Ethyl butyrate
Synonym(s):Butyric acid ethyl ester;Ethyl butanoate
- CAS NO.:105-54-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O2
- Molecular Weight: 116.16
- MDL number: MFCD00009394
- EINECS: 203-306-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:25
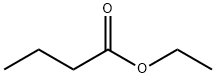
What is Ethyl butyrate?
Description
Ethyl butyrate, also known as ethyl butanoate, or butyric ether, is an ester with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2COO.CH2CH3.It is soluble in propylene glycol, paraffin oil, and kerosene.It has a fruity odor, similar to pineapple.
Chemical properties
Ethyl butyrate is a colorless liquid. Pineapple odor. The Odor Threshold is 0.015 ppm.
Chemical properties
Ethyl Butyrate occurs in fruits and alcoholic beverages, but also in other foods such as cheese. It has a fruity odor, reminiscent of pineapples. Large amounts are used in perfume and in flavor compositions.
Occurrence
Identified by gas chromatography in olive oil and other vegetable oils. Reported found in apple, banana, citrus peel oils and juices, cranberry, blueberry, black currants, guava, grapes, papaya, strawberry, onion, leek, cheeses, chicken, beef, beer, cognac, rum, whiskies, cider, sherry, grape wines, coffee, honey, soybeans, olives, passion fruit, plums, mushroom, mango, fruit brandies, kiwifruit, mussels and pawpaw.
The Uses of Ethyl butyrate
It is commonly used as artificial flavoring resembling orange juice or pineapple in alcoholic beverages (e.g. martinis, daiquiris etc.), as a solvent in perfumery products, and as a plasticizer for cellulose. In addition, ethyl butyrate is often also added to orange juice, as most associate its odor with that of fresh orange juice.
Ethyl butyrate is one of the most common chemicals used in flavors and fragrances. It can be used in a variety of flavors: orange (most common), cherry, pineapple, mango, guava, bubblegum, peach, apricot, fig, and plum. In industrial use, it is also one of the cheapest chemicals, which only adds to its popularity.
The Uses of Ethyl butyrate
Ethyl butyrate is used in flavors and fragrances. It is used as a solvent in perfumery products, and as a plasticizer for cellulose. It is used in the preparation of novel 2-cyanopyrimidines as cathespin K inhibitors. It is also used in the synthesis of pyridobenzimidazole derivatives exhibiting antifungal activity by the inhibition of β-1,6-glucan.
Production Methods
Ethyl Butyrate can be synthesized by reacting ethanol and butyric acid. This is a condensation reaction, meaning water is produced in the reaction as a byproduct.
Preparation
By esterification of n-butyric acid with ethyl alcohol in the presence of Twichell’s reagent or MgCI2; also by heating n-butyl alcohol and ethanol over CuO + UO3 catalyst at 270°C
Definition
ChEBI: Ethyl butyrate is a butyrate ester resulting from the formal condensation of the hydroxy group of ethanol with the carboxy group of butyric acid. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is functionally related to an ethanol.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 0.1 to 18 ppb
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 20 ppm: fruity, sweet, tutti-frutti, apple, fresh and lifting, ethereal.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 52, p. 5570, 1987 DOI: 10.1021/jo00234a012
Tetrahedron Letters, 8, p. 215, 1967 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)90519-7
Synthetic Communications, 25, p. 3395, 1995 DOI: 10.1080/00397919508013861
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a pineapple-like odor. Flash point 78°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Ethyl butyrate is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. May attack some forms of plastics [USCG, 1999].
Hazard
Irritant to eyes and mucous membranes, narcotic in high concentration. Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or ingestion causes headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and narcosis. Contact with liquid irritates eyes.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Vapor is heavier than air and may travel to a source of ignition and flash back. Containers may explode in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water: No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: May attack some forms of plastics; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Safety Profile
Wdly toxic by ingestion. A skin irritant. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also ESTERS.
Potential Exposure
Ethyl butyrate, and aldehyde, is used in flavorings, extracts, perfumery, and as a solvent.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
Not listed by ACGIH, California Proposition 65, IARC, NTP, or OSHA.
Storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Ethyl butyrate is incompatible with oxidizers (such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates, chlorates, and nitrates), strong acids (such ashydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric), bases, and heat. Store intightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames, areprohibited where ethyl butyrate is handled, used, or stored.Metal containers involving the transfer of 5 gallons or moreof ethyl butyrate should be grounded and bonded. Drumsmust be equipped with self-closing valves, pressure vacuumbungs, and flame arresters. Use only nonsparking tools andequipment, especially when opening and closing containersof ethyl butyrate.
Shipping
UN1180; UN1178 Ethyl butyrate, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid
Purification Methods
Dry the ester with anhydrous CuSO4 and distil it under dry nitrogen. [Beilstein 2 IV 787.]
Incompatibilities
Vapor explosive mixture with air. Ethers can act as bases. They form salts with strong acids and addition complexes with Lewis acids. The complex between diethyl ether and boron trifluoride is an example. Ethers may react violently with strong oxidizing agents. In other reactions, which typically involve the breaking of the carbon-oxygen bond, ethers are relatively inert. Incompatible with alkaline materials, strong acids, oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from strong bases and heat
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed
Properties of Ethyl butyrate
| Melting point: | -93 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 120 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.875 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 15.5 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2427 | ETHYL BUTYRATE |
| Flash point: | 67 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in propylene glycol, paraffin oil, and kerosene. |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Odor | Like apple or pineapple. |
| Odor Threshold | 0.00004ppm |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
| JECFA Number | 29 |
| Merck | 14,3775 |
| BRN | 506331 |
| Dielectric constant | 5.1(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids, bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 105-54-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Butanoic acid, ethyl ester(105-54-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethyl butyrate (105-54-4) |
Safety information for Ethyl butyrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. |
Computed Descriptors for Ethyl butyrate
| InChIKey | OBNCKNCVKJNDBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 105-54-4 99%View Details
105-54-4 99%View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethyl butyrate 98%View Details
Ethyl butyrate 98%View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethyl Butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
Ethyl Butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
Ethyl butyrate CAS 105-54-4View Details
105-54-4 -
 Ethylbutyrate CAS No.: 105-54-4, For Industrial, Packaging Size: 50 LtrView Details
Ethylbutyrate CAS No.: 105-54-4, For Industrial, Packaging Size: 50 LtrView Details
105-54-4
