Doripenem
Synonym(s):
- CAS NO.:148016-81-3
- Empirical Formula: C15H24N4O6S2
- Molecular Weight: 420.5
- MDL number: MFCD02092739
- EINECS: 1308068-626-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-15 14:23:52
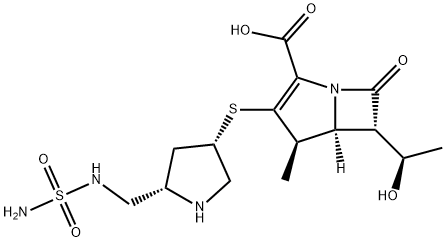
What is Doripenem?
Absorption
Doripenem is administered intravenously as an infusion. There was no accumulation of doripenem following mulitiple infusions of either 500mg or 1g administered every 8 hours for 7-10 days in subjects with normal renal function.
Toxicity
Dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with moderate and severe renal impairment.
Doripenem's FDA label includes a warning against use in ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia, as a clinical trial for that indication resulted in increased mortality with doripenem (23% vs. 16.7% recieving imipenem) as well as lower clinical response rates.
Seizures have been reported with doripenem treatment; patients at greater risk of developing seizures we found to have pre-existing central nervous system (CNS) conditions, compromised renal function, or patients receiving higher doses than 500 mg every 8 hours. Doripenem also reduces plasma levels of valproic acid when administered concomitantly; therefore patients with pre-existing seizure disorders on valproic acid are at even higher risk of breakthrough seizures if receiving both drugs at the same time.
Doripenem is considered pregnancy category B as it was not found to be teratogenic or produce effects on ossification, developmental delays, or fetal weight in rat and rabbit studies. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. It is not known whether doripenem is excreted into breast milk, therefore caution should be exercised with doripenem administration to nursing women.
Description
Doripenem monohydrate is an ultra-broad-spectrum injectable β-lactam antibiotic and belongs to the subgroup of carbapenems. It was introduced by Shionogi Co. of Japan under the brand name Finibax in 2005 and is being marketed outside Japan by Johnson & Johnson. Doripenem act by decreases the process of cell wall growth, which eventually leads to elimination of the infectious cell bacteria together. It is used for treatment of bacterial respiratory and urinary tract infections. Doripenem is a 1β-methyl carbapenem derivative, and it is the fourth analog to be marketed in this series following the launch of meropenem, biapenem, and ertapenem in previous years. The introduction of a 1β-methyl group to the carbapenem skeleton enhances metabolic stability to renal dehydropeptidase-1 (DHP-1) and leads to improved antibacterial potency.
Chemical properties
Doripenem white to somewhat yellowish crystalline powder which is moderately soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, and virtually insoluble in ethanol. Doripenem is also solution in N,N-dimethylformamide. The chemical configuration of doripenem’s has 6 asymmetrical carbon atoms (6 stereocenters) and is most commonly supplied as one pure isomer. In terms of doripenem for injection, the crystallized powered drug can form a monohydrate when mixed with water.
Originator
Shinogi (Japan)
The Uses of Doripenem
Doripenem hydrate is used to treat complicated urinary infection including Pyelonephritis caused by E.coli. Doripenem hydrate is promoted in the United States as DORIBAX(R). This drug is synthesized from p-nitrobenzyl-protected enolphosphate 2b and N-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)-protected aminomethylpyrrolidine.
Indications
Doripenem is indicated in the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections and complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis, caused by designated susceptible bacteria.
Background
Doripenem is a broad-spectrum, carbapenem antibiotic marketed under the brand name Doribax by Janssen. Doripenem injection was approved by the FDA in 2007 to treat complicated urinary tract and intra-abdominal infections. In a clinical trial of doripenem treatment in ventilator associated pneumonia (vs. imipenem and cilastatin), it was found that doripenem carried an increased risk of death and lower clinical cure rates, resulting in a premature termination of the trial. The FDA revised the doripenem label in 2014 to include a warning against use in ventilator-associated pneumonia and to reiterate its safety and efficacy for its approved indications.
What are the applications of Application
Doripenem is an antibacterial agent
Definition
ChEBI: Doripenem is a member of carbapenems.
brand name
Doribax,Finibax
Antimicrobial activity
Doripenem have a broad spectrum of bacterial activity including both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria but it is not active against MRSA. It is stable against β-lactamases including those with extended spectrum, but it is susceptible to the action of carbapenemases (Mandell, 2009). Thus it can be used in the treatment of infections such as: complex abdominal infections, pneumonia within the setting of a hospital, and complicated infections of the urinary tract including kidney infections with septicemia. Doripenem is also more active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa then other carbapenems.
Pharmacokinetics
Similar to other beta-lactam antimicrobial agents, the time that unbound plasma concentration of doripenem exceeds the MIC (T>MIC) of the infecting organism has been shown to best correlate with efficacy in animal models of infection.
Pharmacokinetics
Cmax 500 mg intravenous infusion (1 h): c. 23 mg/L after 1 h
500 mg intravenous infusion (4 h): c. 8 mg/L
Plasma half-life: 1 h
Volume of distribution: 16.8 L (steady state)
Plasma protein binding: 8.1%
Absorption and distribution
Doripenem is not absorbed after oral administration. It penetrates well into most tissues and fluid, achieving concentrations matching or exceeding those required to inhibit most susceptible bacteria at the site of infection for the approved indications.
Metabolism and excretion
Metabolism of doripenem to the microbiologically inactive ring-opened metabolite occurs primarily by renal dehydropeptidase. Based on area under the concentration–time curve (AUC) values in plasma following a single 500 mg dose in healthy volunteers, 18% appears as metabolite and the rest as unchanged drug.
Excretion is primarily by the renal route. Within 24 h after dosing, 78.7% and 18.5% of the dose was recovered in urine as unchanged drug and the ring-opened metabolite, respectively. After administration of radiolabeled doripenem, 0.7% of the total radioactivity was recovered in feces after 1 week.
Clinical Use
Doripenem is indicated for use for the treatment of intra-abdominal infections, and complicated urinary tract infections.
Complicated urinary tract infections, including pyelonephritis
Nosocomial pneumonia, including ventilator-associated pneumonia (Europe)
Side Effects
The most commonly reported adverse effects of doripenem include pain or swelling at the injection site, nausea, headache, and diarrhea.
Seizure and central nervous system (CNS) side effects are observed rarely (<1%), though headache is reported by 2.3% of patients. Other common drug-related adverse reactions are diarrhea (2.0%), nausea (1.9%), anemia (1.4%) and phlebitis (1.4%). Hypersensitivity reactions related to intravenous administration of the study drug and Clostridium difficile colitis occurred at a rate of less than 1%. However, patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to other β-lactam agents should be treated cautiously.
Synthesis
the hydroxyl proline is protected as the PNZ ester 32 first in 95% yield. The protected proline acid 32 was converted to the methyl ester with refluxing sulfuric acid in methanol followed by conversion of the alcohol to the mesylate 34 in 91% overall yield from 30. The mesylate ester was reduced with sodium borohydride to provide alcohol 35, which was converted without purification to thiol ester 36 by reacting with potassium thioacetate. Mitsunobu reaction of alcohol 36 with BOC-sulfonyl urea 38, which was prepared from chlorosulfonyl isocyanate with ammonia in tbutanol in 90% yield, provided the key thioacetate intermediate 39. Finally, protected doripenem 42 was prepared by coupling thiol 40, obtained by hyrolysis of thioacetate 39, with enolphosphate 41 in 88% yield. Deprotection of intermediate ester and carbamate protecting groups via hydrogenation gave the desired carbapenem VI, which was isolated after crystallization. Final form of the drug doripenem was prepared by sterilization, crystallization and granulation.

Metabolism
Metabolism of doripenem is via dehydropeptidase-I (also called dipeptidase-1) into a microbiologically inactive ring-opened metabolite, doripenem-M1. Doripenem does not appear to be a substrate of the hepatic CYP450 enzymes.
Dosage
Doripenem was initially developed in Japan and has received approval there in 2005 as Finibax. Finibax is indicated for multiple bacterial infections, the majority of which are respiratory indications.
The usual dose, according to the Japanese label, is 250 mg intravenously (i.v.) infused over 30 to 60 minutes 2 or 3 times a day; the maximum dose is 500 mg per administration up to a total dose of 1,500 mg/day.
Mode of action
Doripenem's bactericidal function is due to its inhibition of the third stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Binding to penicillin-binding proteins weakens the cell wall and leads to cell death due to lysis of the cell wall.
Doripenem is effective against both grampositive and gramnegative aerobic bacteria.It may be more potent in vitro against Pseudomonas aeruginosa than meropenem.
Properties of Doripenem
| Melting point: | >186°C dec. |
| Boiling point: | 694.8±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.59±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | In water, not known, in DMSO 20 mg/ml, in pBS 3 mg/ml |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.27±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light Beige |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 148016-81-3 |
Safety information for Doripenem
Computed Descriptors for Doripenem
Doripenem manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
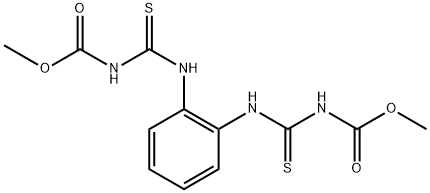
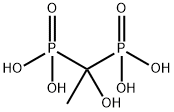
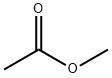
You may like
-
 148016-81-3 Doripenem 98%View Details
148016-81-3 Doripenem 98%View Details
148016-81-3 -
 148016-81-3 98%View Details
148016-81-3 98%View Details
148016-81-3 -
 Doripenem 98%View Details
Doripenem 98%View Details
148016-81-3 -
 Doripenem 99%View Details
Doripenem 99%View Details
148016-81-3 -
 Doripenem 98% (HPLC) CAS 148016-81-3View Details
Doripenem 98% (HPLC) CAS 148016-81-3View Details
148016-81-3 -
 DoripenemView Details
DoripenemView Details
148016-81-3 -
 Doripenem APIView Details
Doripenem APIView Details
148016-81-3 -
 Doripenem ApiView Details
Doripenem ApiView Details
148016-81-3
