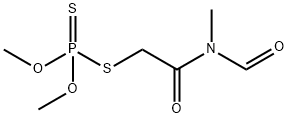
FORMOTHION
Synonym(s):S-[2-(Formylmethylamino)-2-oxoethyl] O,O-dimethyl dithiophosphate
- CAS NO.:2540-82-1
- Empirical Formula: C6H12NO4PS2
- Molecular Weight: 257.27
- MDL number: MFCD00055528
- EINECS: 219-818-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
What is FORMOTHION?
Description
Formothion is a pale yellow liquid or crystalline mass, decomposes on distillation, mp 25–26 ?C, vp 0.113 mPa (20 ?C). It is poorly soluble in water (2.6 g/L at 24 ?C) and miscible with most organic solvents, except aliphatic hydrocarbons. Log Kow = 1.47. Formothion is hydrolyzed in aqueous media to dimethoate (activation) and dimethoate carboxylic acid (degradation): DT50 (23 ?C) at pH 3–9 is less than 1 d.
Chemical properties
Yellow liquid.Insoluble in water; miscible with common organic solvents.
Chemical properties
Formothion is an odorless, yellowish viscous oil or crystalline mass.
The Uses of FORMOTHION
Acaricide, systemic insecticide.
The Uses of FORMOTHION
Formothion is used to control sucking pests and internally feeding larvae in a variety of crops.
Definition
ChEBI: Formothion is a dicarboximide.
General Description
Viscous yellow oil or a crystalline mass. Used as an insecticide and acaricide on crops and ornamentals. Not presently produced commercially in the U.S.
Air & Water Reactions
hydrolyzed by water especially under alkaline conditions. [EPA, 1998].
Reactivity Profile
Organophosphates, such as FORMOTHION, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Hazard
Cholinesterase inhibitor.
Health Hazard
FORMOTHION is one of the least toxic systemic organophosphates. FORMOTHION is a compound of low to moderate toxicity. It causes the depression of cholinesterase, leading to accumulation of acetylcholine in the nervous system, which is believed to be responsible for the symptoms.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, FORMOTHION emits very toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides, phosphorus oxides and sulfur oxides. FORMOTHION is an organophosphorus insecticide. Some of these materials may burn but none of them ignite readily. Container may explode in heat of fire. Fire and runoff from fire control water may produce irritating or poisonous gases. Avoid alkaline pesticides; hydrolyzed by water especially under alkaline conditions.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide: Formothion is a systemic and contact insecticide used to control spider mites, aphids, psyllids, mealy bugs, whiteflies, jassids, leaf miners, ermine moths, and fruit flies. It is used on tree fruits, vines, olives, hops, cereals, sugar cane, rice. Formothion is available as an emulsifiable concentrate and an ultra-low-volume spray. A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP). Not approved for use in EU countries
Trade name
AFLIX®; ANTHIO®; ANTIO®; CP 53926®; S 6900®; SAN 244 I®; SAN 6913 I®; SAN 71071®; SPENCER S-6900®; VEL 4284®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, inhalation, sh contact, and intravenous routes. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, POx, and SOx. See also ESTERS.
Potential Exposure
Formothion is an insecticide and acar icide for use on crops and ornamentals. Formothion is not currently produced commercially in the U.S.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Speed in removing material from skinis of extreme importance. Shampoo hair promptly if contaminated. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, beginrescue breathing (using universal precautions, includingresuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Keepvictim quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Effectsmay be delayed; keep victim under observation.
Metabolic pathway
Formothion is broken down in aqueous solution to approximately equal amounts of dimethoate and dimethoate carboxylic acid, the first of which is an activation step and the latter a degradative one. All studies which have investigated the fate of formothion in biological systems have identified these two metabolites but there is evidence that their formation is purely base-catalysed and not enzyme-catalysed. In this respect, the amide group of formothion is much more labile than that of dimethoate since dimethoate carboxylic acid has only been reported in metabolic studies and is not formed by base-catalysed hydrolysis of dimethoate.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from alkaline materials. Wherepossible, automatically pump liquid from drums or otherstorage containers to process containers.
Shipping
UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Degradation
Formothion is hydrolysed by water to dimethoate (2) and dimethoate carboxylic acid (3). Dilute solutions in non-polar organic solvents are stable (PM). El-Oshar and Dauterman (1977) investigated the hydrolysis of [O-14C-methyl]formothion in 1.0 M phosphate buffer at pH values between 5.5 and 8.0 at 37 °C. The amounts of unchanged formothion and products were assessed after 30 min. At all pH values the amounts of dimethoate (2) and dimethoate carboxylic acid (3) were approximately equal, indicating that the rate of attack by the hydroxyl ion was equal at both carbonyl groups. The rate of hydrolysis was pH dependent with 16.4% hydrolysis at pH 5.5, 65.2% hydrolysis at pH 7.0 and 96.7% hydrolysis at pH 8.0 after 30 min. The route leading to dimethoate carboxylic acid would yield N-methylformamide (4) as the additional product. A suggested route for the base-catalysed hydrolysis of formothion is shown in Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 for rats is 365–500 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats is 3.2 mg/L air. NOEL (2 y) for rats is 80 mg/kg diet (4 mg/kg/d). ADI is 0.02 mg/kg b.w.
Incompatibilities
Strong oxidizers may cause release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Organophosphates, in the pres ence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides, may form highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Keep away from alkaline materials.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR 165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by follow ing package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of FORMOTHION
| Melting point: | 25.5℃ |
| Boiling point: | 317.8±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.361 g/cm3 (20 ºC) |
| vapor pressure | 1.13 x 10-4 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5541 (589.3 nm 20℃) |
| Flash point: | 25 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| form | solid |
| Water Solubility | 2600 mg l-1(24 °C) |
| pka | -1.79±0.70(Predicted) |
| BRN | 5942199 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 2540-82-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Formothion (2540-82-1) |
Safety information for FORMOTHION
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for FORMOTHION
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Anti-NUCKS1 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-NUCKS1 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 Formothion solution CAS 2540-82-1View Details
Formothion solution CAS 2540-82-1View Details
2540-82-1 -
 Anti-NUCKS1 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details
Anti-NUCKS1 antibody produced in rabbit CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8