Fenazaquin
- CAS NO.:120928-09-8
- Empirical Formula: C20H22N2O
- Molecular Weight: 306.4
- MDL number: MFCD01656049
- EINECS: 410-580-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
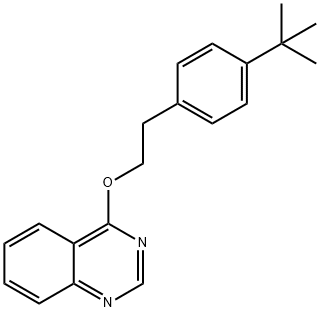
What is Fenazaquin?
The Uses of Fenazaquin
Fenazaquin is a non-systemic acaricide/insecticide used widely in controlling mites and other related pests in fruits, vegetables and tea.
The Uses of Fenazaquin
Acaricide and insecticide.
The Uses of Fenazaquin
Fenazaquin is an acaricide mainly used for control of mites (Eutetranychus, Panonychus and Tetranychus spp.) on pome and citrus fruits and glasshouse-grown ornamental plants.
What are the applications of Application
Fenazaquin is a non-systemic acaricide/insecticide
Definition
ChEBI: Fenazaquin is a member of quinazolines. It has a role as an acaricide and a mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone reductase inhibitor.
Metabolic pathway
Fenazaquin is a lipophilic compound and hence is immobile in soils and is not translocated in plants. The main pathways of metabolism involve cleavage of the bridging group between the quinazoline and phenyl rings, oxidation of the tert-butyl sustituent and of the heterocyclic portion of the quinazoline ring and cleavage of that ring. Most of the information is taken from a pamphlet produced by the manufacturer of the compound in which full experimental details were not given (DowElanco, 1993).
Degradation
Fenazaquin is hydrolysed under acidic conditions but the rate is slow under neutral and alkaline conditions. Half-lives were 8,442 and 584 days (22 °C) at pH values of 5, 7 and 9, respectively. Hydrolysis occurs by cleavage of the ether linkage to form quinazolin-2-ol (2) and an alcohol (3) as shown in Scheme 1. The major route of degradation in aquatic environments is by photolysis, the main products (2 and 3) being formed by cleavage of the ether lmkage and include the alkene (4) (DowElanco, 1993).
Properties of Fenazaquin
| Melting point: | 70-71° (Dreikorn); mp 77.5-80.0° (Gambie) |
| Boiling point: | 447.01°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0970 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 3.4 x l0-6 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5700 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) |
| pka | 2.88±0.30(Predicted) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 0.102 mg l-1 (20 °C, pH 7) |
| BRN | 8331263 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 120928-09-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fenazaquin (120928-09-8) |
Safety information for Fenazaquin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Fenazaquin
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Fenazaquin CAS 120928-09-8View Details
Fenazaquin CAS 120928-09-8View Details
120928-09-8 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4