Flusilazole
- CAS NO.:85509-19-9
- Empirical Formula: C16H15F2N3Si
- Molecular Weight: 315.4
- MDL number: MFCD01076615
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
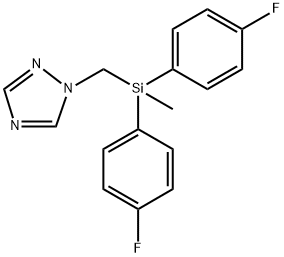
What is Flusilazole?
Chemical properties
Brown-red viscous liquid
The Uses of Flusilazole
Flusilazole is a silicon-containing triazole fungicide. Flusilazole is used to control fungal infections on a variety of fruit and vegetable crops
The Uses of Flusilazole
Agricultural fungicide.
The Uses of Flusilazole
Flusilazole is a broad spectrum fungicide used to control fungal disease caused by pathogens of the Ascomycetes, Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes families. Flusilazole exhibits curative and preventative activities and is recommended for use in agriculture, horticulture and viticulture. Diseases controlled include eyespot, mildew, and rusts of cereals, cercospora and rust of sugar beets, leaf spots of oilseed rape, scab and mildew of pome and stone fruits, mildew and black rot of grapes and Sigatoka disease of bananas.
Definition
ChEBI: Flusilazole is an organosilicon compound that is dimethylsilane in which the hydrogens attached to the silicon are replaced by p-fluorophenyl groups and a hydrogen attached to one of the methyl groups is replaced by a 1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl group. It is a broad-sepctrum fungicide used to protect a variety of crops. It has a role as a xenobiotic, an environmental contaminant, an EC 1.14.13.70 (sterol 14alpha-demethylase) inhibitor and an antifungal agrochemical. It is a member of monofluorobenzenes, a member of triazoles, an organosilicon compound, a conazole fungicide and a triazole fungicide.
Metabolic pathway
Flusilazole is stable to aqueous hydrolytic and photolytic degradation. Although flusilazole is relatively stable in soil and is detected in plant and animal samples, numerous degradation products have been reported. The primary metabolic pathway involves the cleavage of the methylenesilicon or/and methylene-triazole linkage. Another primary pathway involves aryl hydroxylation followed by conjugation. The primary metabolic/degradation pathways of flusilazole in soil, plant and animals are presented in Scheme 1.
Degradation
Aqueous hydrolysis and photolysis are not sigruficant degradation pathways for flusilazole (1). Flusilazole was stable (<5% decomposition) in sterile buffers at pH 5, 7 and 9 (25 °C) for 34 days (Cadwgan, 1983). No significant degradation was observed when fusilazole was irradiated with simulated sunlight for 30 days at 300-450 nm in sterile buffer solution at pH 7 (Carter, 1986).
Properties of Flusilazole
| Melting point: | 55° |
| Boiling point: | 393 °C [760mmHg] |
| Density | 1.17 |
| vapor pressure | 3.9 x l0-8 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.563 |
| Flash point: | 192°C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (317.07 mM; Need ultrasonic) |
| pka | 2.5 at 25℃ |
| form | Solid |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 900 mg l-1 (pH 1.1), 50 mg l-1 (pH 5.7),
45 mg l-1 (pH 7.8) at 25 °C |
| color | White to off-white |
| Merck | 13,4232 |
| BRN | 5824097 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 85509-19-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Flusilazole (85509-19-9) |
Safety information for Flusilazole
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H351:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Flusilazole
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Flusilazole CAS 85509-19-9View Details
Flusilazole CAS 85509-19-9View Details
85509-19-9 -
 Monoclonal Anti-MTDH antibody produced in mouse CASView Details
Monoclonal Anti-MTDH antibody produced in mouse CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1