Fludrocortisone
- CAS NO.:127-31-1
- Empirical Formula: C21H29FO5
- Molecular Weight: 380.45
- MDL number: MFCD00083333
- EINECS: 204-833-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 08:49:36
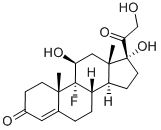
What is Fludrocortisone?
Absorption
Absorption of fludrocortisone following oral administration is rapid and complete. Pharmacokinetic studies have estimated the Cmax to be 0.0012 to 0.20 μg/L with a Tmax between 0.5 and 2 hours. The AUC0-∞ of fludrocortisone after oral administration has been variably estimated to be between 1.22 to 3.07 μg.h/L.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of fludrocortisone in rats is >1g/kg. Acute overdosage of fludrocortisone is likely to result in symptoms consistent with its adverse effect profile. Patients receiving a single large dose should be treated with plenty of water by mouth and should undergo monitoring of serum electrolytes, particularly potassium and sodium, and be treated appropriately for any developing imbalances.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Alflorone Acetate,MSD,US,1954
The Uses of Fludrocortisone
A mineralocorticoid
The Uses of Fludrocortisone
A mineralocorticoid.
Indications
Fludrocortisone is indicated as partial replacement therapy for primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency in Addison's disease. It is also indicated for the treatment of salt-losing androgenital syndrome.
What are the applications of Application
Fludrocortisone is A mineralocorticoid
What are the applications of Application
Fludrocortisone-d5 is a labeled synthetic corticosteroid
Background
Fludrocortisone is a synthetic mineralocorticoid used in conjunction with hydrocortisone to replace missing endogenous corticosteroids in patients with adrenal insufficiency. It is functionally similar to aldosterone, the body's primary endogenous mineralocorticoid, and is structurally analogous to cortisol, differing only by a fluorine atom at the 9-position of the steroid structure - this fluorination is thought to be crucial to fludrocortisone's significant mineralocorticoid potency.
Definition
ChEBI: Fludrocortisone is a C21-steroid, a 3-oxo-Delta(4) steroid, a 20-oxo steroid, a 21-hydroxy steroid, a fluorinated steroid, a mineralocorticoid, a 17alpha-hydroxy steroid and an 11beta-hydroxy steroid. It has a role as an adrenergic agent and an anti-inflammatory drug. It derives from a hydride of a pregnane.
Manufacturing Process
Hydrocortisone acetate is first reacted with phosphorus oxychloride in pyridine to give the corresponding olefin. Then a sequence consisting of hypobromous acid addition, ring closure to the epoxide and ring opening with hydrogen fluoride gives fludrocortisone acetate. Preparation of a crystalline product is described then in US Patent 2,957,013.
brand name
Florinef (King).
Therapeutic Function
9-Fluoro-11β,17,21-trihydroxy-pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione acetate
Pharmacokinetics
Fludrocortisone is a synthetic mineralocorticoid used to replace endogenous aldosterone in conditions resulting in missing or inadequate endogenous synthesis. It acts on the kidneys to increase both sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion. As its effects are exerted at the transcriptional level, a single dose of fludrocortisone may work over the course of 1-2 days despite a relatively short plasma half-life. Like other systemic corticosteroids, fludrocortisone may mask signs of infection by depressing the normal immune response - infections occurring during fludrocortisone therapy should be promptly treated with appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Clinical Use
Fludrocortisone acetate is used orally for mineralocorticoid replacement therapy in patients with adrenocortical insufficiency, such as Addison's disease. This drug, introduced in 1954, helped to provide the impetus for the synthesis and biological evaluation of newer halogenated analogues.
Synthesis
Fludrocortisone, 9|á-fluoro-11|?,17|á,21-trihydroxypregn-4-en-3,20- dione (27.2.14), is synthesized from hydrocortisone acetate (27.1.17). In the first stage of synthesis, dehydration of the hydrocortisone molecules is accomplished using phosphorous chloride in pyridine, which forms a product with a double bond at C9¨CC11 27.2.11. The resulting double bond is synthesized into an epoxide by an initial transformation to a bromohydrine using N-bromoacetamide and subsequent dehydrobromination using sodium acetate, which forms 21-O-acetoxy-9d-11|?-epoxy-17|á-hydroxy-4-pregnen-3,20-dione (27.2.12). As described above, the epoxide ring is opened by hydrofluoric acid, which results in the formation of the 21-O-acetate of fludrocortisone 27.2.13. Hydrolysis of the acetyl group of this compound using potassium acetate gives fludrocortisone (27.2.14).

Metabolism
There exists is a paucity of information regarding the specific metabolic pathway in vivo of fludrocortisone. The 9α-fluorination of fludrocortisone appears to greatly simplify its metabolism as compared to other corticosteroids - while oxidation via 11-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases has been observed, this reaction is greatly impaired as the fluorine moiety appears to confer "protection" from 11β-oxidation by these enzymes. The reduction in 11β-oxidation is thought to be one of the reasons behind fludrocortisone's profound mineralocorticoid potency. An in vitro study generated only two metabolites following incubation in human liver microsomes and cytosol, namely 20β-dihydrofluorocortisol and 6β-hydroxyfluorocortisol, and did not explore in detail the potential enzymes responsible for this reaction.
Given that fludrocortisone is a corticosteroid, a class of medications known to be metabolized by the CYP3A family, and is not recommended to be given with strong inhibitors/inducers of CYP3A, it is likely that the CYP3A family of enzymes contributes in some way to its metabolism (though this information does not appear to have been specifically elucidated for fludrocortisone).
Properties of Fludrocortisone
| Melting point: | 208-212°C |
| Boiling point: | 564.7±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D23 +139° (c = 0.55 in 95% ethanol) |
| Density | 1.1176 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Ethanol (Slightly, Heated), Methanol (Slightly, Sonicated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.11±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 111mg/L(25 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 127-31-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hydrocortisone-9.alpha.-fluoro (127-31-1) |
Safety information for Fludrocortisone
Computed Descriptors for Fludrocortisone
Fludrocortisone manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
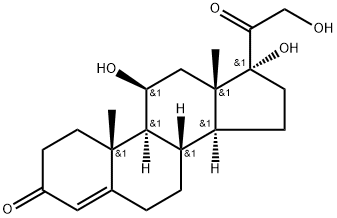
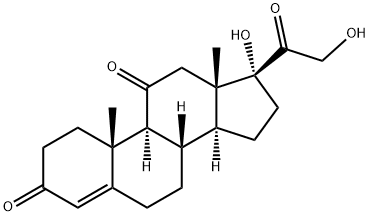

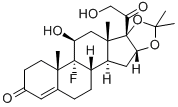
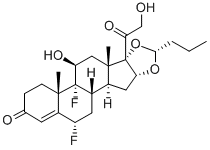
You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
