Fluvoxamine
- CAS NO.:54739-18-3
- Empirical Formula: C15H21F3N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 318.33
- MDL number: MFCD00865345
- EINECS: 611-193-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
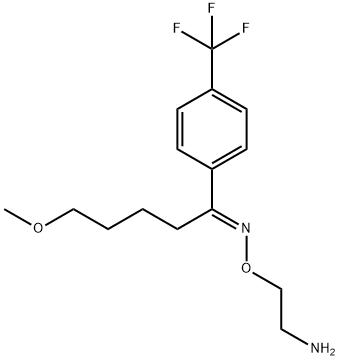
What is Fluvoxamine?
Absorption
Well absorbed, bioavailability of fluvoxamine maleate is 53% .
Toxicity
Fluvoxamine is a member of antidepressants that possess an increased risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behaviour (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages including and and below 24) in short-term studies of major depressive disorder and other psychiatric disorders .
Fluvoxamine maleate tablets are not approved for use in pediatric patients except for patients with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) .
Side effects include anorexia, constipation, dry mouth, headache, nausea, nervousness, skin rash, sleep problems, somnolence, liver toxicity, mania, increase urination, seizures, sweating increase, tremors, or Tourette's syndrome .
Description
Fluvoxamine is an old-line antidepressant that inhibits uptake of serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine. As a?selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, fluvoxamine is effective against major depression as well as obsessive–compulsive, anxiety, panic, and post-traumatic stress disorders.
Fluvoxamine was developed in the mid-1970s by a subsidiary of the Belgian chemical company Solvay. In a 1978 patent1, inventors Hendricus B. A. Antonius and Volkert Claassen described its mode of action. It was marketed under the trade names Luvox and Floxyfral, among others, and is now available as a generic. It is most often formulated as its maleate salt2.
Fluvoxamine has shown anti-inflammatory properties. As a result, it has been investigated as a treatment for COVID-19. In a 2020 clinical trial that involved 152 nonhospitalized adults with mild COVID-19, Eric. J. Lenze and coauthors at Washington University in St. Louis reported statistically significant less clinical deterioration in subjects treated with the drug than subjects treated with placebo.
An April 2021 report from the National Institutes of Health, however, declared the results inconclusive because of the small size of the study. NIH’s recommendation: “Results from adequately powered, well-designed, and well-conducted clinical trials are needed to provide more specific, evidence-based guidance on the role of fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19.”
1. US Patent 4,085,225.
2. CAS Registry No. 61718-82-9.
Chemical properties
Colourless Oil
Originator
Floxyfral, Kali-Duphar ,Switz. ,1983
The Uses of Fluvoxamine
A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used as an anti-depressant
The Uses of Fluvoxamine
A selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) used as an anti-depressant.
Background
Fluvoxamine is an antidepressant which functions pharmacologically as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Though it is in the same class as other SSRI drugs, it is most often used to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder. Fluvoxamine has been in use in clinical practice since 1983 and has a clinical trial database comprised of approximately 35,000 patients. It was launched in the US in December 1994 and in Japan in June 1999. As of the end of 1995, more than 10 million patients worldwide have been treated with fluvoxamine.
What are the applications of Application
Fluvoxamine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Indications
Indicated predominantly for the management of depression and for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) . Has also been used in the management of bulimia nervosa .
Definition
ChEBI: Fluvoxamine is an oxime O-ether that is benzene substituted by a (1E)-N-(2-aminoethoxy)-5-methoxypentanimidoyl group at position 1 and a trifluoromethyl group at position 4. It is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor that is used for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. It has a role as an antidepressant, a serotonin uptake inhibitor and an anxiolytic drug. It is a 5-methoxyvalerophenone O-(2-aminoethyl)oxime and a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes. It is functionally related to a (trifluoromethyl)benzene.
Manufacturing Process
20.4 mmol (5.3 g) of 5-methoxy-4'-trifluoromethylvalerophenone (MP 43°C to 44°C), 20.5 mmol (3.1 g) of 2-aminooxyethylamine dihydrochloride and 10 ml of pyridine were refluxed for 15 hr in 20 ml of absolute ethanol. After evaporating the pyridine and the ethanol in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in water. This solution was washed with petroleum ether and 10 ml of 50% sodium hydroxide solution were then added. Then three extractions with 40 ml of ether were carried out. The ether extract was washed successively with 20 ml of 5% sodium bicarbonate solution and 20 ml of water. After drying on sodium sulfate, the ether layer was evaporated in vacuo. Toluene was then evaporated another three times (to remove the pyridine) and the oil thus obtained was dissolved in 15 ml of absolute ethanol. An equimolar quantity of maleic acid was added to the solution and the solution was then heated until a clear solution was obtained. The ethanol was then removed in vacuo and the residue was crystallized from 10 ml of acetonitrile at +5°C. After sucking off and washing with cold acetonitrile, it was dried in air. The MP of the resulting compound was 120°C to 121.5°C.
brand name
Luvox (Solvay Pharmaceuticals);Faverin.
Therapeutic Function
Antidepressant
General Description
The E-isomer of fluvoxamine (Luvox) can fold after protonation to the β-arylamine–like grouping. Here,the “extra” hydrophobic group is aliphatic.
Hazard
A poison.
Biological Activity
fluvoxamineis is an antidepressant which pharmacologically functions as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. serotonin, also known as 5-ht, is amonoamine neurotransmitter with various physiological functions such as mood, appetite, and sleep[1].
Mechanism of action
Fluvoxamine is a highly selective inhibitor of 5-HT reuptake at the presynaptic membrane. Potency data from in vitro affinity studies suggest that fluvoxamine is less potent than the other SSRIs (e.g., paroxetine, sertraline, and citalopram). Its mechanism of action is similar to that of the other SSRIs. Fluvoxamine appears to have little or no effect on the reuptake of NE or dopamine. In vitro studies have demonstrated that fluvoxamine possesses virtually no affinity for other neuroreceptors. Its onset of action is similar to the other SSRIs (2–4 weeks).
Pharmacokinetics
Fluvoxamine, an aralkylketone-derivative agent , is one of a class of antidepressants known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that differs structurally from other SSRIs . It is used to treat the depression associated with mood disorders. It is also used on occassion in the treatment of body dysmorphic disorder and anxiety . The antidepressant, antiobsessive-compulsive, and antibulimic actions of Fluvoxamine are presumed to be linked to its inhibition of CNS neuronal uptake of serotonin . In vitro studies show that Fluvoxamine is a potent and selective inhibitor of neuronal serotonin reuptake and has only very weak effects on norepinephrine and dopamine neuronal reuptake . Moreover, apart from binding to σ1 receptors , fluvoxamine has no significant affinity for adrenergic (alpha1, alpha2, beta), cholinergic, GABA, dopaminergic, histaminergic, serotonergic (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT2), or benzodiazepine receptors; antagonism of such receptors has been hypothesized to be associated with various anticholinergic, sedative, and cardiovascular effects for other psychotropic drugs . Furthermore, some studies have demonstrated that the chronic administration of Fluvoxamine was found to downregulate brain norepinephrine receptors (as has been observed with other drugs effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder), while others suggest the opposite .
Pharmacokinetics
Fluvoxamine is well absorbed, with a bioavailability of approximately 50%, probably because of first-pass metabolism. At steady-state doses, fluvoxamine demonstrates nonlinear pharmacokinetics over a dosage range of 100 to 300 mg/day, which results in higher plasma concentrations at higher doses than would be predicted by lower-dose kinetics (single dose, 15 hours; multiple dosing, 22 hours). Food does not significantly affect oral bioavailability. The mean apparent volume of distribution for fluvoxamine reflects its lipophilic nature, extensive tissue distribution, and protein binding. Fluvoxamine is distributed into breast milk. Fluvoxamine is preferentially metabolized by CYP2D6 in the liver by O-demethylation to its alcohol metabolite, which subsequently is oxidized to a carboxylic acid. Oxidative deamination and nine other metabolites have been identified, none of which shows significant pharmacological activity.
Clinical Use
Fluvoxamine is approved for use in obsessive-compulsive disorders.
Side Effects
The adverse effects for fluvoxamine include symptoms of drowsiness, nausea or vomiting, abdominal pain, tremors, sinus bradycardia, and mild anticholinergic symptoms. Toxic doses could produce seizures and severe bradycardia.
in vitro
fluvoxamine effectively inhibited 5-ht uptake by blood platelets and brain synaptosomes [1].fluvoxamine (10 mg/kg) increased [5-ht]ex levels in all brain areas and increased [da]ex levels in the striatum. fluvoxamine (10 mg/kg) in combination with of quetiapine (10 mg/kg) increased [da]ex and [5-ht]ex levels in all brain areas when compared with baseline. the combination produced a significant increase of [da]ex levels in the prefrontal cortex and thalamus whereas neither quetiapine nor fluvoxamine in monotherapy affected [da]ex levels [2]. fluvoxamine induced antiallodynic effects on neuropathic pain via descending 5-ht fibers and spinal 5-ht2a or 5-ht2c receptors, and the antinociception on acute mechanical pain via 5-ht3 receptors [3].
in vivo
single administration of fluvoxamine (10 and 30 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently enhanced synaptic efficacy in the hippocampo-mpfc pathway [4]. fluvoxamine (10 and 30 mg/kg, i.p.) treatment suppressed long-term potentiation (ltp) in the hippocampal ca1 field of anesthetized rats. nan-190 (0.5 mg/kg, i.p), the 5-ht(1a) receptor antagonist, completely reversed the fluvoxamine (30 mg/kg, i.p.) suppression of ltp [5].
Drug interactions
In vitro studies have shown fluvoxamine to be a potent inhibitor of CYP1A2, to inhibit CYP3A4 and CYP2C19, and to weakly inhibit CYP2D6. The bioavailability of fluvoxamine is significantly decreased in smokers compared with nonsmokers, possibly because of induction of CYP1A metabolism of fluvoxamine. Therefore, interactions with drugs that inhibit CYP1A2 also should be considered (e.g., theophylline and caffeine).
Metabolism
Fluvoxamine is metabolized extensively by the liver .
References
[1]. claassen v,davies je,hertting g,placheta p. fluvoxamine, a specific 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitor.br j pharmacol.1977 aug;60(4):505-16.
[2]. denys d1,klompmakers aa,westenberg hg. synergistic dopamine increase in the rat prefrontal cortex with the combination of quetiapine and fluvoxamine.psychopharmacology (berl).2004 nov;176(2):195-203. epub 2004 may 11.
[3]. honda m1,uchida k,tanabe m,ono h. fluvoxamine, a selectiveserotoninreuptake inhibitor, exerts its antiallodynic effects on neuropathic pain in mice via 5-ht2a/2c receptors.neuropharmacology.2006 sep;51(4):866-72. epub 2006 jul 17.
[4]. ohashi s1,matsumoto m,otani h,mori k,togashi h,ueno k,kaku a,yoshioka m. changes in synaptic plasticity in the rat hippocampo-medial prefrontal cortex pathway induced by repeated treatments with fluvoxamine.brain res.2002 sep 13;949(1-2):131-8.
[5]. kojima t1,matsumoto m,togashi h,tachibana k,kemmotsu o,yoshioka m. fluvoxamine suppresses the long-term potentiation in the hippocampal ca1 field of anesthetized rats: an effect mediated via 5-ht1a receptors.brain res.2003 jan 3;959(1):165-8.
Properties of Fluvoxamine
| Melting point: | 120-122.5°C |
| Boiling point: | 370.6±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.16±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Oil |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| pka | pKa 8.7 (Uncertain) |
| color | Colourless |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 54739-18-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Fluvoxamine(54739-18-3) |
Safety information for Fluvoxamine
Computed Descriptors for Fluvoxamine
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Fluvoxamine 98% (HPLC) CAS 54739-18-3View Details
Fluvoxamine 98% (HPLC) CAS 54739-18-3View Details
54739-18-3 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1