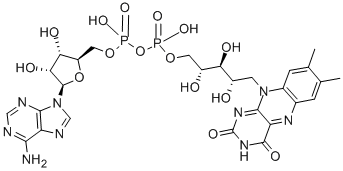
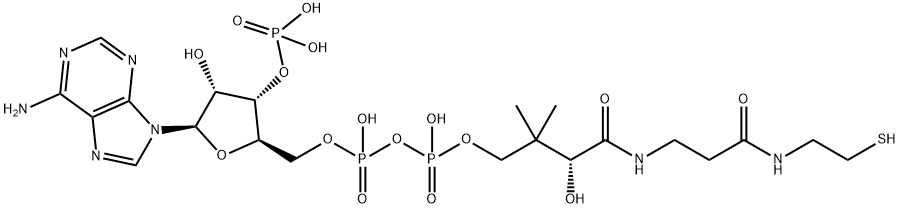
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
- CAS NO.:146-14-5
- Empirical Formula: C27H33N9O15P2
- Molecular Weight: 785.55
- MDL number: MFCD00041835
- EINECS: 205-663-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18
What is Flavin adenine dinucleotide?
Toxicity
Oral mouse LD50 > 7000 mg/kg. Intravenous mouse LD50 589 mg/kg.
Description
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a cofactor for cytochrome-b5 reductase, the enzyme that maintains hemoglobin in its functional reduced state, and for glutathione reductase. This enzyme also protects erythrocytes from oxidative damage. FAD is a redox cofactor of several essential reactions in metabolism. This cofactor exists in two redox states, with FAD and FADH2 being the oxidized and reduced forms, respectively. FAD is formed of a riboflavin moiety (vitamin B2) coupled to a phosphate group of an ADP molecule. The reaction starts with the conversion of riboflavin into flavin mononucleotide catalyzed by riboflavin kinase. Flavin mononucleotide is subsequently transformed into FAD by adding an AMP moiety from ATP catalyzed by FAD-synthase. Therefore, FAD availability is tightly dependent on vitamin B2 and energy metabolism[1].
References
[1] Schnekenburger, M. and M. Diederich. “Nutritional Epigenetic Regulators in the Field of Cancer: New Avenues for Chemopreventive Approaches.”Epigenetic Cancer Therapy (2015): 393-425.
Chemical properties
solid
The Uses of Flavin adenine dinucleotide
The prosthetic group of certain flavoproteins including D-amino acid oxidase, glucose oxidase, glycine oxidase, fumaric hydrogenase, histaminase, and xanthine oxidase. Riboflavin kinase tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 NADPH oxidase
The Uses of Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Labelled Flavine Adenine xidase. Riboflavin kinase tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 NADPH oxidase
The Uses of Flavin adenine dinucleotide
The prosthetic group of certain flavoproteins including D-amino acid oxidase, glucose oxidase, glycine oxidase, fumaric hydrogenase, histaminase, and xanthine oxidase. Riboflavin kinase tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 NADPH oxidase.
Background
A condensation product of riboflavin and adenosine diphosphate. The coenzyme of various aerobic dehydrogenases, e.g., D-amino acid oxidase and L-amino acid oxidase. (Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry, 1982, p972) Flavin adenine dinucleotide is approved for use in Japan under the trade name Adeflavin as an ophthalmic treatment for vitamin B2 deficiency.
Indications
Used to treat eye diseases caused by vitamin B2 deficiency, such as keratitis and blepharitis.
Definition
An adenine nucleotide containing two phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety at the 5′-position.
Metabolism
Not Available
Purification Methods
Small quantities of FAD are purified by paper chromatography using tert-butyl alcohol/water, cutting out the main spot and eluting with water. Larger amounts can be precipitated from water as the uranyl complex by adding a slight excess of uranyl acetate to a solution at pH 6.0, dropwise and with gentle stirring. The solution is set aside overnight in the cold, and the precipitate is centrifuged off, washed with small portions of cold EtOH, then with cold peroxide-free diethyl ether. It is dried in the dark under vacuum over P2O5 at 50-60o. The uranyl complex is suspended in water, and, after adding sufficient 0.01M NaOH to adjust the pH to 7, the precipitate of uranyl hydroxide is removed by centrifugation [Huennekens & Felton Methods Enzymol 3 954 1957]. It can also be crystallised from water. It should be kept in the dark. More recently it was purified by elution from a DEAE-cellulose (Whatman DE 23) column with 0.1M phosphate buffer pH 7, and the purity was checked by TLC. [Holt & Cotton, J Am Chem Soc 109 1841 1987, Beilstein 26 III/IV 3632.]
Properties of Flavin adenine dinucleotide
| Density | 2.08±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly, Heated), Water (Slightly) |
| form | powder |
| pka | 1.13±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | orange |
| Merck | 4091 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 146-14-5 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Riboflavin 5'-(trihydrogen diphosphate), P'.fwdarw.5'-ester with adenosine (146-14-5) |
Safety information for Flavin adenine dinucleotide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Flavin adenine dinucleotide
| InChIKey | VWWQXMAJTJZDQX-ZGGJIJKNNA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide Sodium Salt (FAD) extrapure CAS 146-14-5View Details
Flavine Adenine Dinucleotide Sodium Salt (FAD) extrapure CAS 146-14-5View Details
146-14-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
