Glutathione
Synonym(s):GSH;Glutathione (reduced);Glutathione, Reduced, Free Acid - CAS 70-18-8 - Calbiochem;γ-L -Glutamyl-L -cysteinyl-glycine;γ-Glu-Cys-Gly, GSH
- CAS NO.:70-18-8
- Empirical Formula: C10H17N3O6S
- Molecular Weight: 307.32
- MDL number: MFCD00065939
- EINECS: 200-725-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 18:10:20
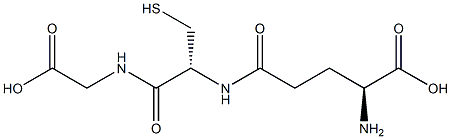
What is Glutathione?
Absorption
Research suggests that glutathione is not orally bioactive, and that very little of oral glutathione tablets or capsules is actually absorbed by the body.
Toxicity
ORL-MUS LD50 5000 mg/kg, IPR-MUS LD50 4020 mg/kg, SCU-MUS LD50 5000 mg/kg, IVN-RBT LD50 > 2000 mg/kg, IMS-MUS LD50 4000 mg/kg
Description
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide (γ-
Description
Glutathione is a tripeptide that consists of the amino acids glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine. This natural antioxidant exists in every cell of most organisms, including all animals and plants. Its reducing power comes from the thiol group in the cysteine linkage.
In 1929, Frederick Gowland Hopkins at the University of Cambridge (UK) isolated glutathione from yeast. He noted that its concentration in yeast is 0.1 wt% or greater and that the substance is also present in red blood corpuscles. The same year, Hopkins and Dutch physician Christiaan Eijkman were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their research on the concept of vitamins*, although the only one they actually discovered was vitamin B1?(thiamine).
The first synthesis of glutathione is credited to chemist Vincent du Vigneaud of Cornell Medical College (New York City; now Weill Cornell Medicine) in 1952. Du Vigneaud was also a Nobel awardee; he won the chemistry prize in 1955 for his work on biologically important sulfur compounds.
This April, Dirk Brenner at the Luxembourg Institute of Health and coauthors in seven countries reported that, in addition to its function as an antioxidant, glutathione also?stimulates T cell energy metabolism. This stimulation allows T cells to generate an optimal immune response and fight off pathogens. This discovery may lead to new therapies against cancer and autoimmune diseases.
*Polish biochemist Casimir Funk made the discovery earlier than Hopkins and Eijkman, but the Nobel committee chose not to include him in the award. See the?Nobel Prize Web site?for this strange story.
Chemical properties
White cryst. powder
Originator
L-Glutathione,Solgar,USA
The Uses of Glutathione
glutathione is a peptide composed of cysteine, glycine, and glutamate. It is believed to enhance the skin’s cellular metabolism and oxygen utilization. It has been found to protect the fibroblast against free radical-induced oxidation and act as a powerful antioxidant. Studies indicate that it can inactivate the tyrosinase enzyme and quench free radicals that contribute to tyrosinase and melanin formation, thereby serving as a skin-lightening or de- pigmenting agent. glutathione is a component of plant and animal tissue, naturally occurring in the body and essential for the proper functioning of the immune system.
The Uses of Glutathione
L-Glutathione is used in the treatment of lung diseases for patients who are HIV positive. It protects the cancerous cells by conferring resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. It is involved in many aspects of metabolism including transport of g-glutanyl amino acids and reductive cleavage of disulfide bonds. As an antioxidant, it prevents damage to important cellular components that arise due to reactive oxygen species like free radicals and peroxide. It is also used to decrease the concentrations of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-18) as well as involved in increasing the level of serum Ca2+ ions. It is also used in white wine production.
Background
A tripeptide with many roles in cells. It conjugates to drugs to make them more soluble for excretion, is a cofactor for some enzymes, is involved in protein disulfide bond rearrangement and reduces peroxides.
What are the applications of Application
Glutathione, reduced is an endogenous antioxidant, representative of the cellular oxidative state
Indications
For nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance
Definition
ChEBI: A tripeptide compound consisting of glutamic acid attached via its side chain to the N-terminus of cysteinylglycine.
Manufacturing Process
The tripeptide thiol glutathione (L-γ-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine (GSH)) found
in virtually all cells functions in metabolism, transport and cellular protection.
Glutathione may be obtained from an yeast or synthetically.
A yeast containing 600 parts of yeast solids is heated just to the boiling point
of water. The yeast solids are removed by centrifuging or filtration. Sulphuric
acid is added to the filtrate to give 0.5 N strength as sulphuric acid 6 parts of
ascorbic acid are added. Then 2 parts of cuprous oxide are added with
stirring. The reaction mixture is then centrifuged and washed until the
precipitate is free from sulphates. The precipitate is suspended in 100 parts of
water and hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through the water until all of the
copper is precipitated as copper sulphide. The filtrate is evaporated and the
glutathione is purified by recrystallization from 50% ethanol. All parts are by
weight.
The preparation of glutathion by methods of peptide synthesis is expansive
and gives 20-30% yield of GHS. For the first time synthetic glutathion was
prepared by M. Bergmann et al.
Therapeutic Function
Anabolic, Antidote
Benefits
Glutathione contentin human blood is 26~34mg/100g,scavenging free radical, anti-oxidant, whiteningand spot-removing.Its recommended dosage in skin care products is 0.5~2%.
General Description
Glutathione (GSH) is the most important nonprotein thiol widely distributed in animal tissues, plants, and microorganisms. GSH is also a key determinant of redox signaling and protection against oxidative stress.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Endogenous antioxidant that plays a major role in reducing reactive oxygen species formed during cellular metabolism and the respiratory burst. Glutathione-S-transferase catalyzes the formation of glutathione thioethers with xenobiotics, leukotrienes, and other molecules that have an electrophilic center. Glutathione also forms disulfide bonds with cysteine residues in proteins. Via these mechanisms, it can have the paradoxical effect of reducing the efficacy of anti-cancer agents.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of SOx and NOx.
Metabolism
Not Available
Storage
Store at +4°C
Purification Methods
Crystallise L-glutathione from 50% aqueous EtOH, dry it in a vacuum and
Properties of Glutathione
| Melting point: | 192-195 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 754.5±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | -16.5 º (c=2, H2O) |
| Density | 1.4482 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | -17 ° (C=2, H2O) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pK1 2.12; pK2 3.53; pK3 8.66; pK4 9.12(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 3 (10g/l, H2O, 20°C) |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,4475 |
| BRN | 1729812 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 70-18-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Glutathione (70-18-8) |
Safety information for Glutathione
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Glutathione
| InChIKey | RWSXRVCMGQZWBV-WDSKDSINSA-N |
Glutathione manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Indexim International
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
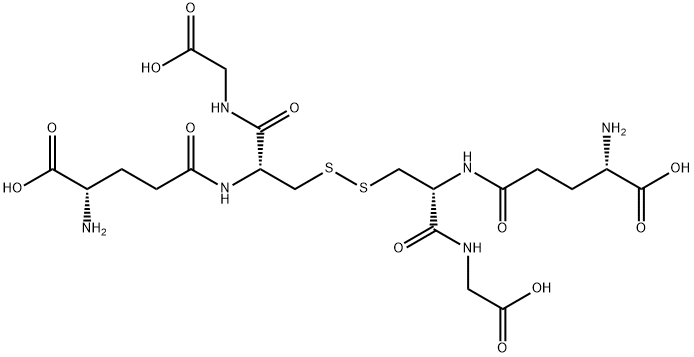
![NAD[P]H: OXIDIZED-GLUTATHIONE OXIDOREDUCTASE,NAD[P]H: OXIDIZED-GLUTATHIONE OXIDOREDUCTASE TYPE II,NAD[P]H: OXIDIZED-GLUTATHIONE OXIDOREDUCTASE TYPE VI](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)


You may like
-
 Glutathione Reduced (GSH) extrapure CAS 70-18-8View Details
Glutathione Reduced (GSH) extrapure CAS 70-18-8View Details
70-18-8 -
 L-Glutathione, Reduced CAS 70-18-8View Details
L-Glutathione, Reduced CAS 70-18-8View Details
70-18-8 -
 L-Glutathione Reduced (CAS Number: 70-18-8)View Details
L-Glutathione Reduced (CAS Number: 70-18-8)View Details
70-18-8 -
 Powder L Glutathione Reduced, Cosmetic GradeView Details
Powder L Glutathione Reduced, Cosmetic GradeView Details
70-18-8 -
 L Glutathione Reduced, 10 Kg Bag For Fairness Cream ManufacturingView Details
L Glutathione Reduced, 10 Kg Bag For Fairness Cream ManufacturingView Details
70-18-8 -
 Reduced Glutathione GSH, For Fairness cream manufacturing, 10 kg BagView Details
Reduced Glutathione GSH, For Fairness cream manufacturing, 10 kg BagView Details
70-18-8 -
 L Glutathione ReducedView Details
L Glutathione ReducedView Details
70-18-8 -
 GLUTATHIONE (Reduced) 99%View Details
GLUTATHIONE (Reduced) 99%View Details
70-18-8
