Ferric silicon
Synonym(s):FE506020
- CAS NO.:8049-17-0
- Empirical Formula: FeSi2
- Molecular Weight: 112.02
- MDL number: MFCD00016087
- EINECS: 227-712-6
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13

What is Ferric silicon?
The Uses of Ferric silicon
Pidgeon process for producing metallic magnesium.
The Uses of Ferric silicon
Ferrosilicon (FeSi), which is widely used in the steel manufacturing process, is usually the source of silicon. The generated hydrogen is recycled and used in the burner to create the flame, so that the overall process is very environmentally friendly.
Definition
An alloy of iron and silicon used to add silicon to steel and iron, d 5.4, insoluble in water. Small quantities of silicon deoxidize the iron, and larger amounts impart special properties.
General Description
A solid alloy of iron and silicon. Used to add silicon to iron and steel. Ferric silicon is an odorless, crystalline solid metal. Ferric silicon is flammable and can react explosively with oxidizing materials. In the presence of moisture or water Ferric silicon may emit toxic and explosive fumes. Ferric silicon is used in magnesium processing.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Reacts with water or moisture in the air to form flammable hydrogen gas. The heat created by the reaction may be sufficient to ignite the hydrogen generated.
Reactivity Profile
Metals, such as Ferric silicon, are reducing agents and tend to react with oxidizing agents. Their reactivity is strongly influenced by their state of subdivision: in bulk they often resist chemical combination; in powdered form they may react very rapidly. Thus, as a bulk metal Ferric silicon is somewhat unreactive, but finely divided material may be pyrophoric. The metal reacts exothermically with compounds having active hydrogen atoms (such as acids and water) to form flammable hydrogen gas and caustic products. The reactions are less vigorous than the similar reactions of alkali metals, but the released heat can still ignite the released hydrogen. Materials in this group may react with azo/diazo compounds to form explosive products. These metals and the products of their corrosion by air and water can catalyze polymerization reactions in several classes of organic compounds; these polymerizations sometimes proceed rapidly or even explosively. Some metals in this group form explosive products with halogenated hydrocarbons.
Hazard
Ferrosilicon containing from 30 to 90% silicon is flammable and evolves gases in the presence of moisture.
Health Hazard
Exposure can cause irritation of eyes, nose and throat. Toxic if inhaled or ingested.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating vapors and toxic gases may be formed when involved in fire.
Industrial uses
This is a high-silicon master alloy used for makingsilicon steels, and for adding silicon to transformerirons and steels. It is made in the electricfurnace by fusing quartz or silica with iron turningsand carbon. Silicon is often added to steelsin combination alloys with deoxidizers or otheralloying elements. Ferrosilicon aluminum is amore effective deoxidizer for steel than aluminumalone. It is also used for adding silicon toaluminum casting alloys. The alloy serves as adeoxidizer, fluxes the slag inclusions, and alsocontrols the grain size of the steel.
Safety Profile
Moderate inhalation hazard. Low skin toxicity. Reaction with moisture releases hydrogen and acetylene gases, whch then ignite; impurities in the alloy may liberate such poisonous and reactive gases as phosphine and arsine. Dry mixtures with sodium hydroxide react incandescently when water is added. Reaction with acid, acid fumes, or oxidzing materials can emit toxic fumes. Reaction hazards increase with decreasing particle size.
Properties of Ferric silicon
| Melting point: | 1,36°C |
| Density | 4,75 g/cm3 |
| RTECS | LK1400000 |
| form | Granules |
| color | Gray |
| Specific Gravity | 4.75 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 2: reacts with aqueous acid |
| Dielectric constant | 10.0(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stability |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 8049-17-0 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferrosilicon (8049-17-0) |
Safety information for Ferric silicon
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H261:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H302:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Ferric silicon
Ferric silicon manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


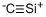

You may like
-
 Ferrosilicon 98%View Details
Ferrosilicon 98%View Details
8049-17-0 -
 Iron silicide CASView Details
Iron silicide CASView Details -
 Iron silicide CASView Details
Iron silicide CASView Details -
 SSL Group Lumps Si 75 Ferro Silicon, For Foundry, GrayView Details
SSL Group Lumps Si 75 Ferro Silicon, For Foundry, GrayView Details
8049-17-0 -
 Lumps Gray Ferro Silicon, For FoundryView Details
Lumps Gray Ferro Silicon, For FoundryView Details
8049-17-0 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
