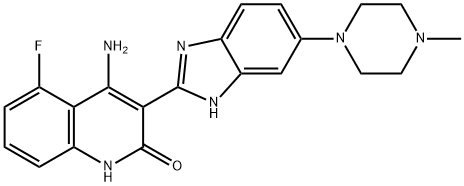
Filgotinib
- CAS NO.:1206161-97-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H23N5O3S
- Molecular Weight: 425.5
- MDL number: MFCD20527867
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
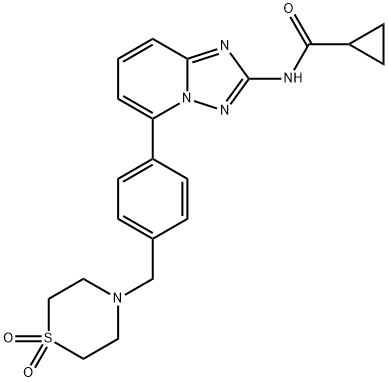
What is Filgotinib?
Absorption
Filgotinib is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Median peak plasma concentrations occurred 2-3 hours post-dose for filgotinib and 5 hours post-dose for GS-829845. Steady-state concentrations can be observed in 2-3 days for filgotinib and in 4 days for GS-829845. Food does not appear to have a significant effect on the absorption of filgotinib; therefore, the medication can be administered without regard to food.
After repeated oral dosing of filgotinib 200 mg, the reported Cmax and AUCτ values of filgotinib were 2.15 ug/mL and 6.77 ugxh/mL, respectively. For GS-829845 (the major metabolite) the reported Cmax was 4.43 ug/mL and the reported AUCτ was 83.2 ugxh/mL.
Toxicity
Toxicity information regarding filgotinib is not readily available; however, it has been administered in clinical trials at doses of up to 450 mg daily. Associated adverse effects were similar to those observed at lower doses. In the event of overdose, the patient should be closely monitored and supportive measures should be initiated as required.
Description
Filgotinib is a JAK1 inhibitor (IC50 = 10 nM). It is selective for JAK1 over JAK3 (IC50 = 810 nM) but also inhibits JAK2 and tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2; IC50s = 28 and 116 nM, respectively), as well as Abl, FLT1, -3, and -4, FMS, Mer, and TBK1 activity by greater than 35% in a panel of 177 tyrosine kinases at 1 μM. Filgotinib inhibits IL-6-induced phosphorylation of STAT1 in CD4+ T cells with an IC50 value of 629 nM in isolated human whole blood. It reduces hind paw macrophage and T cell infiltration and bone erosion in a rat model of collagen-induced arthritis when administered at doses ranging from 0.1 to 30 mg/kg per day for 15 days.
Characteristics
Class: non-receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis
Elimination half-life = 6–11 h
Protein binding = 32%
The Uses of Filgotinib
GLPG-0634 (Filgotinib) is a potent, selective JAK1 inhibitor. Used as an anti-inflammatory agent, it reduces levels of inflammatory cytokines in the bones and tissue of mammals.
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, autoimmune, systemic, and inflammatory disease that causes synovial joint symptoms and can limit range of motion in severe cases. The disease is associated with extra-articular manifestations, progressive disability, and comorbidities including cardiovascular disease and mental disorders. 50-70% of patients with RA are unable to achieve sustained clinical remission despite the availability of several treatments including disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS) like methotrexate, interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockers, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors. New therapeutic developments target other inflammatory pathways implicated in RA including the Janus kinase (JAK) signaling pathway as seen with filgotinib.
There are four JAK subtypes which include JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2. Non-selective JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib target JAK1 and JAK3 subtypes with minimal activity at JAK2. In contrast, the newly approved filgotinib is a highly selective JAK1 inhibitor. JAK2 and JAK3 play important roles in both immune and hematologic functions; therefore, selectivity for JAK1 aims to improve the safety profile of filgotinib while maintaining clinical efficacy. Filgotinib is currently reserved for patients who cannot tolerate DMARDs, or who have been unable to achieve remission in response to one or more DMARDs.
Indications
Filgotinib is indicated for the treatment of active moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis alone or in combination with methotrexate. Filgotinib is currently reserved for patients who are unable to tolerate or who have not responded adequately to one or more disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS).
Filgotinib is also indicated for treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adult patients who had an inadequate response with, lost response to, or were intolerant to either conventional therapy or a biologic agent.
Mechanism of action
Filgotinib acts on the JAK-STAT pathway by selectively inhibiting JAK1 phosphorylation and preventing STAT activation, which ultimately results in reduced proinflammatory cytokine signaling.
Pharmacokinetics
In addition to targeted Janus kinase (JAK) 1 inhibition, filgotinib targets pro-inflammatory cytokine signalling by inhibiting IL-6 induced STAT1 phosphorylation. Serum C-reactive protein levels are also reduced in response to filgotinib administration.
Side Effects
- feeling sick (nausea)
- upper respiratory tract infection
- urinary tract infection.
- dizziness.
Synthesis
The synthesis of Filgotinib is as follows:
With cyclopropanyl chloride in an amidated reaction in a system consisting of N-methylmorpholine and 1,4-dioxane,The amidation reaction time was 4 h,The amidation reaction temperature was 50 ° C,The molar ratio of the intermediate (III), cyclopropanyl chloride, N-methylmorpholine and 1,4-dioxane was 1: 2.8: 2.5:TLC plate to determine the reaction is completed, cooled to room temperature,Adding methylene chloride and water, separating the organic phase with water,Then washed with brine, dried over magnesium sulfate,Evaporated to dryness and the residue was purified over a silica gel column [elution solvent: ethyl acetate / n-hexane (3: 7 v / v)To obtain a solid yellowish solid,That is, Filgotinib, yield 91.2%.
Metabolism
Carboxylesterase enzymes are involved in the metabolism of filgotinib. The carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) isoform is chiefly responsible for metabolizing filgotinib to its major metabolite, GS-829845. Although carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) plays a less prominent role in the biotransformation of filgotinib, in vitro studies have demonstrated that CES1 will partially compensate in the event of CES2 saturation. GS-829845 is thus far the only major circulating metabolite to have been identified.
Metabolism
Filgotinib has favorable metabolic stability in vitro (65%, 45%, and 87% of compound remaining in rat, dog, and human liver microsomes, respectively, after 60 min incubation; and a half-life of more than 200 min in hepatocytes for all species). Filgotinib is a substrate of P-gp, as revealed by an efflux ratio of 16 from the Caco-2 assay. In spite of the high efflux ratio, it still showed 45% and 67% oral bioavailability in rats and dogs, respectively, presumably due to its good solubility (0.18 mg/mL in water), high membrane permeability, and good metabolic stability. It exhibited low plasma protein bindings across species (48% in rats, 29% in dogs, and 32% in humans). The elimination half-lives of filgotinib were 6 and 11 hours in the Japanese and Caucasian volunteers, respectively. In both trials, the active metabolite 3 showed plasma concentrations far beyond those of filgotinib, with half-life values ranging from 17 to 20 hours, which supports once-a-day oral administration. The active metabolite 3 was formed by hydrolysis of the amide functionality to release the free amine. This metabolite is less potent than filgotinib but still maintains good JAK1 selectivity. This metabolite is believed to contribute to the overall therapeutic effects along with the parent drug.
References
Menet et al. (2014), Triazolopyridines as selective JAK1 inhibitors: from hit identification to GLPG0634; Med. Chem., 57 9323 Rompaey et al. (2013), Preclinical characterization of GLPG0634, a selective inhibitor of JAK1, for the treatment of inflammatory diseases; Immunol., 191 3568 Kavanaugh et al. (2017), Filgotinib (GLPG0634/GS-6034), an oral selective JAK1 inhibitor, is effective as monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results from a randomized dose-finding study (DARWIN 2); Rheum. Dis., 76 1009 Wang et al. ?(2019), Oncostatin M inhibits differentiation of rat stem Leydig cells in vivo and in vitro; J. Cell. Mol. Med., 23 426
Properties of Filgotinib
| Melting point: | 229 - 231°C |
| Density | 1.51±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (15 mg/ml with warming) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 8.04±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Off-white |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. |
Safety information for Filgotinib
Computed Descriptors for Filgotinib
Filgotinib manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 GLPG0634 >95% CAS 1206161-97-8View Details
GLPG0634 >95% CAS 1206161-97-8View Details
1206161-97-8 -
![N-(5-(4-((1,1-Dioxidothiomorpholino)methyl)phenyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide 95% CAS 1206161-97-8](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) N-(5-(4-((1,1-Dioxidothiomorpholino)methyl)phenyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide 95% CAS 1206161-97-8View Details
N-(5-(4-((1,1-Dioxidothiomorpholino)methyl)phenyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide 95% CAS 1206161-97-8View Details
1206161-97-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1