Fucoxanthin
Synonym(s):all-trans-Fucoxanthin
- CAS NO.:3351-86-8
- Empirical Formula: C42H58O6
- Molecular Weight: 658.91
- MDL number: MFCD01745140
- EINECS: 200-486-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
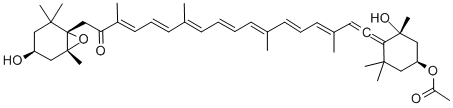
What is Fucoxanthin?
Description
Fucoxanthin is an important lutein widely distributed in heterodinophytes, including brown algae and marine microalgae. It is estimated to be the second most abundant carotenoid globally, after β-carotene. In recent years, research has increasingly focused on its functional properties, confirming its various beneficial physiological activities. These activities include antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-obesity pharmacological effects, as well as neuroprotective effects and the ability to increase arachidonic acid (ARA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) levels in mouse models. Therefore, fucoxanthin is widely used in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and dietary supplement markets.
Chemical properties
Fucoxanthin is an orange-colored pigment found in Chromophyta (Heterokontophyta or Ochrophyta), co-occurring with chlorophylls a and c and β-carotene. Primary sources include brown seaweeds (Phaeophyceae) and diatoms (Bacillariophyta). Fucoxanthin is characterized by its insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents such as ethanol, typically presenting as a lipid-soluble powder or oil.
Occurrence
Fucoxanthin is a xanthophyll carotenoid abundant in macroalgae, such as brown seaweeds and microalgae. Several edible brown algae, including Sargassam fusiforme, Laminaria japonica, Undaria pinnatifida, and Padina tetrastromatica, are consumed in Southeast Asia and Europe. The brown algae are good sources of fucoxanthin. However, diatoms, such as Phaeodactylum tricornutum, are preferred sources of fucoxanthin in the food industry because of their higher fucoxanthin content and extraction efficiency with shorter growth cycles than those of macroalgae[1].
The Uses of Fucoxanthin
Fucoxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid pigment found in certain algae. Dietary inclusion of Fucoxanthin in mice and rats significantly reduces abdominal white adipose tissue (WAT). This effect is mediated by Fucoxanthin's ability to increase the expression of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in WAT, a fatty acid-stimulated protein involved in respiration and thermogenesis. In KK-Ay mice, a model for obese Type 2 diabetes with hyperinsulinemia, Fucoxanthin administration mitigates WAT gain and lowers both blood glucose and plasma insulin concentrations. Beyond its metabolic effects, Fucoxanthin has been investigated for its neuroprotective properties. It is also utilized in calibration procedures to identify the most productive microalgae strains for Fucoxanthin biosynthesis.
What are the applications of Application
Fucoxanthin is a carotenoid pigment
Definition
ChEBI: A natural product found in Sporochnus comosus.
General Description
Fucoxanthin is isolated from brown algae. It has anti-angiogenic, hepatoprotective,?cardiovascular and cerebrovascular protective properties. Fucoxanthin stimulates G1 cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cell lines.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Xanthophyll carotenoid pigment extracted from algae. Exhibits anticancer, antioxidant, anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory properties.
Side Effects
There are some potential dangers associated with taking Fucoxanthin. These include an increased risk of bleeding, liver damage, and allergic reactions. Additionally, it may interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners, and can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Metabolism
Fucoxanthin is unstable and can be easily degraded by heating, aerial exposure, or illumination. The primary metabolites of fucoxanthin are fucoxanthinol and amarouciaxanthin A. Fucoxanthin can be hydrolyzed to fucoxanthinol in the gastrointestinal tract and further converted into amarouciaxanthin A in the liver. In animal studies, no toxicity of fucoxanthin was observed [1].
References
[1] Minkyung Bae . “Health benefits of fucoxanthin in the prevention of chronic diseases.” Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular and cell biology of lipids 1865 11 (2020): Article 158618.
Properties of Fucoxanthin
| Melting point: | 166-168°C |
| Boiling point: | 590.43°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D18 +72.5 ±9° (chloroform) |
| Density | 1.09 |
| refractive index | n20/D1.360-1.362 |
| Flash point: | 14℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Ethanol, |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 14.47±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | Crystalline |
| λmax | λ: 444-454 nm Amax |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 3351-86-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Fucoxanthin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Fucoxanthin
| InChIKey | SJWWTRQNNRNTPU-WEAAWPSVSA-N |
| SMILES | [C@]12(CC(=O)/C(/C)=C/C=C/C(/C)=C/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C=C3[C@@](O)(C)C[C@@H](OC(=O)C)CC3(C)C)C(C)(C)C[C@H](O)C[C@]1(O2)C |&1:0,25,29,42,45,r| |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Fucoxanthin CAS 3351-86-8View Details
Fucoxanthin CAS 3351-86-8View Details
3351-86-8 -
 Fucoxanthin CAS 3351-86-8View Details
Fucoxanthin CAS 3351-86-8View Details
3351-86-8 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
