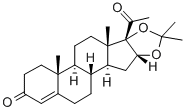
Flurandrenolide
Synonym(s):6α-Fluoro-11β,16α,17,21-tetrahydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione 16,17-acetonide;Fludroxycortide
- CAS NO.:1524-88-5
- Empirical Formula: C24H33FO6
- Molecular Weight: 436.51
- MDL number: MFCD00079290
- EINECS: 216-196-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
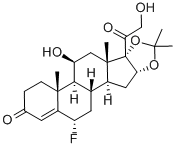
What is Flurandrenolide?
Absorption
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to those of systemically administered corticosteroids
Toxicity
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary- adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients
Originator
Haelan ,Lilly ,UK ,1962
The Uses of Flurandrenolide
Flurandrenolide (Cordran, Cordran SP) is a synthetic fluorinated corticosteroid.
The Uses of Flurandrenolide
antiinflammatory; Glucocorticoid; antipsoriatic.
Indications
For relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses, particularly dry, scaling localized lesions
What are the applications of Application
Flurandrenolide is a glucocorticoid
Background
A corticosteroid used topically in the treatment of various skin disorders. It is usually employed as a cream or an ointment, and is also used as a polyethylene tape with an adhesive. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p733)
Indications
Flurandrenolide (Cordran, Cordran SP) is a synthetic fluorinated corticosteroid.
Definition
ChEBI: Flurandrenolide is a 21-hydroxy steroid.
brand name
Cordran (Oclassen); Cordran (Watson).
Therapeutic Function
Glucocorticoid, Antiinflammatory
Biological Functions
Corticosteroids influence all tissues of the body and produce numerous and varying effects in cells. These steroids regulate carbohydrate, lipid, and protein biosynthesis and metabolism (glucocorticoid effects), and they influence water and electrolyte balance (mineralocorticoid effects). Cortisol is the most potent glucocorticoid secreted by the adrenal gland, and aldosterone is the most potent endogenous mineralocorticoid. Both naturally occurring glucocorticoids and related, semisynthetic analogues can be evaluated in terms of their ability to sustain life, to stimulate an increase in blood glucose concentrations and a deposition of liver glycogen, to decrease circulating eosinophils, and to cause thymus involution in adrenalectomized animals. In addition, corticosteroids can affect immune system functions, inflammatory responses, and cell growth. The primary physiologic function of glucocorticoids is to maintain blood glucose levels and, thus, ensure glucose-dependent processes critical to life, particularly brain functions. Cortisol and related steroids accomplish this by stimulating the formation of glucose, by diminishing glucose use by peripheral tissues, and by promoting glycogen synthesis in the liver to increase carbohydrate stores for later release of glucose.
General Description
Flurandrenolide, 6α-fluoro-11β,21-dihydroxy-16α,17-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(oxy)]pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, although available as a tape product,can stick to and remove damaged skin, so it should beavoided with vesicular or weeping dermatoses.
Mechanism of action
Glucocorticoid action is mediated through the glucocorticoid receptor, which is found primarily in the cytosol of the cell when not bound to glucocorticoids. The GR is stabilized in the cytosol by complexation with phosphorylated proteins, including a 90-kDa protein referred to as a heat shock protein 90. The steroid molecule binds to the GR, resulting in a conformational change of the receptor to dissociate the other proteins and initiate translocation of the steroid–receptor complex into the nucleus. The steroid–nuclear GR complex interacts with particular HRE regions of the cellular DNA, referred to as glucocorticoid-responsive elements and initiates transcription of the DNA sequence to produce mRNA. Finally, the elevated levels of mRNA lead to increased protein synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum. These proteins then mediate glucocorticoid effects on carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. An alternative isoform of the GR has been identified. This isoform of the receptor does not bind known glucocorticoids, and its function remains to be determined.
Pharmacokinetics
Flurandrenolide is primarily effective because of its anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive actions.
Clinical Use
Two major uses of glucocorticoids are in the treatment of rheumatoid diseases and allergic manifestations. Their use in the treatment of severe asthma is well documented, as is the utility of glucocorticoids in sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. They are effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, acute rheumatic fever, bursitis, spontaneous hypoglycemia in children, gout, rheumatoid carditis, sprue, allergy (including contact dermatitis), and other conditions. The treatment of chronic rheumatic diseases and allergic conditions with glucocorticoids is symptomatic and continuous. Symptoms return after withdrawal of the drug.
Side Effects
Although side effects and toxicities vary with the drug and, sometimes, with the patient, facial mooning, flushing, sweating, acne, thinning of the scalp hair, abdominal distention, and weight gain are observed with most glucocorticoids. Protein depletion (with osteoporosis and spontaneous fractures), myopathy (with weakness of muscles of the thighs, pelvis, and lower back), and aseptic necrosis of the hip and humerus are other side effects.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic
Properties of Flurandrenolide
| Melting point: | 247-255° |
| Boiling point: | 578.7±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D +140-150° (CHCl3) |
| Density | 1.0796 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5980 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.87±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 295mg/L(25 ºC) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fluradrenolide (1524-88-5) |
Safety information for Flurandrenolide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Flurandrenolide
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Flurandrenolide CAS 1524-88-5View Details
Flurandrenolide CAS 1524-88-5View Details
1524-88-5 -
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5