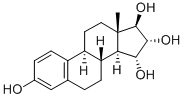
ESTETROL
Synonym(s):15α-Hydroxyestriol;3,15α,16α,17β-Tetrahydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-triene;E4;Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,15α,16α,17β-tetrol;Oestetrol
- CAS NO.:15183-37-6
- Empirical Formula: C18H24O4
- Molecular Weight: 304.38
- MDL number: MFCD00198996
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
What is ESTETROL?
Absorption
Estetrol is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The Cmax of estetrol is 18 ng/mL according to the results of a pharmacokinetic study, with an AUC of 36.4 ng?h/mL. When estetrol and drospirenone are taken in a single product, maximum serum concentrations of approximately 48.7 ng/mL are achieved within 1-3 h. Bioavailability of the combination ranges between 76 and 85%. The Tmax can range from 0.5 to 2 hours and time to steady state is approximately 4 days, according to the results of one clinical study.
Toxicity
LD50 information for estetrol is not readily available in the literature. Subjects receiving a dose of 20 mg, 40 mg or 60 mg of estetrol per day over 12 weeks were tolerated without dose-limiting toxicity. Symptoms that may occur in association with overdose, based on existing information on overdosage with oral contraceptives include nausea, vomiting, and vaginal bleeding. In one clinical study, 1 of 32 healthy research subjects receiving a dose of 75 mg of estretol with 15 mg of drospirenone for 10 days experienced deep vein thrombosis of the lower right limb. There is no known antidote to an estretol overdose; conduct laboratory testing for electrolytes and evidence of metabolic acidosis and provide symptomatic treatment.
Description
Estetrol, also called E4, is a steroid hormone closely related to sex hormones in the estrogen family, including former Molecule of the Week estradiol1. Along with estradiol and other hormones, estetrol occurs in the fetal liver during early pregnancy and in the mother in “exponentially growing concentrations during gestation”. Fetal concentrations are ≈10 times higher than maternal concentrations.
Estetrol was discovered in 1965 by Egon Diczfalusy and colleagues at the Karolinska Institute (Stockholm) during a study of the metabolism of estradiol in early infancy. But Diczfalusy did not realize at the time that estetrol could be a valuable drug; it was largely ignored for 35 years.
In 2000, Herjan Coelingh Bennink at the Dutch contraceptive manufacturer Organon2, recognizing estetrol’s occurrence in pregnant women and fetuses, believed that it should be explored as a safe therapeutic agent. Studies on estetrol as an oral contraceptive at Bennink-founded Pantarhei Bioscience (Zeist, The Netherlands) and later at Mithra Pharmaceuticals (Liège, Belgium) demostrated that it is as effective as the leading product, ethinylestradiol, without its adverse side effects.
Mithra conducted clinical trials on a combination of estetrol and drospirenone3, a progestin commonly included in estrogen-based contraceptives. In 2021, the estetrol–drospirenone combination, tradenamed Estelle, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. It is marketed by Mayne Pharma, an Australian company with facilities in North Carolina.
Estetrol is difficult to synthesize. The commercial manufacturing method begins with a soy-derived phytosterol and requires eight synthetic steps. Mithra recently announced that it chose Seqens (écully, France) to produce estetrol at its 129-year-old manufacturing plant in Villeneuve-la-Garenne, France.
1. CAS Reg. No. 50-28-2.
2. Not to be confused with a recently launched American company with the same name.
3. CAS Reg. No. 67392-87-4.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
The Uses of ESTETROL
Estetrol is an estrogen steroid hormone exclusively produced by fetal liver from estradiol and estriol during pregnancy. It binds to estrogen receptors (ERs) with 4-fold higher affinity for ERα over ERβ and exhibits estrogenic effects in most tissues expressing ERs (bone, brain, vagina, and endometrium). In breast tumors, however, estetrol acts as an estrogen antagonist in the presence of estradiol, preventing tumor growth.
The Uses of ESTETROL
A metabolite of Estradiol. It is an estrogenic steroid synthesized exclusively by the fetal liver during human pregnancy and reaching the maternal circulation through the placenta.
Background
Naturally or synthetically produced steroid estrogens have a wide range of pharmaceutical uses ranging from hormonal contraception to the treatment of menopausal symptoms. Estetrol (E4) is a native estrogen occurring naturally during pregnancy, but can be synthesized from a plant source and used for contraception. It is more potent and is safer than the synthetic estrogen ethinylestradiol (EE2) found in 97% of oral contraceptive pills, reducing the environmental accumulation of unwanted endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) that often lead to harmful epigenetic effects.
On April 15 2021, Mayne Pharma Group Limited and Mithra Pharmaceuticals were granted FDA approval for the oral contraceptive Estelle/Nextstellis, a combination of drospirenone and estetrol. Estetrol is the first new estrogen introduced to the USA in over 50 years and is the first approved estetrol product in the world. The combination of drospirenone and estetrol offers a new choice with a favourable safety profile for women seeking contraceptive therapy. In Canada, Nextstellis was approved for use in March 2021; it was developed by Mithra and is marketed by Searchlight Pharma.
Indications
Estetrol is indicated in combination with drospirenone for the prevention of pregnancy.
What are the applications of Application
Estetrol is a metabolite of Estradiol
Definition
ChEBI: Estetrol is a 3-hydroxy steroid that is 17beta-estradiol which has been substituted at the 15alpha and 16alpha positions by two additional hydroxy groups. It is a natural estrogen produced exclusively during pregnancy by the fetal liver. It has a role as an estrogen, an estrogen receptor agonist, a human metabolite, a human xenobiotic metabolite and an oral contraceptive. It is a 3-hydroxy steroid, a 17beta-hydroxy steroid, a 16alpha-hydroxy steroid, a 15alpha-hydroxy steroid and a steroid hormone. It derives from a hydride of an estrane.
Pharmacokinetics
Estetrol prevents pregnancy by suppressing ovulation.
Metabolism
Estretol is heavily metabolized after oral administration. Phase 2 metabolism of estrogen forms glucuronide and sulfate conjugates with negligible in-vitro estrogenic activity. In vitro metabolism studies demonstrate that UGT2B7 catalyzes the formation of E4-16-glucuronide. Estetrol is combined with drospirenone in a product. The hepatic cytochrome enzyme CYP3A4 metabolizes drospirenone to two primary metabolites: the acid form of drospirenone through the opening of the lactone ring and the 4,5- dihydrodrospirenone formed by reduction, followed by sulfation. Both metabolites are pharmacologically inactive.
Properties of ESTETROL
| Melting point: | 233-236°C |
| Boiling point: | 491.9±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.343±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble20mg/mL, clear |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| form | powder |
| pka | 10.22±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white to beige |
| optical activity | [α]/D +125 to +135, c = 1 in ethanol |
Safety information for ESTETROL
Computed Descriptors for ESTETROL
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Estetrol CAS 15183-37-6View Details
Estetrol CAS 15183-37-6View Details
15183-37-6 -
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
5428-54-6 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3