cause an increase of HDL.
Gemfibrozil is absorbed quickly from the gut and excretedunchanged in the urine. The drug has a plasma half-life of1.5 hours, but reduction of plasma VLDL concentration takesbetween 2 and 5 days to become evident. The peak effect of its hypolipidemic action may take up to 4 weeks to becomemanifest.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Gemfibrozil selectively increases Apolipoprotein A-I levels. In yeast cells, application of gemfibrozil delays the start of DNA replication. It is used as a therapeutic agent for dyslipidemia.
Mechanism of action
From the chemical point of view, gemfibrozil is somewhat related to clofibrate and has analogous pharmacological use. The primary action of gemibrozil as well as clofibrate consists of a significant reduction in the level of very low-density proteins in the plasma and an increase in high-density protein formation.
Pharmacokinetics
Gemfibrozil alters lipid metabolism to treat patients with hyperlipidemia. The duration of action requires twice daily dosing as the mean residence time of gemfibrozil is up to 9.6h in patients with chronic renal failure. Gemfibrozil has a wide therapeutic index as trials with twice the standard dose were not associated with severe side effects. Patients taking gemfibrozil may be at an increased risk of developing cholelithiasis and cholecystitis, as seen in patients taking clofibrate.
Clinical Use
Hyperlipidaemias of types IIa, IIb, III, IV and V
Synthesis
Gemfibrozil, 2,2-dimethyl-5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)valeric acid (20.2.4), is synthesized either by hydrolysis of ethyl ester of 2,2-dimethyl-5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy) valeric acid (20.2.3), which is synthesized by alkylation 2,2-dimethylvaleric acid ethyl ester with 3-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)propylbromide-1 in the presence of lithium diisopropylamide, or by oxidation of the corresponding aldehyde (20.2.4).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Gemfibrozil may be useful to reduce serum triglycerides in those dogs or cats with hypertriglyceridemia and when diet modifications alone have been unsuccessful. One reference (Elliott 2005) suggests not adding drug therapy to treat hypertriglyceridemia unless the serum triglyceride concentration exceeds 500 mg/dL with associated clinical signs.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: increased risk of myopathy with
daptomycin - try to avoid concomitant use.
Anticoagulants: enhances effect of coumarins and
phenindione; dose of anticoagulant should be reduced
by up to 50% and adjusted by monitoring INR.
Antidiabetics: may improve glucose tolerance and
have an additive effect with insulin or sulphonylureas;
possibly enhanced effect with nateglinide; increased
risk of severe hypoglycaemia with repaglinide - avoid.
Antivirals concentration of paritaprevir increased -
avoid.
Ciclosporin: Parke-Davis have one report on file
of an interaction with ciclosporin where serum
ciclosporin levels were decreased. No effects on
muscle were noted.
Colchicine: possible increased risk of myopathy.
Cytotoxics: bexarotene concentration increased
- avoid; concentration of enzalutamide increased -
avoid or halve enzalutamide dose.
Lipid-regulating drugs: increased risk of myopathy
in combination with statins and ezetimibe - avoid
(maximum 20 mg of rosuvastatin).
Metabolism
Gemfibrozil undergoes hydroxylation at the 5'-methyl and 4' positions to form the M1 and M2 metaolites respectively. Gemfibrozil also undergoes O-glucuronidation to form gemfibrozil 1-beta glucuronide, an inhibitor of CYP2C8. This O-glucuronidation is primarily mediated by UGT2B7, but also by UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A9, UGT2B4, UGT2B17.
Metabolism
Gemfibrozil undergoes oxidation of a ring methyl group
to form successively a hydroxymethyl and a carboxyl
metabolite (the main metabolite). This metabolite
has a low activity compared to the mother compound
gemfibrozil and an elimination half-life of approximately
20 hours.
Gemfibrozil is eliminated mainly by metabolism.
Approximately 70% of the administered human dose is
excreted in the urine, mainly as conjugates of gemfibrozil
and its metabolites. Less than 6% of the dose is excreted
unchanged in the urine; 6% of the dose is found in faeces.
Properties of Gemfibrozil
| Melting point: | 61-63°C |
| Boiling point: | 158-159 C |
| Density | 1.1109 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5020 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, very soluble in methylene chloride, freely soluble in anhydrous ethanol and in methanol. |
| form | powder |
| pka | 4.75±0.45(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | >0.5g/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 14,4388 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 25812-30-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 66) 1996 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pentanoic acid, 5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethyl- (25812-30-0) |
Safety information for Gemfibrozil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Gemfibrozil
Gemfibrozil manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 25812-30-0 Gemfibrozil 99%View Details
25812-30-0 Gemfibrozil 99%View Details
25812-30-0 -
 25812-30-0 98%View Details
25812-30-0 98%View Details
25812-30-0 -
 Gemfibrozil 98% CAS 25812-30-0View Details
Gemfibrozil 98% CAS 25812-30-0View Details
25812-30-0 -
 25812-30-0 Gemfibrozil 98%View Details
25812-30-0 Gemfibrozil 98%View Details
25812-30-0 -
 Gemfibrozil 98%View Details
Gemfibrozil 98%View Details
25812-30-0 -
 Gemfibrozil 25812-30-0 98%View Details
Gemfibrozil 25812-30-0 98%View Details
25812-30-0 -
 Gemfibrozil CAS 25812-30-0View Details
Gemfibrozil CAS 25812-30-0View Details
25812-30-0 -
 Gemfibrozil CAS 25812-30-0View Details
Gemfibrozil CAS 25812-30-0View Details
25812-30-0