DL-Menthol
Synonym(s):Menthol;DL-Menthol;Racemic menthol;(1R,2S,5R)-2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol;2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol
- CAS NO.:89-78-1
- Empirical Formula: C10H20O
- Molecular Weight: 156.27
- MDL number: MFCD00064814
- EINECS: 201-939-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-21 21:32:25
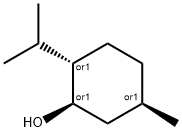
What is DL-Menthol?
Description
Menthol has a mint-like odor and a fresh, cooling taste. It may be prepared by hydrogenation of thymol.
Description
Menthol is a substituted cyclohexanol that is familiar to many as the main constituent of mint. It occurs in peppermint and other mint oils. (–)-Menthol is far more common in nature than its (+)- enantiomer. The molecule has three stereogenic centers, leading to other isomers known as isomenthol, neomenthol, and isoneomenthol.
Racemic synthetic menthol is made by hydrogenating the phenolic compound thymol. The hydrogenation produces all of the stereoisomers; (–)-menthol is isolated by esterification, fractional crystallization, and hydrolysis.
Menthol is a component of a wide range of over-the-counter remedies. It triggers cold-sensitive receptors in human tissues, making it useful in dental products, sunburn medications, shaving creams, and decongestants. It is a flavoring agent in foods such as ice cream, tea, candy, and liqueurs.
So while you suck on your holiday candy cane, think good thoughts about (–)-menthol and its seven isomeric cousins.
Description
(±)-Menthol is a racemic mixture of the monoterpene alcohols (–)-menthol and (+)-menthol , which have been found in Cannabis. (–)-Menthol is more common than (+)-menthol in nature and exhibits analgesic, antibacterial, and anticancer properties, as well as inhibits cholinesterase. (+)-Menthol inhibits the growth of F. verticillioides (MIC = 1.5 mM) but, unlike (–)-menthol, does not exhibit analgesic, antibacterial, anticancer, or cholinesterase inhibitory activities.
Chemical properties
colorless to white crystalline solid
Chemical properties
Menthol has a peppermint-like odor and exerts a cooling sensation when applied to skin and mucosal surfaces. Menthol is a monocyclic terpene alcohol with three asymmetric carbon atoms in its cyclohexane ring resulting in (–) and (+) menthol, neomen thol, isomenthol and neoisomenthol. (–)-Menthol is the isomer that occurs most widely in nature and is the one commonly identified as menthol.
Physical properties
Appearance: colorless or white acicular prismatic crystals or white crystalline powder. Solubility: easily dissolved in ethanol, chloroform, ether, liquid paraffin, or volatile oil and soluble in water. Odor: a cool, refreshing, and pleasant mint aroma, sweet odor, and taste cool early after burning. Boiling point: 212?°C. Melting point: 41–43?°C. Specific optical rotation: ?49 to ?50°.
Occurrence
Reported found in peppermint and other mint oils (e.g., M. arvensis), lemon peel oil, cranberry, pineapple, cab bage, thymus, egg, rum, cocoa, tea, honey, avocado, coriander, mango, rice, litchi, dill herb, calamus, juniper berries, fennel, buchu oil, clam and Roman chamomile oil, Mentha species.
History
In the world of aromatic chemicals, menthol is often described as a unique source of skin and mucous membranes. Menthol is mainly extracted from natural plants. The vast majority of natural menthol in the global market is extracted from numerous Asian mint. In 2006, the world’s natural menthol production is 12,800?tons or more. However, due to various factors, the production of natural menthol is becoming less and less. Since the 1960s, Japan, Germany, and other countries had developed the synthetic menthol products. In 1974 the German company Symrise and Japan Takasago Fluidic Systems company launched chemical synthesis of menthol. At present, attention has been paid to the study of menthol analogy substances and the effect of the changes of molecular structure on the aroma and cool sensation. Some studies have shown that hydroxyl groups located in the branched or 1, 4 chain cannot show a sense of cool. The researchers believed that menthol analogy substances with optical activity should be able to show different, surprising cooling effect, and the structure of hydroxyl alkyl groups is the key point to have a cooling effect. The Japanese chemist Ryoji Noyo and his colleagues found that in BINAP and rhodium complexes as catalysts for asymmetric hydrogenation reaction, the synthesis of menthol is very effective. Because of the contribution of asymmetric organic synthesis, they won the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
The Uses of DL-Menthol
DL-Menthol may be used as an extraction solvent for the determination of parabens in food products, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals using liquid-liquid microextraction with high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection (HPLC-DAD). It may also be used for the preparation of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent (DES) in the extraction and determination of methylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben from cosmetics samples using syringe-to-syringe dispersive magnetic nanofluid microextraction procedure (SS-DMNF-ME) with high-performance liquid chromatography technique (HPLC).
The Uses of DL-Menthol
A chemical which triggers cold-sensitive TRPM8 receptors in the skin neurons in vitro.
The Uses of DL-Menthol
In liqueurs, confectionery, perfumery, cigarettes, cough drops, and nasal inhalers.
What are the applications of Application
(±)-Menthol is a chemical which triggers cold-sensitive TRPM8 receptors in the skin neurons in vitro
Preparation
By hydrogenation of thymol.
Indications
For external application, it is applied locally and often used to relieve pain and itching. A nasal drip is used in the head cold. Inhalation or spray is used for sore throat. Oral administration can promote digestion.
Definition
ChEBI: P-menthan-3-ol is any secondary alcohol that is one of the eight possible diastereoisomers of 5-methyl-2-(propan-2-yl)cyclohexan-1-ol. It has a role as a volatile oil component. It is a p-menthane monoterpenoid and a secondary alcohol.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 950 ppb to 2.5 ppm; aroma characteristics at 1.0%: cooling menthol with a penetrating minty eucalyptus note.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 25 ppm: cooling, camphoreous, minty with a clean eucalyptus note.
General Description
White crystalline solid with a peppermint odor and taste.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
DL-Menthol is incompatible with butyl chloral hydrate, camphor, phenol, chloral hydrate, Exalgine, betanaphthol, resorcinol or thymol in triturations; potassium permanganate, chromium trioxide and pyrogallol. DL-Menthol is also incompatible with strong oxidizers.
Hazard
Irritant to mucous membranes on inhalation.
Fire Hazard
DL-Menthol is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Biochem/physiol Actions
Menthol exhibits antifungal action on the membrane permeability and the cell wall consistency, this might leads to cell death or inhibition of the C. albicans filamentation. Therefore, it can be used as a potential therapeutic agent for candidiasis. In addition to antifungal activity, menthol also exhibits anesthetic, antispasmodic, anti-ulcer and antiviral properties. It is considered as a safe compound for animal life. Therefore, Menthol is widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and food industries.
Pharmacology
Menthol has a wide range of pharmacological effects. Menthol can stimulate the
nerve endings of skin and slowly penetrate into the skin, resulting in prolonged
congestion and reflex caused by deep vascular changes, adjusting the vascular function, and achieving therapeutic effects in topical application. Topical application of
compound has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anesthetic effects.
In respiratory system: For treatment of bronchitis, it could reduce the respiratory
tract foam sputum and increase the effective ventilation cavity road. For treatment
of rhinitis and laryngitis, it exerts mitigation by promoting secretion and diluting
viscous mucus.
In digestive system: Menthol showed the powerful effect on bile.
In central nervous system: A small amount of peppermint can stimulate the central nervous system through the peripheral nerve to expand the skin capillaries, promote the secretion of sweat glands, increase heat dissipation, and show sweating
antipyretic effect.
In addition, menthol has penetration-enhancing effect on many kinds of drugs;
the mechanism is related to the changes of the ultrastructure of the skin, which is
expected to be widely used in transdermal drug delivery agents. In vitro experiments, it had strong antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and
Bacillus proteus. Recently, British scientists found that mint leaves can prevent cancer lesions in the blood vessel growth to decrease blood supply for, showing a certain anti-tumor effect
Clinical Use
It can be clinically used to assist anesthesia, postoperative analgesia, intercostal nerve block, trigeminal nerve block, occipital nerve block, and so on. When applied locally, it can promote blood circulation, diminish inflammation, relieve itching, relieve pain, relieve edema, and so on.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. A severe eye irritant. Incompatible with phenol, p-naphthol, resorcinol or thymol in trituration, potassium permanganate, chromium trioxide, pyrogallol. Combustible liquid. \When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Properties of DL-Menthol
| Melting point: | 34-36 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 216 °C(lit.) |
| alpha | -2 º (c=10, EtOH) |
| Density | 0.89 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.8 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4615 |
| FEMA | 2665 | MENTHOL RACEMIC |
| Flash point: | 200 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 456mg/l |
| form | Crystalline Solid |
| pka | 15.30±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless to white |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. peppermint cool woody |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| JECFA Number | 427 |
| Merck | 14,5837 |
| BRN | 3194263 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 89-78-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | DL-Menthol(89-78-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | (1R,2S,5R)-Menthol (89-78-1) |
Safety information for DL-Menthol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for DL-Menthol
DL-Menthol manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

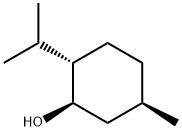
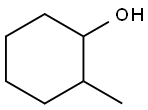
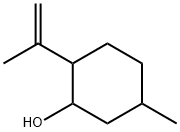
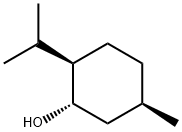
You may like
-
 DL-Menthol CAS 89-78-1View Details
DL-Menthol CAS 89-78-1View Details
89-78-1 -
 (±)-Menthol CAS 89-78-1View Details
(±)-Menthol CAS 89-78-1View Details
89-78-1 -
 DL-Menthol 99% (GC) CAS 89-78-1View Details
DL-Menthol 99% (GC) CAS 89-78-1View Details
89-78-1 -
 DL-Menthol CAS 89-78-1View Details
DL-Menthol CAS 89-78-1View Details
89-78-1 -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
