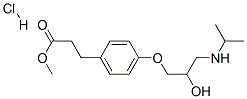
Esmolol hydrochloride
Synonym(s):4-[2-Hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]benzenepropanoic acid methyl ester hydrochloride hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:81161-17-3
- Empirical Formula: C16H26ClNO4
- Molecular Weight: 331.83
- MDL number: MFCD00941432
- EINECS: 636-017-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-16 20:18:48
What is Esmolol hydrochloride?
Description
Esmolol is an ultra-short acting, cardioselective P-blocker with no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. The capability of rapid reversal makes esmolol uniquely suitable for the acute management of supraventricular tachycardia and the control of blood pressure and heart rate during surgery or other cardiac emergencies.
Chemical properties
Esmolol Hydrochloride is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is a relatively hydrophilic compound which is very soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. Its partition coefficient (octanol/water) at pH 7.0 is 0.42 compared to 17.0 for propranolol.
Esmolol Hydrochloride has the empirical formula C16H26NO4Cl and a molecular weight of 331.8. It has one asymmetric center and exists as an enantiomeric pair.
Originator
DuPont Critical Care (USA)
The Uses of Esmolol hydrochloride
Esmolol hydrochloride is indicated for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, the rapid control of ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter in perioperative, postoperative, or other emergent circumstances where short term control of ventricular rate with a short-acting agent is desirable. Esmolol hydrochloride is also indicated in noncompensatory sinus tachycardia where, in the physician's judgment, the rapid heart rate requires specific intervention. Esmolol hydrochloride is not intended for use in chronic settings where transfer to another agent is anticipated.
The Uses of Esmolol hydrochloride
Cardioselective -adrenergic blocker. Antiarrhythmic
The Uses of Esmolol hydrochloride
antiarrhytmic;cardioselective beta1 receptor blocker
What are the applications of Application
Esmolol Hydrochloride is a β-adrenergic blocker
Definition
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of esmolol. A cardioselective and short-acting beta1 receptor blocker with rapid onset but lacking intrinsic sympathomimetic and membrane-stabilising properties, it is used in the management of su raventricular arrhythmias, and for the control of hypertension and tachycardia during surgery.
Manufacturing Process
A solution of 17 g (0.1 mole) of 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid in 500 mL
methanol and 2 mL concentrated sulfuric acid were placed in a Soxhlet
extractor charged with 3A molecular sieves. The solution was refluxed for 72
hours and the sieve were exchanged at 24 hour intervals. The reaction
medium was then evaporated to an oil which was dissolved in 100 mL toluene
and extracted with 100 mL water (3 times). The toluene phase was dried over
magnesium sulfate, treated with activated charcoal and evaporated to provide
15 g (80%) of a clear oil. The NMR spectrum was consistent with the methyl
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate.
The oil described above was utilized directly in the condensation reaction with
the epichlorohydrin. A mixture of 0.1 mole of methyl 3-(4-
hydroxyphenyl)propionate, 0.2 mole potassium carbonate and 0.4 mole
epichlorohydrin in 250 mL acetone was heated to reflux for 24 hours. The
reaction medium was then filtered and evaporated. The residue was taken up
in 100 mL toluene and washed with 100 mL 1.0 N NaOH and 100 mL water (2
times). The toluene phase was then dried over magnesium sulfate and
evaporated to provide the crude product as an oil. Purification was effected by
vacuum distillation (156°C/0.4 mm) and provided methyl 3-[4-(2,3-
epoxypropoxy)phenyl]propionate. The NMR and IR spectra and elemental
analysis data were consistent with the assigned structure.
A mixture of 50 g (0.21 mole) of methyl 3-[4-(2,3-
epoxypropoxy)phenyl]propionate and 100 mL of isopropylamine in 100 mLmethanol was heated to reflux for 4 hours. The reaction medium was then
evaporated and the resulting oil taken up in methanol and treated with
ethereal HCl and provided crystals which were recrystallized in similar fashion
to provide 28 g (47%) of white crystals: melting point 85-86°C. The NMR and
IR spectra and the elemental analysis data were consistent with the structure
of methyl 4-(2-hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)benzenepropanoate.
In practice it is usually used as hydrochloride.
brand name
Brevibloc(Baxter Healthcare).
Therapeutic Function
Beta-adrenergic blocker
Pharmacokinetics
Esmolol Hydrochloride is a beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenergic receptor blocking agent with rapid onset, a very short duration of action, and no significant intrinsic sympathomimetic or membrane stabilizing activity at therapeutic dosages. Its elimination half-life after intravenous infusion is approximately 9 minutes. Esmolol Hydrochloride inhibits the beta1 receptors located chiefly in cardiac muscle, but this preferential effect is not absolute and at higher doses it begins to inhibit beta2 receptors located chiefly in the bronchial and vascular musculature.
Esmolol Hydrochloride is rapidly metabolized by hydrolysis of the ester linkage, chiefly by the esterases in the cytosol of red blood cells and not by plasma cholinesterases or red cell membrane acetylcholinesterase. Total body clearance in man was found to be about 20 L/kg/hr, which is greater than cardiac output; thus the metabolism of Esmolol Hydrochloride is not limited by the rate of blood flow to metabolizing tissues such as the liver or affected by hepatic or renal blood flow. Esmolol Hydrochloride has a rapid distribution half-life of about 2 minutes and an elimination half-life of about 9 minutes.
Clinical Use
Beta-adrenoceptor blockerShort-term treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias (including AF, atrial flutter, sinus tachycardia)Tachycardia and hypertension in the perioperative period
Side Effects
Hypotension (in 20-50% of pts), diaphoresis, pallor, flushing, peripheral ischemia, bradycardia, heart block, heart failure, sudden cardiac death.
Dizziness, confusion, headache, fatigue, anxiety.
Nausea, vomiting, fever.
Bronchospasm, cough, wheeziness, nasal stuffiness.
Urinary retention.
Inflammation and induration at injection site.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Esmolol may be used as test drug to indicate whether beta-blocker therapy is warranted as an antiarrhythmic agent, particularly in cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, or as an infusion in the shortterm treatment of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (e.g., atrial fibrillation/flutter, sinus tachycardia).
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAnaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.Analgesics: NSAIDs antagonise hypotensive effect.Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of myocardial depression and bradycardia; with amiodarone, increased risk of bradycardia and AV block and myocardial depression; increased risk of myocardial depression and bradycardia with flecainide.Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with MAOIs.Antimalarials: increased risk of bradycardia with mefloquine.Antipsychotics: enhanced hypotensive effect with phenothiazinesCalcium-channel blockers: increased risk of bradycardia and AV block with diltiazem; severe hypotension and heart failure occasionally with nifedipine and possibly other dihydropyridines; asystole, severe hypotension and heart failure with verapamil - avoid concomitant verapamil use.Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect; increased risk of withdrawal hypertension with clonidine; increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect with post-synaptic alpha-blockers.Cytotoxics: possible increased risk of bradycardia with crizotinib.Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect.Fingolimod: possibly increased risk of bradycardia.Moxisylyte: possible severe postural hypotension.Sympathomimetics: severe hypertension with adrenaline and noradrenaline and possibly dobutamine
Metabolism
Esmolol hydrochloride is metabolised by esterases into an acid metabolite (ASL-8123) and methanol. This occurs through hydrolysis of the ester group by esterases in the red blood cells. Esmolol hydrochloride is excreted by the kidneys, partly unchanged (less than 2% of the administered amount), partly as acid metabolite that has a weak (less than 0.1% of esmolol) beta-blocking activity. The acid metabolite is also excreted in the urine
Properties of Esmolol hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 48-50°C |
| Density | 1.026 |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble12mg/mL |
| form | buffered aqueous solution |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 81161-17-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Esmolol hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Esmolol hydrochloride
Esmolol hydrochloride manufacturer
Mehta API Pvt. Ltd.
Surajlok Chemicals Pvt Ltd (Neon Laboratories Ltd)
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![6-[[3-[4-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]propyl]amino]-1,3-dimethyluracil](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/34661-75-1.gif)
You may like
-
 81161-17-3 Esmolol hydrochloride 98%View Details
81161-17-3 Esmolol hydrochloride 98%View Details
81161-17-3 -
 81161-17-3 99%View Details
81161-17-3 99%View Details
81161-17-3 -
 Esmolol hydrochloride 98%View Details
Esmolol hydrochloride 98%View Details
81161-17-3 -
 Esmolol hydrochloride CAS 81161-17-3View Details
Esmolol hydrochloride CAS 81161-17-3View Details
81161-17-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8