Flupentiol
- CAS NO.:2709-56-0
- Empirical Formula: C23H25F3N2OS
- Molecular Weight: 434.52
- MDL number: MFCD00242736
- EINECS: 2203049
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
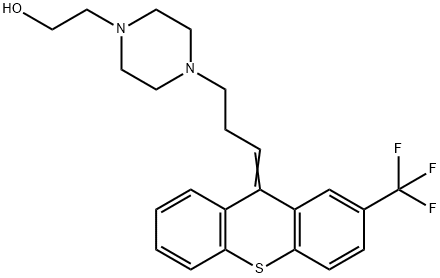
What is Flupentiol?
Absorption
Following oral administration, flupentixol is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with oral bioavailability of about 40%. Tmax ranges from three to eight hours. Steady-state plasma levels are achieved in about seven days and following once-daily oral administration of 5 mg flupentixol, the mean minimum steady-state level was about 1.7 ng/mL (3.9 nmol/L).
From the site of intramuscular injection, esterified flupentixol diffuses slowly from the oil solution and is slowly released into the extracellular fluid and the circulation to be distributed to different tissues. Peak drug concentrations are reached between four and seven days following intramuscular injection. Intramuscularly administered flupentixol is detectable in the blood three weeks after injection and reaches steady-state concentrations after about three months of repeated administration.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 is 423 mg/kg in mice and 791 mg/kg in rats. The intravenous LD50 is 37 mg/kg in rats.
Flupentixol overdose is characterized by sedation, frequently preceded by extreme agitation, excitement, confusion, somnolence, coma, convulsions, and hyperthermia or hypothermia. Extrapyramidal symptoms or respiratory and circulatory collapse may be observed. ECG changes, QT prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, cardiac arrest and ventricular arrhythmias have been reported from the combined use of drugs known to affect the heart with large doses of flupentixol. In case of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be initiated with airway management. In case of severe hypotension, epinephrine should not be used: instead, intravenous vasopressor drugs, such as levarterenol, can be used. Antiparkinsonian medication should be administered only if extrapyramidal symptoms develop. Gastric lavage should be initiated in the case of flupentixol tablet overdose. Further injections of flupentixol should be discontinued in case of an intramuscularly-administered drug overdose until the patient shows signs of relapse, in which the dosage can subsequently be decreased.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is associated with neuroleptic drugs, which should be responded to with immediate discontinuation of the drug and initiation of symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring.
Originator
Emergil ,Labaz, France,1971
Indications
Flupentixol is indicated for maintenance therapy of chronic schizophrenic patients whose main manifestations do not include excitement, agitation or hyperactivity.
It is indicated for the management of depression in adult patients who may, or may not, also be showing signs of anxiety.
Flupentixol in combination with melitracen is indicated to manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, and asthenia in adults.
Background
Flupentixol is an antipsychotic drug of the thioxanthene group. It exists in two geometric isomers, the trans(E) and pharmacologically active cis(Z) forms. Flupentixol decanoate is one of the active ingredients found in injectable drug formulations: it is produced by esterification of cis(Z)‐flupentixol with decanoic acid. Flupentixol is an antagonist of both D1 and D2 dopamine receptors.
Available as oral tablets or long-acting intramuscular injections, flupentixol is marketed under brand names such as Depixol and Fluanxol. It is approved for use in Canada and other countries around the world, but not in the US. It is used for the management of chronic schizophrenia in patients whose main manifestations do not include excitement, agitation or hyperactivity. It has been marketed to manage symptoms of depression in patients who may or may not exhibit signs of anxiety. In combination with melitracen, flupentixol is used to manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, and asthenia.
Definition
ChEBI: A thioxanthene derivative having a trifluoromethyl substituent at the 2-position and a 3-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl)propylidene group at the 10-position with undefined double bond stereochemistry.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 200 grams of 2-benzoyloxyethanol in 2 liters of pyridine at -5°C is treated with 275 grams of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride and the resulting mixture is stirred at 0°C for 2 hours. Water is added slowly at 0° to 5°C. Extracting with chloroform, washing the extract with dilute hydrochloric acid, water and potassium bicarbonate, and evaporating the solvent leaves benzyloxyethyl p-toluenesulfonate.
A mixture of 186 grams of the above prepared p-toluenesulfonate, 106 grams of N-ethoxycarbonylpiperazine, 44 grams of potassium carbonate and 800 ml of toluene is refluxed for 21 hours, then filtered and extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid. The extract is basified with sodium hydroxide and extracted into chloroform. Evaporation of the chloroform and distillation of the residue in vacuo gives 1-benzyloxyethyl-4-ethoxy-carbonylpiperazine, BP 153° to 156°C (0.15 mm).
Hydrolysis and decarboxylation of this ester (188 grams) is accomplished by refluxing with 155 grams of potassium hydroxide, 155 ml of water and 1,550 ml of ethanol for four days. Filtering, concentrating, adding water to the residue, acidifying with hydrochloric acid, heating to 90°C, saturating with potassium carbonate, extracting into chloroform, evaporating and distilling the chloroform gives N-benzoyloxyethylpiperazine.
A mixture of 50 grams of the above prepared piperazine, 30.1 grams of sodium carbonate and 200 ml of benzene is heated to reflux and treated with 39.5 grams of 3-bromopropanol over 1.5 hours. The resulting mixture is refluxed for 2 hours, then filtered, extracted with dilute hydrochloric acid, basified, extracted with benzene, and the extracts are concentrated and distilled to give l-benzyloxyethyl-4-(3-hydroxypropyl)-piperazine, BP 188° to 190°C (0.15 mm). The free base is converted to the dihydrochloride salt by treatment of an alcoholic solution with ethereal hydrogen chloride to separate the salt.
Thionyl chloride (67 grams) is added over 15 minutes to a mixture of 39.5 grams of the above prepared dihydrochloride salt and 400 ml of chloroform. Refluxing for 4 hours, cooling and filtering yields the dihydrochloride salt of lbenzyloxyethyl-4-(3-chloropropyl)-piperazine, MP 201° to 202°C. The salt in aqueous solution is basified. Extraction with ether and evaporation of the solvent yields the free base.
Magnesium (1.3 grams) in 8 ml of refluxing tetrahydrofuran is treated with 1 ml of ethyl bromide. A solution of 22.7 grams of l-benzyloxyethyl-4-(3chloropropyl)-piperazine in 50 ml of tetrahydrofuran is added slowly and the mixture is refluxed for 1 hour.
A solution of 13.2 grams of 2-trifluoromethyl-9-xanthenone in tetrahydrofuran is added over 1 hour to 16.0 grams of 3-(4-benzyloxyethyl-1-piperazinyl) propylmagnesium chloride, prepared as above, in tetrahydrofuran while gentlyrefluxing. Refluxing is continued for 2 hours. Concentrating, pouring the residue into ammonium chloride, ice and water, extracting with ether, evaporating the extracts and treating the residue with concentrated hydrochloric acid at 95°C for 1 hour gives a mixture of cis and trans 9-[3-(4hydroxyethyl-1-piperazinyl)propylidene]-2-trifluoromethylxanthene dihydrochloride. Fractional crystallization from ethanol-ether separates the isomers. The free bases are obtained by neutralizing an aqueous solution of the dihydrochloride, extracting into ether and evaporating the ether in vacuo.
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
Pharmacokinetics
Flupentixol is an antipsychotic agent with anxiolytic and mild sedative actions. It exerts weak anticholinergic and adrenergic effects. It possesses antiemetic actions. As flupentixol works by antagonizing dopamine actions, it can cause extrapyramidal effects, mostly at doses greater than 10 mg. In clinical trials, flupentixol-induced extrapyramidal effects have been managed with anti-Parkinsonian drugs. Drug esterification in the intramuscular formulation of the drug results in slow release of the drug from the injection site and a prolonged duration of action. Flupentixol has been investigated for use in mild to moderate depression: compared to other antidepressant agents, flupentixol has a rapid onset of action, where antidepressive effects were observed within the first two to three days after administration.
As with other antipsychotic agents, flupentixol can cause QTc prolongation and increase the risk of arrhythmias. In clinical trials, flupentixol was associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular adverse events, stroke, and venous thromboembolism. Flupentixol can elevate the levels of prolactin; however, the clinical significance of hyperprolactinemia caused by neuroleptic drugs is unclear. Long-term hyperprolactinemia, when associated with hypogonadism, may lead to decreased bone mineral density in both female and male subjects.
Interestingly, recent studies show that flupentixol exhibits anti-tumour properties alone or synergistically with other anticancer drugs like gefitinib. One study demonstrated that in vitro, flupentixol docks to the ATP binding pocket of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), a lipid kinase that activates signalling pathways that are often hyperactivated in some cancers. Flupentixol inhibited the PI3K/AKT pathway and survival of lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
Metabolism
Flupentixol is metabolized in the liver via sulfoxidation, dealkylation, and glucuronidation to form pharmacologically inactive metabolites. Flupentixol decanoate, the active ingredient in the intramuscular formulation, is hydrolyzed to flupentixol.
Properties of Flupentiol
| Boiling point: | 554.7±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.2118 (estimate) |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | solid |
| pka | pKa 7.80 (Uncertain) |
| color | white or off-white |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Flupentixol(2709-56-0) |
Safety information for Flupentiol
Computed Descriptors for Flupentiol
New Products
1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid Cycloleucine 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 2-Methyl-2-phenylpropyl acetate 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride Decanonitrile tert-butyl 4-(1H-benzo[d]iMidazol-2-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate 4-Ethylbenzylamine Methyl 5-bromo-2-chloro-3-nitrobenzoate N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 2-Chloro-3-nitropyridine 5-Bromo-2,3-dimethoxypyridine methyl 6-chloro-2-(chloromethyl)nicotinate 2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 2-iodo-5-bromo pyridine 2-amino-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 5-Fluoro-2-Oxindole methyl L-alaninate hydrochloride diethyl L-glutamate hydrochloride Ethyl tosylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2709-56-0 Flupenthixol 99%View Details
2709-56-0 Flupenthixol 99%View Details
2709-56-0 -
 Ethoxymethylenemalononitrile 99% HPLCView Details
Ethoxymethylenemalononitrile 99% HPLCView Details
123-06-8 -
 3-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid 602-00-6 98%View Details
3-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid 602-00-6 98%View Details
602-00-6 -
 Diethyl Disulfide 99% HPLCView Details
Diethyl Disulfide 99% HPLCView Details
110-81-6 -
 6285-05-8. 1-(4-chlorophenyl) propan-1-one 98%View Details
6285-05-8. 1-(4-chlorophenyl) propan-1-one 98%View Details
6285-05-8. -
 4-chloro-3,5-dinitropyridine 98%View Details
4-chloro-3,5-dinitropyridine 98%View Details -
 401-95-6 99% HPLCView Details
401-95-6 99% HPLCView Details
401-95-6 -
 171663-13-1 tert-Butyl 3-bromobenzylcarbamate 98%View Details
171663-13-1 tert-Butyl 3-bromobenzylcarbamate 98%View Details
171663-13-1