Fenarimol
- CAS NO.:60168-88-9
- Empirical Formula: C17H12Cl2N2O
- Molecular Weight: 331.2
- MDL number: MFCD00055325
- EINECS: 262-095-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
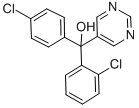
What is Fenarimol?
The Uses of Fenarimol
Fenarimol is a broad spectrum pyrimidine carbinol fungicide with protective, curative and eradicative activities against powdery mildew (Erysiphe spp., Pudusphaera leucutricha, Uncinula necatur, Sphaerutheca spp., Leveillula spp.) and scab (Venturia spp.) in many crops. It also controls powdery mildew (Sphaerutheca pannusa) in ornamentals and Fusarium patch (Micruduccium niuale), Take-all patch (Laefisaria fuciformis), Dollar spot (Sderutina humeucavpa) and red thread (Gaeumannumyces graminis) in turf and amenity grasses.
The Uses of Fenarimol
Plant fungicide.
The Uses of Fenarimol
Fenarimol is a pyrimidine based fungicide which acts against rusts, blackspot and mildew fungi and it works by inhibiting the fungus’s biosynthesis of important steroid molecules.
Definition
ChEBI: (2-chlorophenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)pyrimidin-5-ylmethanol is a member of the class of pyrimidines that is pyrimidin-5-ylmethanol in which one of the hydrogens attached to the carbon bearing the hydroxy group is replaced by a 2-chlorophenyl group while the other is replaced by a 4-chlorophenyl group. It is a tertiary alcohol, a member of monochlorobenzenes and a member of pyrimidines.
General Description
Pure white crystalline solid. Used as a fungicide. Irritates skin and mucous membranes.
Reactivity Profile
Fenarimol produces toxic gases when heated to decomposition.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cland NOx.
Metabolic pathway
The primary dissipation mechanism of fenarimol in the environment involves photolysis on plants/soil surfaces and water. More than 80 photoproducts have been observed, resulting from the reduction of the pyrimidine ring, hydrolysis, ring migration and cleavage of the phenyl and pyrimidine ring moieties. Under laboratory conditions in the dark, fenarimol is relatively persistent in soil, but a more rapid dissipation was observed under field conditions with DT50 values of 18-140 days, attributed to photolysis of fenarimol on the soil surface. Fenarimol degrades in/on plant foliage/fruit surfaces mainly by photochemical processes. In animals, fenarimol is metabolised extensively to yield hydroxylated, cleavage and dechlorination products. The primary photolytic and metabolic pathways of fenarimol are presented in Schemes 1 and 2.
Degradation
Fenarimol(1) is stable in sterile buffered water in the dark at pH 3,6 and 9
at 25 °C, 37 °C and 52 °C for 28 days (Decker and Sullivan, 1975) but is
readily degraded via photolysis. The photolytic DT50 in distilled water
under natural sunlight and clear sky conditions at 40°N in mid-summer
was approximately 12 hours (Day, 1975). The primary aqueous photolysis
reaction involved the migration of the pyrimidine ring to one of
the chlorophenyl rings, followed by the oxidation of the carbinol moiety
to the corresponding ketone to yield 4-chloro-2-(5-pyrimidyl)-2'-chlorobenzophenone
(2).
Fenarimol was extensively photodegraded on solid surfaces. More than
80 photodegradation products were formed when fenarimol was exposed
to sunlight on a stainless steel surface for up to 200 hours (Althaus and
Bewley, 1978a). All photoproducts were formed at very low levels (less
than 3% each) and 14 were identified. An abbreviated photogradation
pathway of fenarimol is presented in Scheme 1. These products were
generated from the following reactions: the migration of the pyrimidine
ring to one of the chlorophenyl rings, followed by the oxidation of the
carbinol moiety to yield compound 2; cleavage of either one of the
chlorophenyl (to yield 3,4) or pyrimidine rings (5,6); aryl hydroxylation
of one of the chlorophenyl rings (7); carbinol dehydroxylation reaction
to yield 8 and a bridged fluorene product (9) from the dechlorination
reaction. Various cleavage products (carboxylic acids) derived from the
chlorophenyl (10-13) and the pyrimidine moieties (14) were also
observed.
Properties of Fenarimol
| Melting point: | 117-119°C |
| Boiling point: | 0°C |
| Density | 1.3886 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 6.5 x 10-5 Pa at 25 °C |
| refractive index | 1.5490 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 0°C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 14.6 mg l-1 (pH 3), 13.7 mg l-1 (pH 7),
13.8 mg l-1 (pH 10) at 25 °C |
| pka | 2.58 |
| color | Off-White to Light Yellow |
| Merck | 13,3986 |
| BRN | 5972869 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 60168-88-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 5-Pyrimidinemethanol, «alpha»-(2-chlorophenyl)-«alpha»-(4-chlorophenyl)-(60168-88-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Fenarimol (60168-88-9) |
Safety information for Fenarimol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Fenarimol
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
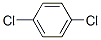

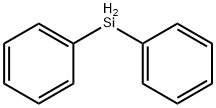
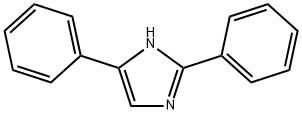
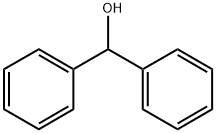
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8