Fluoroboric acid
- CAS NO.:16872-11-0
- Empirical Formula: BF3.FH
- Molecular Weight: 87.81
- MDL number: MFCD00011345
- EINECS: 240-898-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
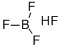
What is Fluoroboric acid?
Description
Fluoboric acid is a colorless liquid which doesnot exist as a free, pure substance. Used as an aqueous solution. Molecular weight=87.82; Boiling point=130C(decomposes). Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704M Rating System): Health 3, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0.Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Fluoboric acid is a colourless liquid, completely solvable in water. Fluoboric acid is a stable chemical substance and extremely reactive or incompatible with strong bases, cyanides. It is very corrosive in the presence of steel, aluminium, zinc, and copper and highly corrosive in the presence of glass and stainless steel.
Chemical properties
Fluoboric acid is a colorless liquid which does not exist as a free, pure substance. Used as an aqueous solution.
The Uses of Fluoroboric acid
Tetrafluoroboric acid is used in conjunction with various methods of cleaning and treat the surface of substrates. It is used as radiotracers.
The Uses of Fluoroboric acid
As catalyst for preparing acetals, esterifying cellulose; to clean metal surfaces before welding; to brighten aluminum; as a solute in electrolytes for plating metals such as chromium, iron, nickel, copper, silver, zinc, cadmium, indium, tin, and lead (has a high throwing power). Reagent for sodium in the presence of magnesium and potassium ions; for making stabilized diazo salts (diazonium and tetrazonium fluoborates). An 0.1 to 0.5% solution retards fermentation: Homeyer, Pharm. Ztg. 34, 761 (1889).
What are the applications of Application
Tetrafluoroboric acid solution is a precursor to Tetrafluoroborate salts
Definition
ChEBI: Tetrafluoroboric acid is a boron fluoride. It is a conjugate acid of a tetrafluoroborate(1-).
General Description
A colorless odorless poisonous liquid. Boiling point 130°C. Corrosive to metals and tissue. Fluoroboric acid is used in electroplating, metal cleaning and making diazo salts.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water with release of heat.
Reactivity Profile
Fluoroboric acid is a strong acid. Reacts exothermically with chemical bases (examples: amines, amides, and inorganic hydroxides). These reactions can generate dangerously large amounts of heat in small spaces. Dissolution in water or the dilution of a concentrated aqueous solution may generate significant heat. Reacts with active metals, including such structural metals as aluminum and iron, to release hydrogen, a flammable gas. Can initiate the polymerization of certain alkenes. Reacts with cyanide compounds to release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Generates flammable and/or toxic gases in contact with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides, and strong reducing agents. Additional gas-generating reactions occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and carbonates. May catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions. Attempted drying of the acid with acetic anhydride caused an explosion at 0°C [J. Organomet. Chem., 1975, 94, 319].
Hazard
Highly toxic, corrosive, irritant.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
A corrosive acid. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of B and F-.
Potential Exposure
Used as a catalyst for acetal synthesis and cellulose esters; a metal surface cleaning agent; an alu minum electrolytic finishing agent; a stripping solution for the removal of solder and plated metals; and an intermedi ate in making fluoroborate salt.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water ormilk. Do not induce vomiting. Medical observation isrecommended for 24-48 h after breathing overexposure, aspulmonary edema may be delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or authorized paramedic may consideradministering a corticosteroid spray.
storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or Contact Hazard;Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location. Prior toworking with this chemical you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from chemicallyactive metals and strong bases. Where possible, automatically pump liquid from drums or other storage containers toprocess containers.
Shipping
UN1775 Fluoroboric acid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Crystallise fluoroboric acid several times from conductivity water. It can be stored in a glass vessel at room temperature. [Kwasnik in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I pp 221-222 1963.]
Incompatibilities
A strong acid. Reacts violently with chemically active metals; strong bases, releasing flammable hydrogen gas.
Properties of Fluoroboric acid
| Melting point: | -90°C |
| Boiling point: | 130°C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.38 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 5 mmHg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | nD20 of a 20% aq soln 1.3284 |
| Flash point: | −40 °F |
| solubility | very soluble in H2O, ethanol |
| pka | -4.9[at 20 ℃] |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Light Yellow |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | MISCIBLE |
| Merck | 14,4149 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 250 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, cyanides. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 16872-11-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fluoroboric acid (16872-11-0) |
Safety information for Fluoroboric acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for Fluoroboric acid
Fluoroboric acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
S B Chemicals
Madras Fluorine Private Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


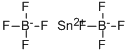
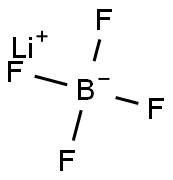
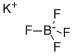
You may like
-
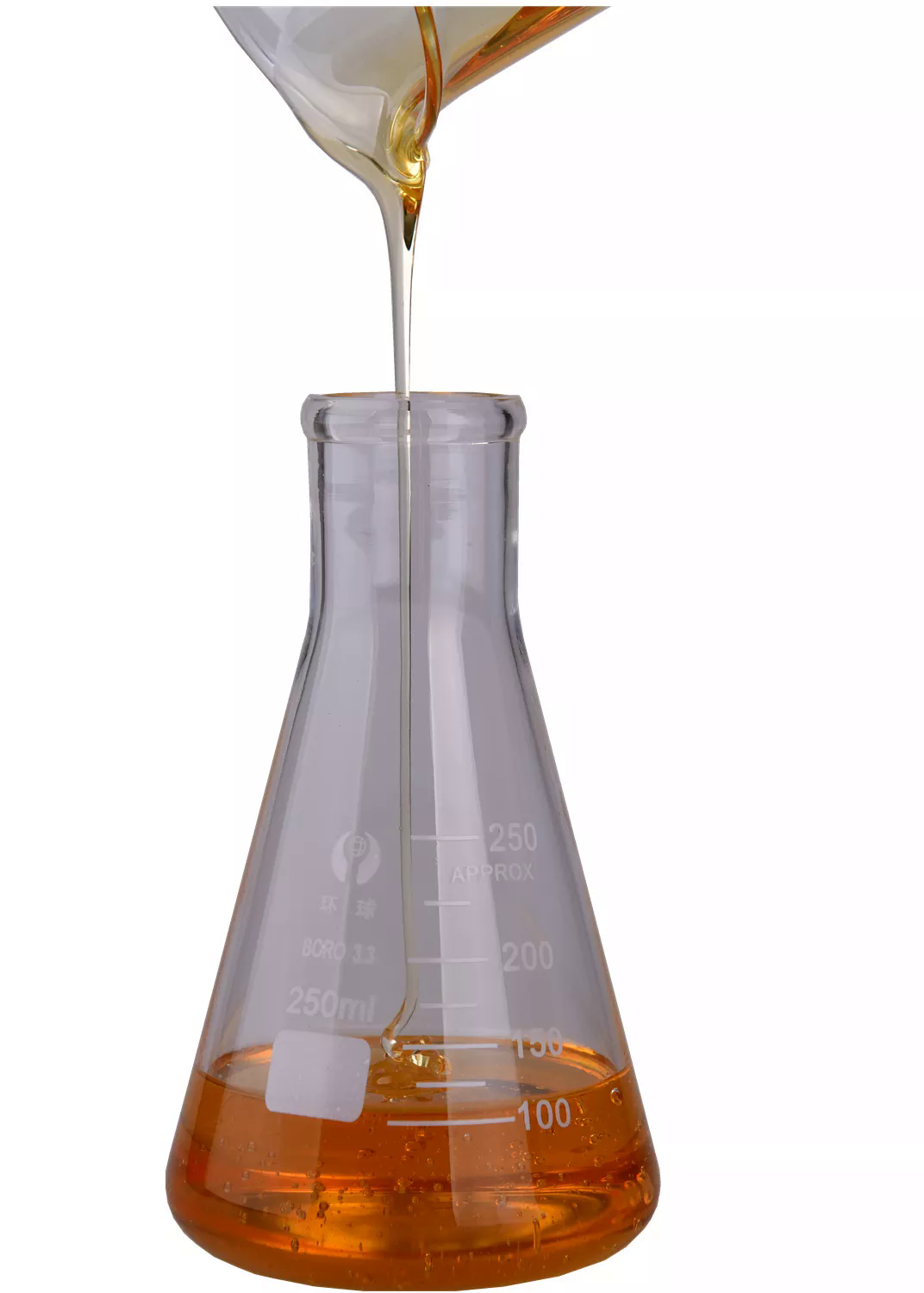 Fluoroboric acid 98%View Details
Fluoroboric acid 98%View Details -
 Tetrafluoroboric Acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
Tetrafluoroboric Acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
16872-11-0 -
 Tetrafluoroboric Acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
Tetrafluoroboric Acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
16872-11-0 -
 Fluoboric Acid CASView Details
Fluoboric Acid CASView Details -
 Fluoroboric acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
Fluoroboric acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
16872-11-0 -
 Fluoboric acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
Fluoboric acid CAS 16872-11-0View Details
16872-11-0 -
 Borofluoric Acid CASView Details
Borofluoric Acid CASView Details -
 FLUOROBORIC ACID For Synthesis CAS 16872-11-0View Details
FLUOROBORIC ACID For Synthesis CAS 16872-11-0View Details
16872-11-0