Ectoine
Synonym(s):(S)-2-Methyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid;Thp(B)
- CAS NO.:96702-03-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H10N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 142.16
- MDL number: MFCD03419286
- EINECS: 431-910-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 19:01:08
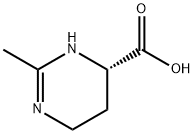
What is Ectoine?
Description
Ectoine is a cyclic tetrahydropyrimidine organic osmolyte, which was discovered in the halophilic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira halochloris. It is the most abundant solute produced by aerobic heterotrophic eubacteria and has been extensively characterized as an osmoprotectant and stabilizer for cells and biomolecules.
Ectoine is considered a member of the small molecule chaperones family (SMCs). SMCs accumulate to high intracellular concentrations, preventing the misfolding/ denaturation of proteins and other labile macromolecules. Ectoine preserves enzymes and whole cells against harmful conditions such as freezing, drying, or heating. This molecule, among other compatible solutes, possesses the ability to conserve the proteolytic activity of trypsin and chymotrypsin. It has been shown to induce heat shock proteins and downregulate proinflammatory signals in human keratinocytes. It is not toxic to the cellular environment, even at concentrations as high as 100 mM.
Ectoine strongly inhibits the Ab42 amyloid formation in vitro, reducing the toxicity to human neurblastoma cells. Ab42 was found to be the most predominant proteolytic fragment found in amyloid plaques, thus, ectoine may act as a potential inhibitor associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
Description
Ectoine helps salt-tolerant microbes (including the one that causes cholera) adjust to changes in the salinity of the water in which they live. In highly saline environments, ectoine slows the diffusion of water through the cell membrane, ensuring that the single-celled organisms maintain the proper level of hydration.
The Uses of Ectoine
Ectoine is a natural protector that stabilizes proteins and other cell structures and protects the skin from stresses such as UV exposure and dryness.
What are the applications of Application
Ectoine is An osmoprotectant
Definition
Ectoine is a carboxamidine heterocycle obtained by formal condensation of (2S)-2,4-diaminobutanoic acid with acetic acid. It has a role as an osmolyte. It is a carboxamidine, a member of 1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidines and a monocarboxylic acid. It is a conjugate acid of an ectoinate. It is a tautomer of an ectoine zwitterion.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ectoine is an osmoprotectant in a variety of microorganisms, including heterotrophic, halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria, such as Streptomyces and E. coli. This compatible solute is also protective for E. coli during drying and storage. Ecdysone is associated with the stabilization of protein and lipid bilayers. It also regulates the retention of bulking pressure and reduces desiccation stress. It can be used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ecdysone causes structural changes in DNA in vitro and protects DNA from ionizing radiation (IR). It prevents the formation of insulin amyloid in vitro.Ecdysone is an osmoprotectant in a variety of microorganisms, including heterotrophic, halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria, such as Streptomyces and E. coli. This compatible solute is also protective for E. coli during drying and storage. Ecdysone is associated with the stabilization of protein and lipid bilayers. It also regulates the retention of bulking pressure and reduces desiccation stress. It can be used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ecdysone causes structural changes in DNA in vitro and protects DNA from ionizing radiation (IR). It prevents the formation of insulin amyloid in vitro.
References
1. Galinski, E.A., et al., 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-2-methyl-4- pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur. J. Biochem., 149, 135 - 139 (1985).
2. Kanapathipillai, M. et al., Ectoine and hydroxyectoine inhibit aggregation and neurotoxicity of Alzheimer’s b-amyloid. FEBS Letters, 579, 4775- 4780 (2005).
3. Kolp, S. et al., Compatible solutes as protectants for zymogens against proteolysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1764, 1234-1242 (2006).
4. Buommino, E. et al., Ectoine from halophilic microorganisms induces the expression of hsp70 and hsp70B′ in human keratinocytes modulating the proinflammatory response. Cell stress & chap., 10, 197-203 (2005).
Properties of Ectoine
| Melting point: | ~280° |
| Boiling point: | 381.5±35.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 +140° (c = 1.0 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.37 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: 20 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 3.14±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Water : 250 mg/mL (1758.58 mM) |
| BRN | 7288977 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C6H10N2O2/c1-4-7-3-2-5(8-4)6(9)10/h5H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t5-/m0/s1 |
Safety information for Ectoine
Computed Descriptors for Ectoine
| InChIKey | WQXNXVUDBPYKBA-YFKPBYRVSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C)=NCC[C@@H](C(O)=O)N1 |
Ectoine manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 96702-03-3 Ectoine 98%View Details
96702-03-3 Ectoine 98%View Details
96702-03-3 -
 Ectoine CAS 96702-03-3View Details
Ectoine CAS 96702-03-3View Details
96702-03-3 -
 Ectoine CAS 96702-03-3View Details
Ectoine CAS 96702-03-3View Details
96702-03-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1